DOL issues finalized overtime regulation
The DOL recently released their finalized overtime rule. This new rule raises the minimum salary level to $35,568 per year for a full-year worker to earn overtime wages. Read this blog post from Employee Benefit News to learn more about this new rule.
The DOL on Tuesday released its highly anticipated finalized overtime rule, raising the minimum salary level to $35,568 per year for a full-year worker to earn overtime wages.
“Today’s rule is a thoughtful product informed by public comment, listening sessions and long-standing calculations,” Wage and Hour Division Administrator Cheryl Stanton says in a statement. “The DOL’s wage and hour division now turns to help employers comply and ensure that workers will be receiving their overtime pay.”
The final rule, effective Jan. 1, 2020, updates the earnings thresholds necessary to exempt executive, administrative or professional employees from the FLSA’s minimum wage and overtime pay requirements, and allows employers to count a portion of certain bonuses (and commissions) toward meeting the salary level.
The new thresholds account for growth in employee earnings since the currently enforced thresholds were set in 2004. In the final rule, the department is:
- Raising the standard salary level from the currently enforced level of $455 to $684 per week (equivalent to $35,568 per year for a full-year worker);
- Raising the total annual compensation level for highly compensated employees from the currently-enforced level of $100,000 to $107,432 per year;
- Allowing employers to use nondiscretionary bonuses and incentive payments (including commissions) that are paid at least annually to satisfy up to 10% of the standard salary level, in recognition of evolving pay practices; and
- Revising the special salary levels for workers in U.S. territories and in the motion picture industry.
This finalized rule is a shift from the previous administration's proposed rule, which would have doubled the salary threshold.
Under the Obama administration, the Labor Department in 2016 raised the minimum salary to roughly $47,000, extending mandatory overtime pay to nearly 4 million U.S. employees. But the following year, a federal judge in Texas ruled that the ceiling was set so high that it could sweep in some management workers who are supposed to be exempt from overtime pay protections. Business groups and 21 Republican-led states then sued, challenging the rule.
The overturning of the 2016 rule that increased the salary level from the 2004 level has created a lot of uncertainty, says Susan Harthill, a partner with Morgan Lewis. The best way to create certainty is to issue a new regulation, which is what the administration's done, Harthill adds.
While the final rule largely tracks the draft, there are two changes that should be noted: the salary level is $5 higher and the highly compensated employee salary level is dramatically reduced from the proposed level, she says.
“This is an effort to find a middle ground, and while it may be challenged by either or maybe both sides, the DOL’s salary test sets a clear dividing line between employees who must be paid overtime if they work more than 40 hours per week and employees whose eligibility for overtime varies based on their job duties,” Harthill adds.
The DOL estimates 1.3 million employees could now be eligible for overtime pay under this rule (employees who earn between $23,600 and $35,368 no longer qualify for the exemption).
A majority of business groups were critical of Obama’s overtime rule, citing the burdens it placed particularly on small businesses that would be forced to roll out new systems for tracking hours, recordkeeping and reporting.
SHRM, for example, expressed it's opposition to the rule, noting it would have fundamentally changed the rules for employee classification, dramatically increased the salary under which employees are eligible for overtime and provided for automatic increases in the salary level without employer input.
“Today’s announcement finalizing DOL’s overtime rule provides much-needed clarity for workplaces," SHRM says in a statement. "This rule marks the first increase to the salary threshold since 2004 and gives employers more flexibility to plan for the future. We appreciate DOL’s willingness to work with SHRM, other organizations and America’s workers to enact an overtime rule that benefits both employers and their employees.”
But the finalized rule still will have implications for employers.
“Education and health services, wholesale and retail trade, and professional and business services, are the most impacted industries, according to DOL, but all industries are potentially impacted,” Harthill, also former DOL deputy solicitor of labor for national operations, adds. “Also often overlooked is the impact on nonprofits and state and local governments, which are subject to the FLSA and often have lower salaries.”
All companies should be taking a close look at their employees to make sure workers are properly classified, but what they do after that will depend entirely on individual business needs, she says. “Some will hire additional employees to reduce the amount of overtime, while others will just pay overtime if their workers in this salary bracket spend more than 40 hours a week on the job.”
Employers who haven’t already reviewed their exempt workforce should do so now, before the Jan. 1 effective date, Harthill advises.
“They can opt to pay overtime, raise salary levels above $35,368, or review and tighten policies to ensure employees do not work more than 40 hours per week,” she says. “There could be job positions that need to be reclassified and that might have a knock-on effect for employees who earn above the new salary level.”
Many employers increased their salaries when DOL issued the 2016 rule, and some states have higher salary levels, so not all businesses will need to make an adjustment. “But even those employers should review their highly compensated employees — they may still be exempt even if they earn less than $107,432 but the analysis will be more complicated,” she adds.
“We did not hear any objections from employers when these rules were initially proposed," adds Jason Hammersla, vice president of communications at the American Benefits Council. "That said, aside from the obvious compensation and payroll tax implications, this rulemaking is significant for employers who include overtime compensation in the formula for retirement plan contributions as it could increase any required employer contributions."
"The change could also affect plans that exclude overtime pay from the plan’s definition of compensation if the new overtime pay causes the plan to become discriminatory in favor of highly compensated employees," he adds.
SOURCE: Otto, N. (24 September 2019) "DOL issues finalized overtime regulation" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/news/dol-issues-finalized-overtime-regulation
Health insurance surpass $20,000 per year, hitting a record
According to an annual survey of employers, the cost of family health coverage has now surpassed $20,000, a record high. The survey also revealed that while most employers pay most of the costs of coverage, workers' average contribution for a family plan is now $6,000. Read this blog post from Employee Benefit News to learn more.
The cost of family health coverage in the U.S. now tops $20,000, an annual survey of employers found, a record high that has pushed an increasing number of American workers into plans that cover less or cost more, or force them out of the insurance market entirely.
“It’s as much as buying a basic economy car,” said Drew Altman, chief executive officer of the Kaiser Family Foundation, “but buying it every year.” The nonprofit health research group conducts the yearly survey of coverage that people get through work, the main source of insurance in the U.S. for people under age 65.
While employers pay most of the costs of coverage, according to the survey, workers’ average contribution is now $6,000 for a family plan. That’s just their share of upfront premiums, and doesn’t include co-payments, deductibles and other forms of cost-sharing once they need care.
The seemingly inexorable rise of costs has led to deep frustration with U.S. healthcare, prompting questions about whether a system where coverage is tied to a job can survive. As premiums and deductibles have increased in the last two decades, the percentage of workers covered has slipped as employers dropped coverage and some workers chose not to enroll. Fewer Americans under 65 had employer coverage in 2017 than in 1999, according to a separate Kaiser Family Foundation analysis of federal data. That’s despite the fact that the U.S. economy employed 17 million more people in 2017 than in 1999.
“What we’ve been seeing is a slow, slow kind of drip-drip erosion in employer coverage,” Altman said.
Employees’ costs for healthcare are rising more quickly than wages or overall economy-wide prices, and the working poor have been particularly hard-hit. In firms where more than 35% of employees earn less than $25,000 a year, workers would have to contribute more than $7,000 for a family health plan. It’s an expense that Altman calls “just flat-out not affordable.” Only one-third of employees at such firms are on their employer’s health plans, compared with 63% at higher-wage firms, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation’s data.
The survey is based on responses from more than 2,000 randomly selected employers with at least three workers, including private firms and non-federal public employers.
Deductibles are rising even faster than premiums, meaning that patients are on the hook for more of their medical costs upfront. For a single person, the average deductible in 2019 was $1,396, up from $533 in 2009. A typical household with employer health coverage spends about $800 a year in out-of-pocket costs, not counting premiums, according to research from the Commonwealth Fund. At the high end of the range, those costs can top $5,000 a year.
While raising deductibles can moderate premiums, it also increases costs for people with an illness or who gets hurt. “Cost-sharing is a tax on the sick,” said Mark Fendrick, director of the Center for Value-Based Insurance Design at the University of Michigan.
Under the Affordable Care Act, insurance plans must cover certain preventive services such as immunizations and annual wellness visits without patient cost-sharing. But patients still have to pay out-of-pocket for other essential care, such as medication for chronic conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure, until they meet their deductibles.
Many Americans aren’t prepared for the risks that deductibles transfer to patients. Almost 40% of adults can’t pay an unexpected $400 expense without borrowing or selling an asset, according to a Federal Reserve survey from May.
That’s a problem, Fendrick said. “My patient should not have to have a bake sale to afford her insulin,” he said.
After years of pushing healthcare costs onto workers, some employers are pressing pause. Delta Air Lines Inc. recently froze employees’ contributions to premiums for two years, Chief Executive Officer Ed Bastian said in an interview at Bloomberg’s headquarters in New York last week.
“We said we’re not going to raise them. We're going to absorb the cost because we need to make certain people know that their benefits structure is real important,” Bastian said. He said the company’s healthcare costs are growing by double-digits. The Atlanta-based company has more than 80,000 employees around the globe.
Some large employers have reversed course on asking workers to take on more costs, according to a separate survey from the National Business Group on Health. In 2020, fewer companies will limit employees to so-called “consumer-directed health plans,” which pair high-deductible coverage with savings accounts for medical spending funded by workers and employers, according to the survey. That will be the only plan available at 25% of large employers in the survey, down from 39% in 2018.
Employers have to balance their desire to control costs with their need to attract and keep workers, said Kaiser’s Altman. That leaves them less inclined to make aggressive moves to tackle underlying medical costs, such as by cutting high-cost hospitals out of their networks. In recent years employers’ healthcare costs have remained steady as a share of their total compensation expenses.
“There’s a lot of gnashing of teeth,” Altman said, “but if you look at what they do, not what they say, it’s reasonably vanilla.”
SOURCE: Tozzi, J. (25 September 2019) "Health insurance surpass $20,000 per year, hitting a record" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/articles/health-insurance-costs-surpass-20-000-per-year
6 voluntary benefits your employees want
Multigenerational workforces are no longer finding the run-of-the-mill benefits plans adequate. This is making voluntary benefits more important than ever in this age of the multigenerational workforce and a tight labor market. Read this blog post from for six voluntary benefits employees want.
In this age of the multigenerational workforce and a tight labor market, a one-size-fits-all group benefits model with medical, prescription, dental, vision and a retirement plan just doesn’t cut it. A workforce with Baby Boomers, Gen X’ers, Millennials and Generation Z means that employees are going to find the run-of-the-mill benefits plan inadequate. Ditto for job seekers.
What follows is that voluntary benefits are more important than ever. Offering a range of voluntary benefits can help meet the needs of employees at all life stages.
Voluntary benefits add value to benefit plans and are typically easy to administer. They’re low-to-no-cost because employees pay for them, and maintenance is often handled through a payroll deduction. Many voluntary benefits also offer guaranteed acceptance at a lower rate than medical benefits, so even if a small group within your company chooses a particular benefit, they’ll be covered.
This landscape is changing quickly. Here are six trending voluntary benefits your employees want.
Student loan debt repayment assistance
Debt among college graduates has grown to nearly $1.6 trillion. It’s preventing the largest employee segment at most companies from buying houses or cars, saving for retirement, having kids and getting married. To help employees repay their student loan debt, some employers are helping employees pay down student loan debt through a direct payroll deduction.
Others are offering a new, IRS-allowable retirement plan match swap where an employer can opt to increase its defined contribution match, enabling employees to reduce their retirement match and contribute funds to repaying student loans instead.
Interest in this benefit continues to grow. Employers looking to offer student loan debt repayment should be aware that not all platforms are created equal. Look out for high per-employee, per-month fees.
Individual long-term care
A growing number of people are beginning to understand the value of long-term care insurance because they have taken care of or currently care for a friend or relative who needs round-the-clock care. Long-term care insurance covers home or institutional care if a person is no longer able to perform at least two activities of daily living--eating, bathing, dressing, moving from a bed to a chair or using a toilet.
Employees are interested in buying long-term care insurance through their employer because they can offer better rates for simplified issue plans. If you plan to offer long-term care as an employer-sponsored benefit, I recommended rolling it out with a strategic project plan and a benefit counselor or a technology platform capable of providing decision-making tools for a smooth application process.
Executive reimbursement plans
Employee retention — especially executive retention — is on the minds of many employers in the midst of this thriving economy. Filling gaps in medical and prescription coverage is one way to provide executive teams with premium benefits they may be looking for.
Executive reimbursement plans provide reimbursement for out-of-pocket expenses, access to facilities and level of service not normally covered under most group health plans. Rather than simply increasing compensation to help cover out-of-pocket expenses, premiums for these plans are tax-deductible for the employer, and benefits are non-taxable for employees.
Executive individual disability insurance
Traditional employer-sponsored long-term disability (LTD) is likely not enough coverage for highly-compensated employees or some sales staff who depends heavily on commission and bonuses. Normally, LTD pays employees 50-70% of their salary up to a certain amount.
Employers can carve out additional coverage for employees based on their management level, performance or tenure. Individual disability insurance plans can protect employees until they turn 65; they can also protect job titles or levels until employees are well enough to return to work. Executive individual disability insurance, like executive reimbursement, can be offered as a form of compensation, or a form of financial asset protection for higher incomes.
Telemedicine
The rise of consumer-driven health plans has led to the need for telemedicine. Telemedicine provides a way for employees to see a physician or provider by video and get a diagnosis and/or prescription quickly. The success of telemedicine is leading some carriers to integrate it within their plan. However, standalones still exist and can provide employees with an easy way to get care faster and cheaper than before.
Pet Insurance
Pet parents spend nearly $70 billion on veterinarian costs for their pets, but just 10% of dogs and 5% of cats are covered by medical insurance. As pets begin to play a larger role in our lives, more employers are offering pet insurance to their employees to help defray the cost of unexpected medical expenses.
There are a number of plan options, and setting up a plan for employees’ pets is simple. However, it’s vital that employers do their research to ensure the veterinarian network includes the best vets.
As part of a voluntary benefit offering, be sure to develop a rollout strategy and communications plan so employees are thoroughly educated and you meet group minimums.
SOURCE: Park, N. (25 September 2019) "6 voluntary benefits your employees want" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/list/6-voluntary-benefits-your-employees-want
Key elements to consider when researching financial wellness programs
With financial wellness programs becoming a staple employee benefit, organizations find themselves implementing programs that only offer a few tools or resources. Read the following blog post from Employee Benefit Advisor for key elements to consider when researching financial wellness programs.
Financial wellness programs are becoming a staple in the employee benefit universe. But what should a successful financial wellness program encompass? As a rapidly growing industry, we often lack a consistent definition for financial wellness. This leads to organizations believing they have implemented a financial wellness program, when they may only be offering a few tools like education or counseling.
I define financial wellness as the process by which an individual can efficiently and accurately assess their financial posture, identify personal goals, and be motivated to gain the necessary knowledge and resources to create behavioral change. Behavioral change will result in improved emotional and mental well-being, along with short- and long-term financial stability.
As the administrator of your company’s benefits, you are responsible for bringing the best possible solution to your employees. That’s a tough ask, given the growing number of service providers. So, what is the most efficient and effective way to assess financial wellness services to determine which solution best fits your organizational needs? Ask yourself these questions:
Does the platform offer a personal assessment of each employee’s current financial situation and help them identify their financial goals? If the answer is yes: Does the assessment return quantifiable and qualifiable data unique to each individual employee?
Does the platform address 100% of your employee base, including the least sophisticated employees at various levels of employment? Much of your ROI from a financial wellness program does not come from your top performers. It comes from creating behavioral changes within your employees who need the most financial guidance.
Does the platform integrate the various components to provide a personalized roadmap for each employee? It should connect program elements like personal assessments, educational resources, tools, feedback and solutions to ensure the employee is presented with a cohesive, comprehensive plan to attack and improve their financial situation.
Does the platform offer solutions for short-term financial challenges like cash flow issues, as well as long-term financial challenges associated with saving and planning? A major return on your investment comes from reduced employee stress, which is substantially driven by short-term needs versus long-term objectives. The program must help employees deal with current financial challenges before they can focus on their longer-term vision.
About 78% of U.S. workers live paycheck to paycheck to make ends meet, according to data from CareerBuilder.com. The need for financial wellness is clear, but there are consistent pillars that must be addressed in any successful financial wellness program to affect change: spend, save, borrow and plan. When evaluating financial wellness programs, it’s important that these dots all connect if you are truly going to motivate behavioral change and recognize the ROI of a comprehensive financial wellness program.
SOURCE: Kilby, D. (13 September 2019) "Key elements to consider when researching financial wellness programs" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/opinion/key-considerations-for-employee-financial-wellness-programs
4 pitfalls of paid leave and how clients can avoid them
Employers are using paid leave options to help boost their employee benefits packages in efforts to better attract and retain talent. Read the following blog post from Employee Benefit Advisor for 4 common pitfalls of paid leave and how employers can avoid them.
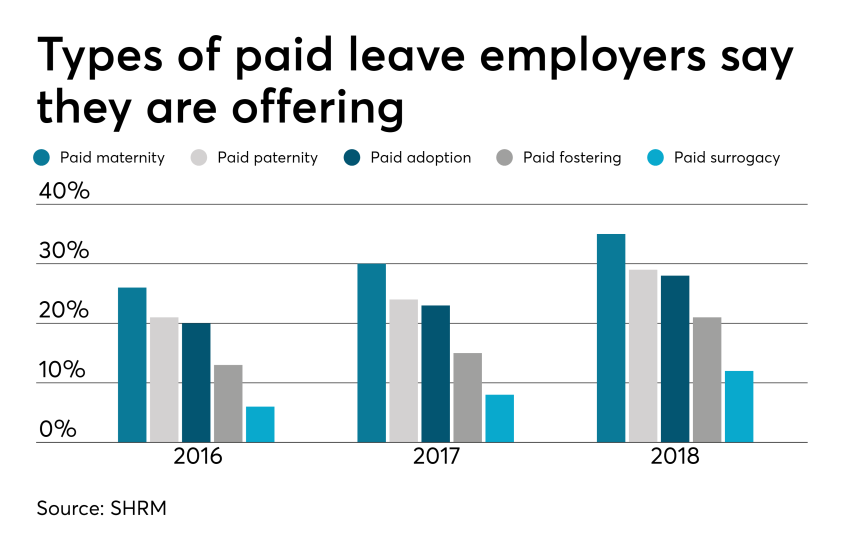 Smart employers are boosting their benefits packages with paid family leave — the most coveted work perk among all generations. In today’s low unemployment environment, paid leave benefits can be a huge differentiator in attracting and retaining talent.
Smart employers are boosting their benefits packages with paid family leave — the most coveted work perk among all generations. In today’s low unemployment environment, paid leave benefits can be a huge differentiator in attracting and retaining talent.
But some employers are getting themselves into trouble in the process, facing accusations of gender discrimination or improper use of leave.
Here are four potential pitfalls of paid leave, and how employers can avoid them.
1. Be careful what you call “maternity leave.”
Employers have long been granting leave for new moms in the form of disability coverage. In fact, the top cause of short term disability is pregnancy. Disability insurance usually grants new moms six to eight weeks of paid leave to recover from childbirth.
Because this coverage applies to the medical condition of recovering from childbirth, it shouldn’t be lumped in with bonding leave.
Guidance from the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission says leave granted for new moms for bonding must also be extended to new dads, so separating disability leave from bonding leave is crucial to avoiding gender discrimination.
2. Don’t make gender assumptions.
The amount of bonding time for new parents after birth, adoption or fostering must be granted equally for men and women. Companies that don’t provide the same amount of paid leave for men and women may find themselves in a discrimination lawsuit.
It’s not just the time away from work that matters, but also the return-to-work support provided. If new moms are granted temporary or modified work schedules to ease the transition back to work, new dads must also have access to this.
Some companies may choose to differentiate the amount of leave and return-to-work support for primary or secondary caregivers. That’s compliant as long as assumptions aren’t made on which gender is the primary or secondary caregiver.
The best way to avoid potential gender discrimination pitfalls is to keep all parental bonding and related return-to-work policies gender neutral.
3. Avoid assuming the length of disability.
Be careful about assuming the length of time a new mom is disabled, or recovering medically, after birth. Typical coverage policies allot six to eight weeks of recovery for a normal pregnancy, so assuming a new mom may be out for 10 weeks might be overestimating the medical recovery time, and under-representing the bonding time, which must be gender neutral.
4. Keep up with federal, state and local laws.
Mandated leave laws are ever-evolving, so employers should consistently cross-check their policies with state and local laws. For instance, do local paid leave laws treat adoption the same as birth? Are multistate employers compliant? What if an employee lives in one state but works in another: Which state’s leave policies take precedence?
Partnering with a paid leave service provider can mitigate the risk of improperly administering leave. Paid leave experts can help answer questions, review guidelines and provide information regarding job-protecting medical or family leave.
They can also help flag potential pitfalls, ensuring leave requests from all areas of your company are managed uniformly and in accordance with state and federal laws, including the EEOC.
SOURCE: Bennett, A. (12 September 2019) "4 pitfalls of paid leave and how clients can avoid them" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/list/4-pitfalls-of-paid-leave-and-how-clients-can-avoid-them
8 renewal considerations for 2020
Are you prepared for open enrollment 2020? With renewal season quickly approaching, plan administrators have a lot of considerations to make regarding employee health plans. Read the following blog post from Employee Benefit News for eight things to consider this year.
The triumphant return of the Affordable Care Act premium tax (the health insurer provider fee).
This tax of about 4% is under Congressional moratorium for 2019 and returns for 2020. Thus, fully insured January 2020 medical, dental and vision renewals will be about 4% higher than they would have been otherwise. Of note, this tax does not apply to most self-funded contracts, including so-called level-funded arrangements. Thus, if your plans are presently fully insured, now may be a good time to re-evaluate the pricing of self-funded plans.
Ensure your renewal timeline includes all vendor decision deadlines.
As the benefits landscape continues to shift and more companies are carving out certain plan components, including the pharmacy benefit manager, you may be surprised with how early these vendors need decisions in order to accommodate benefit changes and plan amendments. Check your contracts and ask your consultant. Further, it seems that our HRIS and benefit administration platforms are ironically asking for earlier and earlier decisions, even with the technology seemingly improving.
Amending your health plan for the new HSA-eligible expenses.
In July of this year, the U.S. Treasury loosened the definition of preventive care expenses for individuals with certain conditions.
While these regulations took effect immediately, they won’t impact your health plan until your health plan documents are amended. Has your insurer or third-party administrator automatically already made this amendment? Or, will it occur automatically with your renewal? Or is it optional? If your answer begins with “I would assume…,” double-check.
Amending your health plan for the new prescription drug coupon regulations.
As we discussed in July of this year, these regulations go into effect when plans renew in 2020. In short, plans can only prevent coupons from discounting plan accumulators (e.g., deductible, out-of-pocket maximum) if there is a “medically advisable” generic equivalent.
If your plan is fully insured, what action is your insurer taking? Does it seem compliant? If your plan is self-funded, what are your options? If you can keep the accumulator program and make it compliant, is there enough projected program savings to justify keeping this program?
Is your group life plan in compliance with the Section 79 nondiscrimination rules?
A benefit myth that floats around from time to time is that the first $50,000 in group term life insurance benefits is always non-taxable. But, that’s only true if the plan passes the Section 79 nondiscrimination rules. Generally, as long as there isn’t discrimination in eligibility terms and the benefit is either a flat benefit or a salary multiple (e.g., $100,000 flat, 1 x salary to $250,000), the plan passes testing. Ask your attorney, accountant, and benefits consultant about this testing. If you have two or more classes for life insurance, the benefit is probably discriminatory. If you fail the testing, it’s not the end of the world. It just means that you’ll likely need to tax your Section 79-defined “key employees” on the entire benefit, not just the amount in excess of $50,000.
Is your group life maximum benefit higher than the guaranteed issue amount?
Surprisingly, I still routinely see plans where the employer-paid benefit maximum exceeds the guaranteed issue amount. Thus, certain highly compensated employees must undergo and pass medical underwriting in order to secure the full employer-paid benefit. What often happens is that, as benefit managers turnover, this nuance is lost and new hires are not told they need to go through underwriting in order to secure the promised benefit. Thus, for example, an employee may think he or she has $650,000 in benefit, while he or she only contractually has $450,000. What this means is the employer is unknowingly self-funding the delta — in this example, $200,000. See the problem?
Please pick up your group life insurance certificate and confirm that the entire employer-paid benefit is guaranteed issue. If it is not, negotiate, change carriers, or lower the benefit.
Double-check that you haven’t unintentionally disqualified participant health savings accounts (HSAs).
As we discussed last December, unintentional disqualification is not difficult.
First, ensure that the deductibles are equal to or greater than the 2020 IRS HSA statutory minimums and the out-of-pocket maximums are equal to or less than the 2020 IRS HSA statutory maximums. Remember that the IRS HSA maximum out-of-pocket limits are not the same as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) out-of-pocket maximum limits. (Note to Congress – can we please align these limits?)
Also, remember that in order for a family deductible to have a compliantly embedded single deductible, the embedded single deductible must be equal to or greater than the statutory minimum family deductible.
Complicating matters, also ensure that no individual in the family plan can be subject to an out-of-pocket maximum greater than the ACA statutory individual out-of-pocket maximum.
Finally, did you generously introduce any new standalone benefits for 2020, like a telemedicine program, that Treasury would consider “other health coverage”? If yes, there’s still time to reverse course before 2020. Talk with your tax advisor, attorney, and benefits consultant.
Once all decisions are made, spend some time with your existing Wrap Document and Wrap Summary Plan Description.
For employers using these documents, it’s easy to forget to make annual amendments. And, it’s easy to forget, depending on the preparer, how much detail is often in these documents. For example, if your vision vendor changes or even if your vision vendor’s address changes, an amendment is likely in order. Ask your attorney, benefits consultant, and third party administrators for help.
SOURCE: Pace, Z. (Accessed 9 September 2019) "8 renewal considerations for 2020" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/list/healthcare-renewal-considerations-for-2020
A 401(k) plan administrators’ guide to the recent IRS revenue ruling
The IRS recently released a new revenue ruling that provides 401(k) plan administrators with helpful guidance on reporting and withholding from 401(k) plan distributions. Read the blog post below to learn more about this new ruling.
The IRS recently issued revenue ruling 2019-19. The revenue ruling provides 401(k) plan administrators with helpful guidance on how to report and withhold from 401(k) plan distributions when a plan participant actually receives the distribution but for some reason, does not cash the check.
Unfortunately, this new guidance does not provide answers to the complex issues that 401(k) plan administrators face when the plan must make a distribution, but the plan participant is missing.
Let’s hope revenue ruling 2019-19 is just the first in a series of much-needed guidance from the IRS and the Department of Labor about how 401(k) plan administrators should handle the increasingly common administrative issues related to uncashed checks and missing plan participants.
There are many situations in which a 401(k) plan must make a distribution to a plan participant. For example, plans must distribute small benefit cash outs (e.g., account balances that are $1,000 or less) or required minimum distributions to plan participants who reach age 70 and a half. This may come as a surprise, but plan participants fail to actually cash these checks with some regularity.
In the ruling, the IRS confirmed that 401(k) plan administrators should withhold taxes on a 401(k) plan distribution and report the distribution on a Form 1099-R in the year the check is distributed to the participant, even if the participant does not cash the check until a later year.
Similarly, the participant needs to include the plan distribution as taxable income in the year in which the plan makes the distribution even if the participant fails to cash the check until a later year. While this guidance is not surprising, it does provide clarity to 401(k) plan administrators as to how they must withhold and report normal course and required plan distributions. In particular, 401(k) plan administrators should not reverse the tax withholding or reporting of the distribution when the participant receives the distribution and simply does not cash the check until a later year.
Unfortunately, this new IRS guidance has limited use because the ruling uses an example that specifically concedes that the plan participant actually received the plan distribution check, but simply failed to cash it. What should 401(k) plan administrators do when the participant may not have received the distribution check at all (e.g., a check is returned for an invalid address) or the plan itself does not have current contact information for the participant?
Retirement plan administrators have an ERISA fiduciary obligation to implement a diligent and prudent process to find missing plan participants and to take additional steps to make sure participants actually receive plan distributions. Uncashed 401(k) plan distribution checks are still retirement plan assets which means the 401(k) plan administrator is still subject to ERISA fiduciary standards of care, prudence and diligence related to those amounts. As a result, the IRS and DOL have increased their focus on uncashed checks and missing participants in retirement plan audits.
Plan administrators would be well-served by establishing and implementing a consistent process to stay on top of any missing plan participants or uncashed checks and taking steps to locate those participants and properly address uncashed checks. Plan administrators should also carefully document the steps that they take in this regard. The IRS and DOL have currently provided limited guidance on the steps a 401(k) plan administrator can take to locate missing participants, but more guidance is needed — let’s hope revenue ruling 2019-19 is just the beginning.
This article originally appeared on the Foley & Lardner website. The information in this legal alert is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as specific legal advice.
SOURCE: Dreyfus Bardunias, K. (6 September 2019) "A 401(k) plan administrators’ guide to the recent IRS revenue ruling" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/401k-administrators-guide-to-the-irs-revenue-ruling-2019-19
Employers look to virtual services to curb rising health costs
Employers are looking for ways to stem the rising costs of healthcare and find ways to better engage employees. According to the National Business Group on Health, 64 percent of employers believe virtual care will play a significant role in healthcare delivery. Read this blog post to learn more about virtual services.
WASHINGTON — With the continued cost of healthcare benefits expected to increase by another 5%, topping $15,000 per employee, employers are looking for ways to stem the increase and better engage employees in holistic well-being.
One of those ways is through virtual care. The number of employers who believe virtual care will play a significant role in how healthcare is delivered in the future continues to grow, up to 64% going into 2020 from 52% in 2019, according to the National Business Group on Health’s annual healthcare strategy survey.
“Virtual care solutions bring healthcare to the consumer rather than the consumer to healthcare,” Brian Marcotte, president and CEO of NBGH said at a press briefing Tuesday. “They continue to gain momentum as employers seek different ways to deliver cost-effective, quality healthcare while improving access and the consumer experience. Of particular note is the growing interest among employers to offer virtual care for mental health as well as musculoskeletal conditions.”
The majority of respondents (51%) will offer more virtual care programs next year, according to the survey. Nearly all employers will offer telehealth for minor, acute services while 82% will offer virtual mental health services — a figure that’s expected to grow to 95% by 2022.
Virtual care for musculoskeletal management shows the greatest potential for growth, the study noted. While 23% of employers will offer musculoskeletal management virtual services next year, another 38% are considering it by 2022. Physical therapy is the best way to address musculoskeletal conditions and help avoid surgery, but it can be inconvenient and costly, said Ellen Kelsay, chief strategy officer at NBGH.
“Where we’ve seen a lot of development in areas of virtual solutions is to provide remote physical therapy treatments,” she said. “Employees can access treatment through their virtual app wherever it’s convenient for them.”
Regardless, employee utilization of virtual services still remains low. For example, while roughly 70% of large companies provide telemedicine coverage, only 3% of employees use it, according to prior NBGH data.
But many resources are out of sight and out of mind, Kelsay said. However, employers are focusing on offering high-touch concierge services to help workers better navigate the healthcare system.
Employers are reaching a point of saturation with the number of solutions that are available, but from the employee’s perspective, they just don’t know where to start, she added. “These concierge and navigator services really help point employees in the direction to the solution at the point in time they need it.”
In addition, the use of predictive analytics and claims data is also an opportunity to help employers get the right programs in front of employees in the moment, Marcotte added.
“Some of these engagement platforms are getting at personal messaging and predictive analytics. It’s not where we want it to be yet, but as that continues to get better, I think you’ll see utilization go up,” he said.
Employers shouldn’t fear expansion of Medicare
A new survey from the National Business Group on Health found that only 23 percent of large employers believe Medicare eligibility should drop to age 50. Read this article from Employee Benefits Advisor to learn more about the potential expansion of Medicare.
Like a significant chunk of American voters, a majority of large employers want to expand Medicare. Just not too much.
A new survey of 147 large employers from the National Business Group on Health found that 55% of them support a Medicare expansion that’s limited to older Americans. Only 23% think eligibility should drop to age 50, however, and 45% don’t think it should expand at all. A majority believe that a broader “Medicare for All” plan would increase health costs.
The same survey also highlights why employers should consider coming around on health reform that reduces their role in the system. The growth in health costs has outpaced inflation and wage growth for years, and the surveyed businesses expect it to rise 5% to $15,375 for each employee next year.
About 70% of those costs will fall on the companies, which plan to try everything from boosting virtual health services to investing in health concierges to rein them in, according to the survey.
History suggests that their best efforts might not amount to much.
Employer-sponsored insurance is America’s single largest source of health coverage. That’s mostly true because the IRS exempted employer health benefits from taxes in 1943, a move that created the federal government’s single biggest tax expenditure. Large companies derive some benefit from the current system because they can provide a significant tax-free benefit that helps them compete for talent and pay people less. But it comes with significant drawbacks. Employers have to devote substantial resources to providing healthcare and controlling costs. Many of them have no particular expertise or advantage in doing so.
The results are mixed. Yes, individuals with private insurance are generally satisfied with the quality of their coverage. They’re not nearly as happy about the cost as deductibles rise. The U.S. pays more than any other developed country for healthcare and medicines and receives worse results on a variety of metrics.
Employers pay particularly high prices and spend heavily on plans that have higher overhead than public alternatives. A recent RAND study found that employer-sponsored plans paid hospitals at 241% of Medicare rates in 2017. Employers are already effectively subsidizing public programs, not to mention the profitability of insurers, health care providers and drugmakers.
It’s not entirely their fault. The American system inherently fragments negotiating power, which gives providers a significant advantage and makes it difficult for even the largest employers to get a good deal. Turning a larger piece of healthcare over to the government would free companies to focus more time and resources on their actual business instead of on navigating the world’s most expensive and convoluted healthcare market.
Big businesses most likely fear big Medicare expansion in large part because it would lead to a significant tax increase. But looking at any tax increase as an enemy is a mistake. Those taxes represent a trade-off; they would replace some or all of the billions of dollars that employers are currently spending on care. Depending on what taxes are imposed and whether the public plan is able to control costs better than the current system — and it could hardly do worse — many employers could come out ahead.
There are a lot of unknowns when it comes to Medicare for All and plans that move the country in that direction. Employers are right to be skeptical until they know more, but the results could well shake out in their favor, and they shouldn’t be so quick to discount the approach.
SOURCE: Nisen, M. (15 August 2019)"Employers shouldn’t fear expansion of Medicare" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/articles/employers-shouldnt-fear-expansion-of-medicare
15 states where $1 million in retirement savings will last the longest
How much do you have saved for retirement? According to GOBankingRates data, employees who have $1 million in retirement savings can make it last for more than 20 years in Mississippi, Arkansas, Oklahoma and Missouri. In this article, Paola Peralta writes on the importance of understanding what better retirement choices can do for your future.
Employees with $1 million in retirement savings can make it stretch for more than 20 years in Mississippi, Arkansas, Oklahoma and Missouri, according to GOBankingRates data in an article from Business Insider. Retirees in New Mexico, Tennessee, Michigan and Kansas can also live on a similar amount of savings, data shows. Retirees with $1 million can expect their savings to last in average span of 19 years, GOBankingRates estimates.
Less choice could mean better retirement outcomes
The amount of income that seniors can replace in retirement is a good measure to determine whether there is a looming retirement crisis in the U.S., according to retirement expert Mark Miller in this article from Morningstar. However, it is hard to make generalizations, he explains. “I think it varies tremendously, depending which demographic group you’re looking at, you can do it generationally or otherwise,” Miller says.
Retirement requires a shift in thinking
As retirees needs change, they should be ready to adjust their mindset and modify their investment strategies, an expert in Kiplinger writes. Retirees should focus more on preservation and distribution after the accumulation phase, the expert writes. “In retirement, it’s important to think of your savings as income rather than a lump sum. It’s not all about achieving maximum return on investment anymore," the expert says. "It’s about how you can get the maximum return from your portfolio and into your pocket."
Employees nearing retirement? 12 features to look for in their next home
Seniors who intend to move to a new home in retirement should consider a property that offers low yard maintenance, a single-story open floor plan and easy access to loved ones and essential amenities, according to a Forbes article. They should ensure that the new house is cheap to maintain and won’t trigger a hefty tax bill, says one expert. “If those costs are low, it can be a great investment.”
SOURCE: Peralta, P. (15 August, 2019) "15 states where $1M in retirement savings lasts the longest"(Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/news/states-where-retirement-savings-will-last-the-longest