Civic time off: The benefit getting employees to the polls
Does your organization offer civic time off as an employee benefit? Some companies are looking to change low voter engagement by offering new benefits to employees who vote. Read on to learn more.
Voter engagement for midterm engagement historically has been poor. Some companies are offering new benefits to change that — even offering the day off to encourage employees to vote.
American employers that provide paid time off stands at about 44%, a record high, according to the latest research from the Society for Human Resource Management survey. The human resource organization estimates 29% of these companies offer employers more than an hour or two of voting time.
Despite such accommodations, about 60% of Americans didn’t vote in the last midterm election, according to research by Vote.org, a voters’ advocacy organization. The biggest obstacle to voting was scheduling conflicts; 35% of people said they couldn’t vote because of work and school.
“There’s no federal protection for voting leave for employees, which means it’s up to the states to set their own policies. Policies are inconsistent, but some states have no laws at all,” says Colette Kessler, director of partnerships at Vote.org. “This puts employers in a powerful position to enable employees to get to vote.”
But as more Americans prepare to head to the polls for key elections in 46 states, employers including Patagonia, Zenefits and Honest Tea, are opting to give employees paid time off to make their voice heard.
Outdoor retailer Patagonia, for instance, is closing its stores as well as its headquarters and distribution and customer-service center to give employees paid time off to vote. “No American should have to choose between a paycheck and fulfilling his or her duty as a citizen,” Patagonia CEO Rose Marcario wrote in a company blog post.
Meanwhile, human resource software company Zenefits implemented a new program in which employees can take time off to vote the same way they would for a doctor’s appointment. Voting won’t cut into their sick days, vacation time or paid time off. Instead, voting gets its own designation — civic time off, or CTO. That free time can be used for voting, volunteering for a candidate, attending a school board meeting or canvassing.
“Civic time off is a new concept for the industry, and we’re excited to be among the first to offer such a benefit,” says Beth Steinberg, chief people officer at Zenefits, in a letter on the company blog. “At Zenefits, it’s been a priority to help build our team’s skill set not only as it pertains to professional career growth, but also to encourage their development outside of the workplace as engaged and empowered citizens.”
Vote.org consults with companies interested in implementing a CTO program. Based on individual business models and company culture, the organization will suggest either full days off, half days or flexible scheduling.
“One benefit we’re really excited about is offering employees a half day. It gives employees the ability to get to their polling places and do their morning routine — like getting the kids to school and running errands,” Kessler says. “And later they can convene with colleagues and celebrate Election Day. We’re seeing HR teams create afternoon lunch parties to celebrate.”
Kessler says some companies are hesitant to provide time off for voting because they’re worried about losing productivity. However, most of the companies she’s worked with have been enthusiastic about providing their workforce with time off to vote.
“We don’t see any drawbacks to offering our employees flexibility on Election Day,” says Seth Goldman, co-founder and CEO emeritus of beverage company Honest Tea, which allows its 50 employees to take a few hours of paid time off go to the polls on Election Day, at their convenience. “It’s a right we all should be proud to recognize and support however we can.”
SOURCE: Webster, K. (5 November 2018) "Civic time off: The benefit getting employees to the polls" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from: https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/news/civic-time-off-the-benefit-getting-employees-to-the-polls?feed=00000152-a2fb-d118-ab57-b3ff6e310000
Interact Sensitively with Employees Addicted to Opioids
Opioid addiction is running rampant across the U.S. According to the National Institute of Drug Abuse, 8-12 percent of patients prescribed opioids develop an opioid use disorder. Read this blog post to learn more.
Employees who abuse opioids often are given a second chance by their employers. But well-meaning employers could wind up being sued for discriminating against those workers in violation of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) if they don't handle the situation very carefully.
Opioid addiction has been rampant in the U.S. for some time. More than three out of five drug overdose deaths last year involved an opioid, and overdoses rose 70 percent in the 12 months ending September 2017, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
So what can HR professionals do about it? If a worker admits to the problem, the path is fairly clear. But if the employer merely suspects that an employee is addicted to prescription pain relievers but has no real proof, the employee should be treated like any other employee who is having attendance or performance issues, said Kathryn Russo, an attorney with Jackson Lewis in Melville, N.Y.
An employer should never accuse someone of having an addiction, because if the employer is wrong, the accusation could lead to an ADA claim, Russo cautioned. Although current drug use isn't considered an ADA disability, a history of drug addiction is. Moreover, someone using prescription drugs might have an underlying condition covered by the ADA.

If an employee admits to opioid abuse, or the problem is discovered through drug testing, the employer should discuss it with the employee to determine if he or she needs a reasonable accommodation, such as leave to obtain treatment, Russo said. The illegal use of drugs need not be tolerated at work, she added.
Reasonably accommodate the employee so long as there's no direct threat to the health and safety of himself or herself, or others, recommended Nancy Delogu, an attorney with Littler in Washington, D.C.
Drug Testing
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission has opined that employers may ask about an employee's use of prescribed medicine or conduct a drug test to determine such use only if the employer has reasonable suspicion that its use will interfere with the employee's ability to perform the job's essential functions or will pose a direct threat.
Many employers are expanding their drug-testing panels to include semisynthetic opioids such as hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone and oxymorphone, in addition to traditional opioids such as heroin, codeine and morphine, Russo said. This is lawful in most states as long as the employer does not take adverse employment actions when drugs are used legally, she noted, which is why an employer should use a medical review officer in the drug-testing process. If the medical review officer concludes that the positive test result is the result of lawful drug use, the result is reported to the employer as negative.
Sometimes an employer will say it has reasonable suspicion that the employee came to work impaired by drug use and is considering a mandatory drug test. At that point, some employees will say the drug test would be positive and the test consequently is not necessary.
Discussions with Employees
If there are performance problems and the employee has admitted to opioid addiction, some employers tell employees that they can remain employed so long as they go through inpatient treatment. Delogu discourages that approach. Employers aren't workers' doctors, so they shouldn't be deciding whether someone needs a treatment program, she explained.
But if someone voluntarily seeks to enter an addiction-recovery program, that person may have legal protections under state law, said Wendy Lane, an attorney with Greenberg Glusker in Los Angeles. For example, California has a law requiring employers with 25 or more employees to reasonably accommodate alcohol and drug rehabilitation.
Delogu recommended that employers that believe there is a problem with substance abuse ask if the addicted employee needs assistance from the employee assistance program.
An employer can require that an employee who has violated a policy be evaluated by a substance abuse professional and complete treatment prescribed for them, without dictating what that treatment will be, she said. The employer may choose to forgo disciplinary action if an employee agrees to these terms and signs an agreement to this effect. The employer then would not have to be informed about the person's decided course of treatment, whether inpatient, outpatient or no treatment at all, she said. The employee typically will be subjected to follow-up drug testing to make sure he or she hasn't resumed the use of illegal drugs.
Many employers are willing to give employees with performance problems resulting from opioid addiction a second chance, she noted.
SOURCE: Smith, A. (1 November 2018) "Interact Sensitively with Employees Addicted to Opioids" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/ResourcesAndTools/legal-and-compliance/employment-law/Pages/employees-addicted-to-opioids.aspx
How to Handle Employee Requests for Time Off to Vote
Do you know how to handle employee requests for time off to vote? In some states, it is a requirement to give employees time off to vote. Read this blog post to learn more.
Many employees will be eligible to cast their ballot on Nov. 6, but will they have time to vote? Some states require employers to give workers time off to vote, and even in states that don't, some businesses are finding other ways to get employees to the polls.
With Election Day around the corner, employers should be mindful that, while no federal law provides employees leave to vote, many states have enacted laws in this area, said Marilyn Clark, an attorney with Dorsey & Whitney in Minneapolis. Depending on the state, employers may have to give workers notice about their voting rights and provide paid or unpaid time off to vote.
Even in states where there is no voting leave law, it is good practice to let employees take up to two hours of paid time off to vote if there isn't enough time for the employee to vote outside of working hours. "Encouraging and not discouraging employees should be the general rule," said Robert Nobile, an attorney with Seyfarth Shaw in New York City.
Encourage Employees
"Here in the United States, too many people don't vote because they don't have time due to jobs, child care and other responsibilities," said Donna Norton, executive vice president of MomsRising, an organization of more than 1 million mothers and their families. "Getting to the polls can be especially challenging for people in rural communities [or] single-parent households, and those who are juggling multiple jobs."
About 4 in 10 eligible voters did not vote in the 2016 presidential election, according to research conducted by Nonprofit VOTE and the U.S. Elections Project. And voter turnout has been historically lower for midterm elections, such as this year's, which are held near the midpoint of a president's four-year term, according to Pew Research Center.
"Businesses can help solve this problem by making sure that all employees have paid time off to vote," Norton said.
Some employers are offering solutions by making Election Day a corporate holiday, offering a few hours of paid time off for employees to vote and giving employees information about early and absentee voting, according to TheWashington Post.
Giving employees time off to participate in civic or community activities tends to improve worker performance, said Katina Sawyer, Ph.D., an assistant professor of management at George Washington University. Employers who are offering paid time off to vote will likely reap the benefits through improved employee attitudes and performance.
Know the Law
Employers in states with voting-leave laws should be familiar with the specific requirements, as some state laws have a lot of details. Even in states without such laws on the books, employers should check to see if there are any local voting leave ordinances in their cities.
Employers required to give workers time off to vote should plan for adequate work coverage to ensure that all employees can take time off, Clark said.
In many states, the employer may ask workers to give advance notice if they need time off and may require that workers take that leave at a specific time of the workday. In some states where leave is paid, employers might have the right to ask employees to prove they actually voted. Most states prohibit employers from disciplining or firing an employee who takes time off from work to vote.
"Ultimately, fostering an environment that generally encourages employees to exercise this important right is a good practice to mitigate the risk of a potential retaliation claim," Clark said.
Although state laws vary, "the general theme across the U.S. with respect to voting laws is that employees will be given time off to vote if there is insufficient time between the time the polls open and close within the state and the time employees start and finish work," Nobile said. "Typically, two to three consecutive nonworking hours between the opening and closing of the polls is deemed sufficient."
Some state laws provide unpaid leave to vote or do not address whether the leave must be paid. Oregon and Washington no longer have voting leave laws because they are "vote-by-mail" states.

In some states, such as California and New York, employers must post notices in the workplace before Election Day to inform employees of their rights. Employers might have to pay penalties if they don't comply.
The consequences for denying employees their voting rights can be harsh, with some states even imposing criminal penalties, Clark noted.
Create a Policy
At a minimum, employers should adopt a policy spelling out the voting rights available to employees under applicable laws, Clark said. For businesses that operate in states that don't have a voting-leave law, employers may still wish to adopt a policy outlining their expectations about time off for voting.
Multistate employers may elect to adopt a single policy that includes the most employee-friendly provisions of the state and local laws that cover them. "By taking this approach, employers avoid the administrative burden of adopting and promulgating multiple policies for employees working in different locales," Clark said. All voting-leave policies should be sure to include strong anti-retaliation provisions, which make clear that the employer will not take any adverse action against employees for exercising their voting rights.
"It's important to remember that the law sets the floor," said Bryan Stillwagon, an attorney with Sherman & Howard in Atlanta. "Companies with the happiest and most-engaged employees recognize that positive morale comes from doing more than what is required."
Nagele-Piazza, L. (29 October 2018) "How to Handle Employee Request for Time Off to Vote" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/ResourcesAndTools/legal-and-compliance/state-and-local-updates/Pages/How-to-Handle-Employee-Requests-for-Time-Off-to-Vote.aspx
Dana Wilkie contributed to this article.
Why employee performance management needs an HR tech overhaul
Are annual performance reviews necessary? A recent survey by Adobe reveals that 58 percent of people feel that performance reviews are not necessary. Continue reading to learn more.
According to a recent survey conducted by Adobe, 58% of people feel that performance reviews “are a needless HR requirement.” Adobe, in fact, no longer has an annual performance review process and instead has adopted an approach involving ongoing discussions between managers and employees that emphasize talent development and future productivity instead of formal ratings and rankings based on past performance.
Still, the vast majority of companies continue to persist with a backward-looking evaluation process that is time-consuming for managers, demotivating for employees and of negligible benefit to the business as a whole. They do this because, as Adobe’s survey respondents suspected, performance reviews are more about “compliance than customer service.”
Focusing on past performance is an industrial-era hangover from when employees were mainly required to hit targets in easily measurable, repetitive tasks. Although most people’s jobs have evolved to be more complex and creative since then, the process and the tools used to manage their efficacy and performance in those roles have not.
In many respects, HR is still a defensive function whose role is to protect the business from its own employees. This is reflected by HR technology that is built for compliance, rather than helping managers and employees become more productive.
HR’s on-premise or enterprise resource planning systems can track performance reviews to prove a dismissal was not unfair, rank employees to justify compensation distribution and demonstrate effective people management to the board or shareholders. What they can’t do is react positively to the ever-changing demands of the modern business world and help employees and managers meaningfully improve their skills to meet the challenges of tomorrow.
Performance management is changing — but HR tech is not
These days, a company’s and individual employee’s goals can change dramatically in the time between end-of-year reviews. Individual roles are more specialized and require frequent skill updates, while cross-functional teams have long since replaced the siloed departments that were standard just 10 years ago. In this environment, HR’s focus on past compliance is detrimental to future development.
Forward-thinking companies are changing the performance process to focus on development and continuous feedback that makes managers and employees more productive and engaged. The success of these trailblazers will encourage other businesses from a wide range of industries to follow suit.
This new model of performance management needs help from technology, but existing HR tech vendors are not keeping up. Their services are so embedded in the world of compliance, they cannot change to support the development needs of managers and employees. Fortunately, the solution already exists.
Creating a connected system of productivity
One of the key issues with performance reviews is that so much of the process involves looking back to gather the data. For managers, it is a huge time investment. For employees, end-of-year feedback about an issue that occurred months beforehand is too late to be useful.
The process seems doubly inefficient when you realize that real-time, instantly-actionable performance data is already available in productivity systems like JIRA and Salesforce that are used by different teams. The problem is HR’s defensive mindset has made it difficult to integrate existing internal or ERP systems with these tools.
Dedicated performance management services that connect to both HR systems and the departmental productivity tools can take HR technology out of its silo. This will create a connected system of productivity that uses real-time data alongside transparent and flexible goal-tracking to drive ongoing development conversations between managers and employees.
It’s time for HR to evolve from a defensive function to make a positive contribution to key business goals and become what HR analyst Josh Bersin calls the “chief of productivity.” This demands a shift from a performance review process based on compliance to a human-centered, development-focused experience.
Adopting new performance technology that integrates with widely-used productivity tools is a key step to ensuring everyone from employees to managers to HR can work on what matters most in order to meet today’s goals and tomorrow’s challenges.
SOURCE: Dennerline, D. (15 October 2018) "Why employee performance management needs an HR tech overhaul" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/why-employee-performance-management-needs-an-hr-tech-overhaul?brief=00000152-14a7-d1cc-a5fa-7cffccf00000
Culture is key to attracting younger talent, but you can make it mutually beneficial
According to an article in Harvard Business Review, six in ten millennials are ready to change jobs at any moment, creating a great opportunity for recruitment. Read this blog post to learn how organizations can attract younger talent.
Millennials with jobs are more likely to be looking for a new job than any other generation in the workplace, according to a Harvard Business Review article by Brandon Rigoni and Amy Adkins. They report that six in ten millennials are ready to jump ship at any given time.
This is a challenge for keeping workers, but it’s also a golden opportunity for recruitment. For the most part, these are bright workers who are deconstructing the great American job search.
Firms can seize this opportunity by honing their HR brand to appeal to younger generations and balancing this with assessments that assure a good match with most new hires.
Compensation is still important, but millennials are looking for jobs that are in sync with their values and can help define who they are. Getting hired has become a matter of personal identity.
As an employer, you are being evaluated more than the candidates. How will your firm make the cut? And if you do, will you hire the right people?
Major corporations have overhauled their approach in the scramble for talent.
- General Mills began using virtual reality headsets to allow candidates to see themselves working inside General Mills, including using the company’s gym.
- Two Volvo engineers recently built a Baja racer for collegiate competitions to attract young engineers to the legacy truck builder.
- General Electric’s humorous “What’s the Matter with Owen” television campaign said bupkis about GE products. Instead, Owen touted the company’s geek chic HR brand as a bespectacled new employee being effusive about his job of programming life-changing technology to help people.
- McDonald’s eschews traditional media to engage 16 to 24-year-old candidates via Snapchat, offering “Snaplications” and video clips of young McDonald’s employees talking about their jobs.
Not everyone can serve up cold brew coffee in a corporate cafeteria. Still, there are practical steps most firms can take to enhance their HR brand for millennial and Gen Z values.
Does your organization operate with a high degree of transparency? Is it socially responsible? Do employees have paid leave for volunteer work? Are young team members valued and encouraged to contribute to relevant and visible projects and products?
Are there ways to present your products and services to be more relevant and important to society? For example, a textile manufacturer might not actually make exciting products anyone can buy, but its fabrics are used in the space program or to save lives in emergency rooms. Maybe a law firm has a pro bono clinic for low-income families.
Yes. HR needs to make your employer brand attractive to these talented but fickle job seekers, but this doesn’t mean that everyone who’s attracted to your organizational hipness is going to be cool for your company.
There are two tools to make sure both parties get what they want. The first is assessments.
Talent acquisition assessments greatly improve your odds of hiring an individual who is well matched to your company’s needs. The best are scientifically valid and EEOC compliant, focusing on the candidate’s motivation and likely work traits as compared to the job description. You’ll save a lot of money in not having to re-hire for a position.
The second tool is the “Shared Success Model,” which is a process hiring managers can establish that aligns individual development plans with organizational strategies to identify where overlap exists and where there may be gaps.
It has five components:
- Individual needs—What is important to the candidate, both professionally and personally? What aligns with their values and interests?
- Individual offer—What value does the organization bring to the candidate?
- Company needs—What does your organization require for success now and in the future? What do you need from your leaders and employees?
- Company offer—What is your corporate value proposition to the candidate? What opportunities do you provide? What culture do you provide?
- Plan—Analyze the gaps and overlap between each quadrant. Develop and implement a plan that balances your grid for shared success.
As younger candidates seek more of a cultural match, the Shared Success Model is a good way to make sure the culture you promise is a culture that supports your mission and business model.
SOURCE: Warrick, D. (8 October 2018) "Culture is key to attracting younger talent, but you can make it mutually beneficial" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitspro.com/2018/10/08/culture-is-key-to-attracting-younger-talent-but-yo/
What employers can do to combat risks of workplace opioid abuse
How can employers combat the risks associated with workplace opioid abuse? With an increase in opioid use, employers are now tasked with the challenge of addressing opioid misuse in the workplace. Continue reading to learn more.
The opioid epidemic presents a unique challenge for employers. While opioids can be beneficial for employees suffering from pain, they also pose grave risks and dangers for companies as even appropriate use of the drugs can cause impairment and lead to accidents.
For example, if an employee had an accident and suffers an injury, you may see the physical signs of the injury. However, it’s not as obvious if the employee was prescribed opioids for the pain associated with that injury. If the employee doesn’t disclose the prescription, they could resume their everyday duties, like operating machinery, when they should be restricted while using the drug.
Due to the increasing prevalence of opioid use, employers are likely now challenged with addressing misuse in the workplace. Often, companies may not know the best approach to supporting employees dealing with an opioid addiction. When speaking with employers, it’s important to stress the need for organizations to be well-versed in opioid misuse and ways to proactively identify and address it.
Employers can work to combat opioid use in their organization by providing accommodations and updating their policies, procedures and employee communications. Here are a few ways they can get started.
Short-term accommodations
If an employee is taking prescribed opioids for an injury and has specific limitations or restrictions, an employer can work with a disability carrier to determine potential short-term accommodations that can be made to meet the employee’s needs. Short-term accommodations can help keep an employee comfortable and productive at work during his or her recovery.
Policies and procedures
If an employer hasn’t done so already, it should consider putting a comprehensive drug policy in place to help it address issues that may arise if an employee misuses prescription drugs. The policy should include a description of available assistance options for employees who are struggling with substance abuse and clearly state consequences for employees who violate the policy, empowering supervisors to take appropriate action in response to employee issues.
Destigmatizing use
It’s easier to help someone if they come forward, but right now, stigma surrounding opioids can cause employees to keep their prescription use to themselves. Encouraging open lines of communication can help companies destigmatize prescription drug use so their employees feel comfortable disclosing the medications they’re taking that could limit them at work.
Fostering transparency, combined with short-term accommodations and clear policies, can help employees feel more comfortable coming forward with their condition. Remind employers that their disability carrier can be a great resource to help with education, recommend proactive ways to address misuse at their organization and create accommodation plans for employees in need. With these steps, employers can help support their employees and, ultimately, make the workplace a safer place for all.
SOURCE: Jolivet, D (16 October 2018) "What employers can do to combat risks of workplace opioid abuse" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/what-employers-can-do-to-combat-workplace-opioid-abuse-risk
Ready for the sounds of office sniffles?
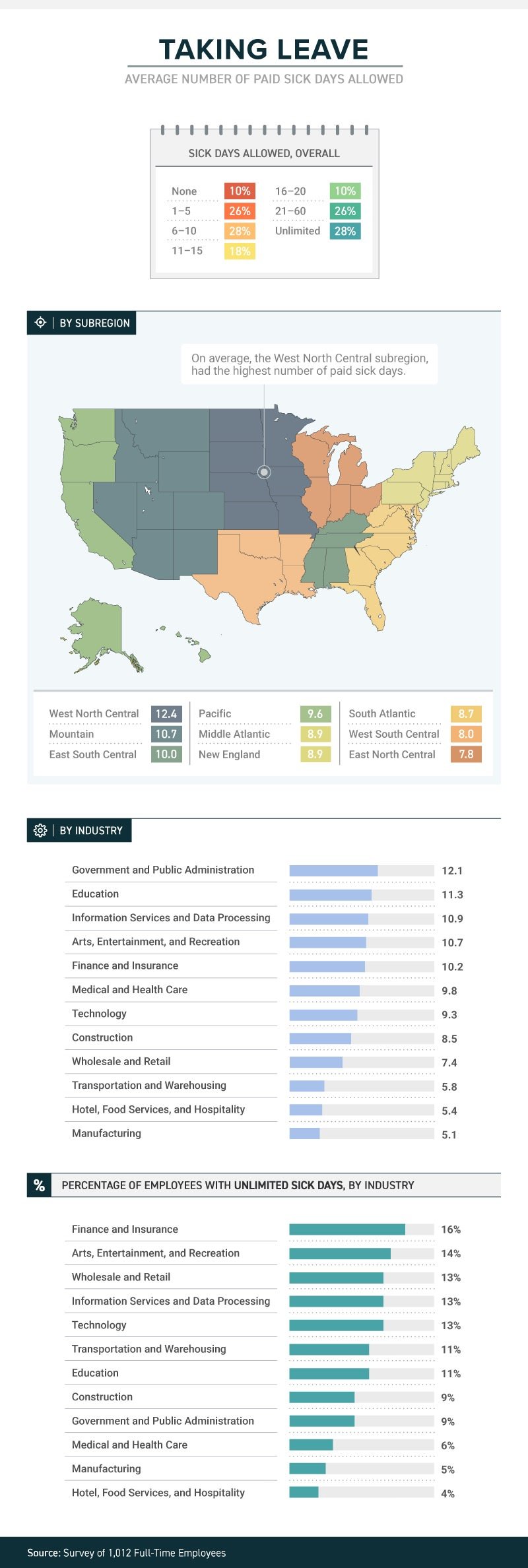
A recent study by law firm, Farah and Farah, states that one in four full-time workers receive between 1 and 5 sick days. Continue reading to learn more.
It’s not just a matter of whether they feel well enough to work, or whether they have sick days. The boss’s attitude about whether workers should take sick days or not can determine whether they actually do stay home when they’re sick, or instead come to work to spread their germs to all and sundry.
A new study from law firm Farah & Farah finds that even though it can take a person some 10 days to fully recover from a cold, approximately 10 percent of full-time workers in the U.S. get no sick days at all (part-timers don’t usually get them either), while more than 1 in 4 have to make do with between 1 and 5 sick days. Just 18 percent get enough sick time to actually recover from that cold—between 11 and 15 days.
The amount (or presence) of sick time varies from industry to industry, with government and public administration providing the most (an average of 12.1) and both hotel, food services and hospitality and manufacturing providing the least (an average of 5.4 for the hospitality industry and 5.1 for manufacturing). Some lucky souls actually get unlimited sick days, although even then they don’t always use them.
Regardless of industry, or quantity, just because workers get sick days it doesn’t mean they use them. Workers often worry that they’ll be discouraged from using them, with employers who may provide them but not encourage employees to stay home when ill. In fact, 38 percent of workers show up to work whether they’re contagious or not. Sadly for the people they encounter at work, the most likely to do so are in hospitality, medical and healthcare and transportation. Plenty of germ-spreading to be done in those professions!
And their employers’ attitudes play a role in how satisfied they are with their jobs. Among those who work for the 34 percent of bosses who encourage sick employees to stay home, 43 percent said they’re satisfied with their jobs in general. Among those who work for the 47 percent of bosses who are neutral about the use of sick days, that drops to 21 percent—and among the unfortunate workers who work for the 19 percent of bosses who actually discourage workers from staying home while ill, just 12 percent were satisfied with their jobs.
When it comes to mental health days (no, not that kind; the ones people really need to deal with diagnosed mental health conditions), fewer than 1 in 10 men and women were willing to call in sick. Taking “mental health days” when physically healthy, however, either to play hooky or simply have a vacation from the office, is something that 15 percent of respondents admitted to.
SOURCE: Satter, M (5 October 2018) "Ready for the sounds of office sniffles?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitspro.com/2018/10/05/ready-for-the-sounds-of-office-sniffles/
Original report retrieved from https://farahandfarah.com/studies/sick-days-in-america
U.S. Unemployment Drops to Lowest Rate in 50 Years
Last month the U.S. unemployment rate fell to 3.7 percent, the lowest it’s been in 50 years. Continue reading to learn how the low jobless rate is affecting the U.S. labor market.
Unemployment in the U.S. fell to 3.7 percent in September—the lowest since 1969, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
The low jobless rate, down from 3.9 percent in August, is further evidence of a strong economy—employers added 134,000 new jobs in September, extending the longest continuous jobs expansion on record at 96 months. The continued gains run counter to economists' expectations for a significant slowdown in hiring as the labor market tightens. Through the first nine months of the year, employers added an average of 211,000 workers to payrolls each month, well outpacing 2017's average monthly growth of 182,000.
"This morning's jobs report marked a new milestone for the U.S. economy," said Andrew Chamberlain, chief economist at Glassdoor. "With good news in most economic indicators today, it's likely the economy will continue its march forward through the remainder of 2018."
Cathy Barrera, chief economist at online employment marketplace ZipRecruiter, pointed out that the jobless rate ticked down for all education levels. "Anecdotal evidence has suggested that employers have experienced labor shortages for entry-level positions, and the decline in unemployment for these groups reflects that," she said. "More of those joining or rejoining the labor force are moving directly into jobs, reflecting the high demand for workers."
The sectors showing the strongest jobs gains in September include:
- Professional and business services (54,000 new jobs).
- Healthcare (26,000).
- Transportation and warehousing (24,000).
- Construction (23,000).
- Manufacturing (18,000).
"Retail job losses—20,000 jobs—were widespread, and the leisure and hospitality sector lost 17,000 jobs, largely confined to restaurants," said Josh Wright, chief economist for recruitment software firm iCIMS, based in Holmdel, N.J.
"We can clearly point to a slowdown in retail trade for the dip in [overall] payroll numbers in September," said Martha Gimbel, research director for Indeed's Hiring Lab, the labor market research arm of the global job search engine. "Retail trade had a strong first half of the year but has slowed down in recent months. In addition, recent Hiring Lab research saw a slight dip in the number of holiday retail postings, suggesting that the sector may struggle in months to come."
Prior to September, employment in leisure and hospitality had been on a modest upward trend and the losses last month may reflect the impact of Hurricane Florence.
The Department of Labor said it's possible that employment in some industries was affected by Hurricane Florence which struck the Carolinas in September. Nearly 300,000 workers nationwide told the BLS that bad weather kept them away from their jobs last month.
"That's far below the level in September 2017 amid hurricanes Harvey and Irma, but significantly above the average of about 200,000 over the prior 13 years," Wright said. Upward revisions are likely, he added.
Wages Stubborn but Rising
In September, average hourly earnings for private-sector workers rose 8 cents to $27.24. Over the year, average hourly earnings have increased by 73 cents, or 2.8 percent.
"That's down slightly from the 2.9 percent pace last month, but consistent with a steady upward trend in wage growth we've seen as the job market tightens and more employers face labor shortages," Chamberlain said. "We expect to see that pace continue to rise throughout the holiday season, likely topping 3 percent within the next six months."
Glassdoor has recorded strong wage growth in tech-heavy metropolitan areas such as San Francisco, New York and Los Angeles.
"If the true wage growth rate is at or below 2.8 percent year-over-year, it is disappointing that it is not growing faster," Barrera said. "Given how tight the labor market has been not only with overall unemployment below 4 percent, but particularly so at the entry level, we would expect wage growth to be higher. The labor turnover numbers suggest that mobility is lower than it historically has been in periods where unemployment is very low. This is one reason wages may not be rising as quickly as we'd expect."
Labor Force Participation Stalled?
The nation's labor force participation rate held at 62.7 percent.
"Looking at the labor flows data, the rate of movement of the civilian population into the labor force hasn't moved much in the last couple of years, however, more of those folks are moving directly into employment rather than into unemployment," Barrera said.
Wright noted that the number of new labor force entrants and reentrants going directly to unemployment was just 33,000. "This raises interesting questions—whenever we get a recession, how long will these reentrants and new entrants continue searching for jobs before leaving the labor force?" he asked.
The percentage of the population in their prime working years with a job also held around 79 percent, where it's been for about eight months, Gimbel said, adding that the measure suggests that the number of workers remaining to pull into the labor force may be exhausted.
"The share of the labor force working part-time but who wants a full-time job unfortunately ticked up," she said. "Any remaining slack in the economy may be concentrated in part-time workers who want more hours."
SOURCE: Maurer, R. (5 October 2018) "U.S. Unemployment Drops to Lowest Rate in 50 Years" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/hr-topics/talent-acquisition/pages/us-unemployment-drops-lowest-50-years-bls-jobs.aspx/
4 best practices for implementing a gamification-based compliance training system
Many employees may dislike and even disengage when their employer mentions implementing training sessions. Continue reading to learn how implementing a gamification-based training system can help improve employee engagement.
For most employees, compliance training is the Brussels sprouts on the kid’s plate of working life. Everyone knows it’s good for you — one mistake could lead to violations, accidents, reputation issues and maybe a not-so-friendly visit from regulatory body officials — but most workers turn up their noses and disengage when it’s time to dig in.
Considering that merely a third of American workers report feeling engaged at work as it stands, anything that makes matters worse is dangerous. Why risk inflaming indifference — not to mention spending money for on-site instructors — with dull-as-dry-toast workshops?
A far better bet is to embrace technology and go virtual. Of course, online-based compliance training won’t guarantee heightened participation or enthusiasm unless they have one specific aspect: gamification.
Gaming elements can turn any virtual compliance training learning management system (LMS) into an immersive experience. ELearning compliance training participants can enjoy customization and flexibility while getting up to speed on the latest rules, guidelines and protocols. With LMS gamification, HR managers and chief learning officers can cultivate and retain top talent. Best of all, it’s far easier to get buy-in for a robust LMS system with badges, bells and whistles than it is to make a pile of Brussels sprouts disappear from a toddler’s tray.
What exactly is so exciting about game-based learning? In essence, the process prompts active and immediate participation because of extra motivation in the form of rewards. Whether it’s badges or points, these features make eLearning interesting and enjoyable.
In one study, workers who enjoyed themselves retained concepts 40% better than those who weren’t having fun. As you might guess, this is what game-based learning is all about. Engaged employees who rapidly earn rewards are less likely to make errors, so they naturally increase a company’s bottom line and lower the likelihood of compliance fees and penalties. Plus, according to research from TalentLMS, 87% of employees report that gamification makes them more productive.
Merging gamification with training makes plenty of sense. It’s also easy to build a gamification-based compliance training LMS by following a straightforward LMS implementation checklist.
1. Identify your training goals and gaps. Before you can find the best LMS for your needs and move forward with an implementation project plan, you need to spot the inefficiencies of your existing compliance training program. For example, your strategy might not facilitate real-world applications. Knowing this, you would want a compliance training LMS that bridges gaps and imparts practical experience.
2. Discover what motivates and drives employees. Employee gamification only works when employees are properly incentivized, so find out what motivates your team based on their backgrounds and experience levels. Whether a task is challenging or boring, people respond better when they are internally driven to succeed.
Do you need an intuitive LMS with a personalized dashboard? Are the introverts on your team more driven by badges and points than by a sense of competition? Conduct surveys to gauge expectations, and try to follow a 70:20:10 model of training amplified by gaming to foster experimentation and collaboration.
3. Choose the right rewards for desired outcomes. With the plethora of LMS choices on the market, you can select from rewards and mechanics that lead to the exact behaviors and criteria you desire. Want employees to achieve safety online training certifications? Reward “graduates” with points after they have displayed their proficiency. Reinforce favorable behaviors without punishing workers who lag behind. Carrots are far more effective than sticks.
4. Invest in a feature-rich, gamification-supported LMS. Your LMS should not only be user-friendly, but it should also be a portal to game-based learning support and an online asset library. Ideally, your gamified learning platform should include themes and templates that allow you to design visually appealing rewards without reinventing the wheel. Just make sure you have game-based reporting on your side, which makes it simple to track employee performance, completion rates, and other LMS metrics.
Implementing a gamification-based compliance training strategy requires careful budgeting, planning, and analysis. Once you find an LMS platform that delivers the features you need within your price range, you’ll be on your way to mitigating risks and retaining superstar employees. And thanks to gamification, everyone can have a little fun along the way.
SOURCE: Pappas, C. (10 October 2018) "4 best practices for implementing a gamification-based compliance training system" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/4-best-practices-for-implementing-a-gamification-based-compliance-training-system?brief=00000152-14a5-d1cc-a5fa-7cff48fe0001
8 keys to developing a successful return to work program
What does your return to work program look like? Read this blog post for 8 tips to developing a successful return to work program at your organization.
No matter the size of your organization, there’s about a 99% chance at some point dealing with employees going on leave. Most HR professionals are well-versed on the logistics of what to do when an employee is on short- or long-term disability — but what sort of culture do you have in place that encourages and supports them with a return to work (RTW)? Developing a positive and open RTW culture benefits not only the organization but the employee and their teams as well.
An effective RTW program helps an injured or disabled employee maintain productivity while recuperating, protecting their earning power and boosting an organization’s output. There also are more intangible benefits including the mental health of the employee (helping them feel valued), and the perception by other team members that the organization values everyone’s work.
See also: 7 Ways Employers Can Support Older Workers And Job Seekers
Some other benefits of an RTW program can include improvement of short-term disability claims, improvement of compliance and reduction of employer costs (replacing a team member can cost anywhere from half to twice that employee’s salary, so doing everything you can to keep them is a wise investment).
Some of these may seem like common sense, but I’m continually surprised how many (even large) organizations don’t have an established RTW program. Here are eight critical elements of a successful program.