Strategies for communicating with all five generations in the workforce
Did you know: Thirty-eight percent of Americans work for a boss who is younger than they are. According to the Labor Department and U.S. Census Bureau data, there are more employees over the age of 85 working than ever before. Read this article for strategies for communicating with all five generations in today's workforce.
The age gap in today’s workforce is getting increasingly wide. Just look at the Democratic primary for the nation’s highest office.
With Pete Buttigieg, 37, and Sen. Bernie Sanders, 78, running for president, the age range of the job applicants for the biggest job in the U.S. now spans four decades. There are also more workers over 85 working than ever before, according to Labor Department and U.S. Census Bureau data.
Here’s another fact: Today 38% of Americans work for a boss who is younger than they are, said Lindsey Pollak, author of “Remix: How to Lead and Succeed in the Multigenerational Workplace,” at the Atlantic’s Aging Up conference on Wednesday.
“This is the first time in our country's history that we have five distinct generations in the workplace,” said Pollak, who has spent more than 10 years researching and studying millennials. “They are the largest generation in the workplace. You've heard a lot from millennials today, but all of the rest of us are here too.”
“To succeed in this environment, however you approach it, you have to think about all of those generations,” she said.
How can employers win the war on talent with such a diverse age range in the modern workforce? Pollak uses the example of a music remix to frame various engagement strategies — an idea she got based on her interview of a DJ. For example, playing a remix of a classic song at a party could entice both the younger and older generations to get on the dance floor, she said.
“[The DJ] said the trick is to play a remix because the older people at the party recognize the classic and say I know that song. And they come and dance,” Pollak said. “The younger people recognize the remix… and they come and dance. So the solution to a five-generation workplace is not either-or. We did it the millennial way or we do it the boomer way. It's always about, how can we bring everybody together?“
Pollak offered three examples of how employers can appeal to multiple generations. The first centers on recruitment. Employers should recruit from across generations. One example was a solution by a pool and beach club in Galveston, Texas, which began recruiting older workers after they experienced a downturn in teenage applicants, she said.
“[The beach club] looked around and said, who really comes and swims here every day? It's the people over 50 who want a low-impact exercise,” she said. “And so they started putting up posters saying, do you want to turn your passion into a career?”
The idea worked. Lifeguard staff became people over 55 including one 83-year-old lifeguard, Pollak said.
A second strategy involves communication, she said. Asking employees about their preferred communication style is one key way to ease multigenerational differences.
“The simple [strategy] here is to not look for the one way that everybody wants to communicate. There isn't one. It depends on your personality. It depends on the work that you do. It depends on your personal preferences,” she said.
The solution is to simply get in the habit of asking everyone at work how they prefer to communicate. Asking employees their communication style of preference — whether that be over text, a phone call or social media — can help improve communication.
Employers should look for mentoring opportunities, along with reverse mentoring experiences, where younger workers can help guide older workers on new skills, she said.
“Mentoring is an example of a classic practice that should never go out of style. There is nothing old fashioned or outdated about mentoring,” she said.
Mentoring also goes in both directions. Junior staff may be more proficient using various apps, for instance, and be good candidates to train other colleagues. To have a successful multi-generational workforce, employers should consider input from employees in a variety of age groups.
“Think of yourself as having a multigenerational board of advisers,” Pollak said. “What if you had a person from each generation who was advising you on how to look at the world and how to think about your job and your career?”
SOURCE: Siew, W. (31 October 2019) "Strategies for communicating with all five generations in the workforce" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/news/strategies-for-communicating-with-all-five-generations-in-the-workforce
DOL proposes rule on digital 401(k) disclosures
A new rule has been proposed by the Department of Labor (DOL) that is meant to encourage employers to issue retirement plan disclosures electronically. This rule would allow plan sponsors of 401(k)s and other defined-contribution plans to default participants with a valid email address to receive plan disclosures electronically. Read the following blog post to learn more.
The Department of Labor proposed a rule Tuesday that's meant to encourage more employers to issue retirement plan disclosures electronically to plan participants.
The rule would allow sponsors of 401(k)s and other defined-contribution plans to default participants with valid email addresses into receiving all their retirement plan disclosures — such as fee disclosure statements and summary plan descriptions — digitally instead of on paper, as has been the traditional route.
Participants can opt-out of e-delivery if they prefer paper notices. The proposed rule covers the roughly 700,000 retirement plans subject to the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974.
"DOL rules have largely relied on a paper default," said Will Hansen, chief government affairs officer for the American Retirement Association. "Everything had to be paper, unless they opted into electronic default. This rule is changing the current standing."
Proponents of digital delivery believe it will save employers money and increase participants' retirement savings. The DOL also believes digital delivery will increase the effectiveness of the disclosures.
Plan sponsors are responsible for the costs associated with furnishing participant notices, and many small and large plans pass those costs on to plan participants, Mr. Hansen said. The DOL estimates its proposal will save retirement plans $2.4 billion over the next 10 years through the reduction of materials, printing and mailing costs for paper disclosures.
Opponents of digital delivery maintain that paper delivery should remain the default option. They have noted that participants are more likely to receive and open disclosures if they come by mail, and claim that print is a more readable medium for financial disclosures that helps participants better retain the information.
"We are reviewing the proposal carefully and look forward to providing comments to the Department of Labor, but we already know that in a world of information overload, many people prefer to get important financial information delivered on paper, not electronically," said Cristina Martin Firvida, vice president of financial security and consumer affairs at AARP. "The reality is missed emails, misplaced passwords and difficulties reading complex information on a screen mean that most people do not visit their retirement plan website on a regular basis."
President Donald J. Trump issued an executive order on August 2018 calling on the federal government to strengthen U.S. retirement security. In that order, Mr. Trump directed the Labor secretary to examine how the agency could improve the effectiveness of plan notices and disclosures and reduce their cost.
The DOL proposal, called Default Electronic Disclosure by Employee Pension Benefit Plans under ERISA, is structured as a safe harbor, which offers legal protections to employers that follow the guidelines laid out in the rule.
Retirement plans would satisfy their obligation by making the disclosure information available online and sending participants and beneficiaries a notice of internet availability of the disclosures. That notice must be sent each time a plan disclosure is posted to the website.
A digital default can't occur without first notifying participants by paper that disclosures will be sent electronically to the participant's email address.
The 30-day comment period on the proposal starts Wednesday. In addition, the DOL issued a request for information on other measures it could take to improve the effectiveness of ERISA disclosures.
SOURCE: Lacurci, G. (22 October 2019) "DOL proposes rule on digital 401(k) disclosures" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.investmentnews.com/article/20191022/FREE/191029985/dol-proposes-rule-on-digital-401-k-disclosures
Putting Humanity into HR Compliance: 3 Steps to Active Listening
How is your HR department communicating with your employees? One of the most common complaints people hear about HR professionals is that they don't listen. Read this blog post from SHRM for three practices of active listening.
When I work with executives and managers, a common complaint I hear about HR professionals is "They don't listen. They just tell."
So when I work with HR professionals, I encourage them to adopt three practices of active listening:
- The period-to-question-mark ratio.
- The EAAR listening method.
- Confront, then question.
The Period-to-Question-Mark Ratio
When you're engaged in a conversation, what's the ratio of your sentences that end with periods to those that end with question marks? If you're like most people, the ratio is overwhelmingly tilted toward sentences that end with periods. This could show that you are telling people what to do more often than you are looking for consensus on how to solve a problem. When you engage in a discussion with an executive, manager or employee, keep the ratio in mind. Strive to correct the imbalance by making yourself ask questions. The fact that you ask matters more than what the question is.
People I've coached have found that keeping the ratio in mind acts as a self-regulating device to ask more questions.
The EAAR Listening Method
E: Explore
A: Acknowledge
A: Apply
R: Response
It's a sequence. Begin the discussion with an exploratory, open-ended question: "Ms. Manager, what are the reasons that led you to conclude Mr. Employee should be fired?" "Tell me more." "Please share some examples." "Help me understand."
Once you've explored the other person's position and reasons for it, move to acknowledgment. Get the person to acknowledge that you understand his or her point. "So, Ms. Manager, if I understand you correctly, you believe Mr. Employee should be terminated because of the following reasons… Is that correct?
Although critical, the acknowledge step is often overlooked. Instead of confirming the understanding, the listener makes an assumption, which often proves erroneous and leads to unnecessary conflict. The EAAR method eliminates this possibility. If the person says, "No, that's not my position," simply go back to the exploration step: "I'm sorry. Please explain what I missed."
In your response, apply portions of what the person said, even actual words the person used. Even if your response isn't substantively what the person originally sought, this approach creates optimal conditions for acceptance.
"Ms. Manager, I agree with you that Mr. Employee's behavior is unacceptable. What you described [list the employee's actions] makes a compelling case. However, because of the following reasons, I think termination now would be premature and present undue legal risk.
"Nevertheless, I'm happy to work with you on an intervention strategy. If Mr. Employee is willing and able to close the gap in your legitimate management expectations, he will do so. If not, we will be in a much stronger position to terminate his employment, and I will support you."
Many HR professionals have told me that when they've used the EAAR method, conversations they feared would turn ugly became positive. Instead of a clash of wills and arguments, the discussion became collaborative and solution-oriented.
Confront, Then Question
What if you are the bearer of bad news? You must deliver a message you know won't make the recipient happy.
The approach here is to confront, then question. Make a short opening statement. State your position succinctly and without elaboration. Next, switch to question mode.
You can think of this approach as beginning the EAAR method with a short opening response to frame the conversation.
"Mr. Executive, based on our investigation, we found that Mr. Employee in your department engaged in actions that violate our anti-harassment policy. Although we understand he has been with the company for a long time and is one of your best performers, given the seriousness of the misconduct, we believe the appropriate action is termination of his employment."
Next, go to question mode: "What do you think?" "What questions do you have?" "How do you see things at this point?"
Assuming the executive doesn't respond by saying "Great idea! Go for it!" and wants to argue his or her point, pivot to exploration and start the EAAR process at that point. "I want to make sure I understand you, so please tell me what you agree with, what you disagree with and your reasons."
After that comes your acknowledgment: "Let me make sure I understand you. You agree that Mr. Employee's behavior was unacceptable and violated policy. However, you disagree that the proper remedy is termination. Instead, you recommend a suspension and written warning for these reasons. [List the reasons.] Is that accurate?"
Now you're ready to apply. From what the executive said, extract what you can use in your response.
"I appreciate the fact that you support our investigation and finding of misconduct. Our only disagreement is the appropriate remedy. Your points about Mr. Employee's long service and stellar performance are valid. Yet for these reasons [list them], I still believe termination is called for. How do you suggest we resolve our differing views? For example, should we present them to the CEO and let her decide?"
These types of conversations can go in all sorts of directions, including ones you don't anticipate. That's OK, so long as you don't lose sight of the value of questions during a dispute.
Avoid cross-examination questions, such as "Isn't it true that … ?" Your questions should not state or imply your view. They should be curiosity-based, as you're genuinely trying to find out what the other person thinks.
The confront-then-question approach allows you to go directly to the heart of the matter. Even if you sense rising tension and hostility, the negative emotions will soon be arrested by your open-ended, exploratory questions.
When HR professionals make a commitment to active listening, executives, managers and employees become their biggest fans instead of being their biggest critics.
SOURCE: Janove, J. (9 October 2019) "Putting Humanity into HR Compliance: 3 Steps to Active Listening" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/hr-topics/employee-relations/pages/putting-humanity-into-hr-compliance-active-listening-.aspx
6 Practical Ways to Recruit More Strategically
How can HR departments recruit more strategically? Successful recruiters will go above and beyond and come up with ways to change how they work in order to deliver better results. Read this blog post for six low-cost things recruiters can do to become more strategic and to improve the hiring process at their organizations.
DALLAS—The most successful recruiters will go beyond doing more of the same and instead come up with ways to fundamentally change how they work in order to deliver better results.
"Every hiring manager wants more strategy from recruiters," said John Vlastelica, former recruiting director at Amazon and Expedia and founder of Recruiting Toolbox, a Seattle-based recruitment management consulting and training firm.
But what does that mean? "Just calling yourself a talent advisor doesn't mean you're going to be strategic," Vlastelica told attendees at the recent LinkedIn Talent Connect 2019 conference for recruiting and HR professionals. "PowerPoint decks do not make you strategic. Strategic does not mean being innovative. Business executives want speed, quality and diversity."
He shared six low-cost, practical things recruiters can do to become more strategic and to improve the hiring process at their organizations.
1. Get Hiring Managers Involved Early
The companies that are most strategic about pipeline recruiting get hiring managers engaged at the start of the process, Vlastelica said. "Every hiring manager I've spoken to wants pipelines, and they see that as being your job, not theirs," he said. But candidates are more likely to respond to outreach from hiring managers than recruiters.
Vlastelica advised talent acquisition professionals to train managers on how "to show up online"; by that, he meant "be thought leaders who engage with the communities they will be sourcing from and have conversations across social media channels that aren't just interviews of potential candidates.
"Getting them to be more visible among the communities they want to hire from is key to getting passive talent," he said. Hiring managers can also help by hosting meetups, game nights, sourcing jams and thought-leader webinars.
2. Know Your Source-of-Hire Mix
Vlastelica said facilities management company Sodexo recently realized that 90 percent of the source of hire for one of its core higher-volume jobs was internal candidates, so it changed the role to an internal requisition.
"Take a look at common roles and see what kind of internal versus external fill you have," he said. "Have a conversation with your department leaders about the hiring mix they want and then allocate your resources to the jobs you intend to hire externally. That saves the company time and money and provides a good development opportunity for employees."
3. Give the Gift of Time
Hiring managers are busy, and most of the time recruiters are giving them more to do.
"Whenever you are able to give back time, you are winning," Vlastelica said.
The Walt Disney Co. recently decided that hiring managers didn't need to screen all candidates.
"What if recruiters were qualified to screen candidates and send finalists to onsite interviews?" he asked. "You'd be giving managers hundreds of hours back."
Another way to streamline the interview process is to reduce the number of people involved. Too many interviewers in the process leads to slow hiring and bad consensus decisions. How many interviews are needed depends on job function, but "you don't need 16 interviewers for most jobs," he said.
4. Help Your Candidates Out
If the candidates you bring in don't have much experience with interviewing, "it's important to set them up for success," Vlastelica said. "I want candidates to bring their best selves to the interview."
He recommended that recruiters coach them on what to expect and ask them if they would like to meet with any employee resource groups.
5. Change the Approval Process
One of the biggest misalignments between recruiters and the business is when the time-to-fill countdown starts. To talent acquisition professionals, the clock begins when the requisition is approved, or even when the job is posted. But for hiring managers, the process started weeks prior.
"Hiring managers hate the approval process for opening a new requisition," Vlastelica said. Talent acquisition leaders at KPMG studied turnover and discovered that they could predict position vacancies in advance for certain jobs.
"Why wait for people to resign before starting the hiring process? Start it earlier, so the approval is already done. This is a planning issue. Tell the business you need to open certain requisitions now if you want the jobs filled quickly when they're needed."
6. Conduct Batch Interviews
Batch interviews—grouping several onsite interviews on one day—serves both speed and quality, he said. "One of the biggest constraints we find in time-to-fill is scheduling. Scheduling can add five, 10, 20 days to your process, which is ridiculous."
Instead, Vlastelica recommended "finding high-volume open jobs you always need and plan the interview days far in advance—have dedicated sourcers and recruiters to fill 12 interviewing slots each day."
He said that was the strategy when he was at Amazon, with Mondays and Fridays reserved for interviews. "We made same-day decisions and sometimes same-day offers," he said.
SOURCE: Maurer, R. (14 October 2019) "6 Practical Ways to Recruit More Strategically" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/hr-topics/talent-acquisition/pages/6-practical-ways-to-recruit-more-strategically.aspx
What would a workplace emergency-savings benefit look like?
Data from a recent survey indicates that a significant portion of American workers could face a financial emergency if they were hit with sudden bills, lost wages or other unforeseen expenses. Read this blog post to learn more about emergency-savings benefits.
An alarming number of workers don't have enough money saved away to carry them through even a short-lived financial emergency, and experts are urging employers to take steps to address that shortfall with changes to their benefits programs.
Survey data indicate that while savings rates vary based on a number of factors, substantial portions of American workers across income levels could face a financial emergency if they were hit with sudden medical bills, lost wages or other unforeseen expenses, such as a major home or car repair.
"Regardless of income we still see a significant percentage of people that do not have a rainy day fund that could cover three months of expenses," Craig Copeland, senior research associate at the Employee Benefit Research Institute, said on a recent online presentation the group hosted.
The AARP has been studying the issue, and recently reported that 53% of all American households have no emergency savings. Moreover, the retirement group reported a direct link between emergency funds and overall financial confidence. According to its recent report, Americans with rainy day funds are 2.5 times more likely to feel confident about their long-term financial prospects than those who do not.
"If people are living on such thin margins that an unexpected bill requires their complete attention and all existing resources to address it, it is extremely difficult to keep the longer-term in mind or to make progress toward longer-term goals," said Genevieve Melford, who helps lead a financial security program at the Aspen Institute.
As employers increasingly come to view emergency savings as a crucial element of their employees' financial well-being, more have been exploring a separate benefit to help encourage workers to put away money for some unforeseen contingency.
Catherine Harvey, senior policy advisor at the AARP's Public Policy Institute, has been taking a hard look at how workplace emergency savings benefits could be structured, what features would make them most attractive, and how, as a practical matter, employees could be moved to actually participate.
"There's a lot of evidence from behavioral science about what makes employer-based interventions effective, and not surprisingly one aspect of an effective program to maximize participation in an employee benefit is to make participation really easy," she said.
"That's true in 401(k)s, that's true in health programming, it's true in marketing -- any time that you get something in the mail or are automatically signed up for Spotify beyond your 50-day free trial you're subject to a default [that works] to make enrollment really easy," Harvey said.
Some employers have offered a feature that allows workers to split their paychecks through direct deposit into separate accounts, one being set aside for emergency savings. But the early analysis of those programs, which tend to rely on the employee proactively opting to set up and contribute to the emergency account via direct deposit -- rather than through auto-enrollment -- has found the results underwhelming.
"That's where we think automatic enrollment, that frictionless enrollment, really distinguishes this from everything else that's on the market right now," Harvey said.
"If split direct deposit were as powerful as it could be, more employers would be doing that and people would be saving for emergencies," she said. "We know that that's just not the case."
But emergency savings programs, executed properly, could become a key component of employers' expanding financial wellness benefits packages, a hot topic in the benefits world, but one where employers are still grappling with the best way to drive engagement.
"We know that information for employees on a website is not going to cut it," Harvey said. "Education alone just doesn't work, and so employers over the years have gotten really savvy and have taken up the behavioral finance tools and concepts to make participation the default."
The AARP also surveyed workers of a variety of income and age ranges about the types of features that would entice them to contribute to an emergency savings plan.
"Not surprisingly," Harvey said, survey respondents cited "the power of the employer match, which speaks to the incentive behind savings as being a very important feature -- one that basically blows all of the other features out of the water."
That held true across the board, as even workers who reported strong savings rates independent of an employer plan said they would welcome matching funds.
"If there's a match on the table, people don't want to leave dollars on the table," Harvey said.
In addition to a matching feature, workers AARP surveyed indicated strong preferences for programs that would protect their privacy, extend them complete control over access to their funds, and generally limit complicating red tape that would make the programs less functional.
"The idea here behind an employer-based emergency savings program is let the employee define the emergency," Harvey said. "Putting up rules and barriers, eligibility criteria, is just going to frustrate people and they won't use the money when it's needed at that moment."
SOURCE: Corbin, K. (11 October 2019) "What would a workplace emergency-savings benefit look like?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/news/what-would-a-workplace-emergency-savings-benefit-look-like
As Daylight-Saving Time Ends, Wages & Hour Problems Begin
On November 3 this year, daylight saving time will end in most states. This change presents challenges for employers who have nonexempt employees working at 2 a.m. when the clocks are set back one hour. Read this blog post from SHRM for wage and hour implications that stem from the end of daylight savings time and how to prepare to "spring forward".
On Sunday, Nov. 3, 2019, at 2:00 a.m., daylight saving time will end and in most states clocks will be set back one hour. As it does every year, this change presents a challenge for employers whose nonexempt employees are working during that time.
This wage and hour issue will affect all employers that employ nonexempt employees with the exception of those working in Arizona and Hawaii, both of which do not observe daylight savings time.
Below are some of the wage and hour implications stemming from the end of daylight savings time:
- Employers are required to pay employees for all hours worked. However, employers whose nonexempt employees are working at 2:00 a.m. on Sunday, Nov. 3, must pay them one additional hour of pay unless the start/end times of their shifts are adjusted in anticipation of the time change. In essence, such an employee will have worked the hour from 1:00 a.m. to 2:00 a.m. twice.
- Employers whose nonexempt employees are working at that time might owe those employees overtime compensation as a result of the time change. That is, employers must include the additional hour of work in determining the employee's overtime compensation for the week.
- In addition, employers must take this additional hour of work into account when computing the employee's regular rate of pay for purposes of calculating the employee's overtime rate.
Preparing to 'Spring Forward'
Employers also should be aware of their pay obligations at the beginning of daylight savings time in the spring. Nonexempt employees who are working on Sunday, March 8, 2020, at 2:00 a.m.—when clocks will spring forward to 3:00 a.m.—are entitled to one less hour of pay than they otherwise would have been. So, an employee scheduled to work an eight-hour shift from 11:00 p.m. to 7:00 a.m. will only have worked seven hours because essentially the employee did not work from 2:00 a.m. to 3:00 a.m.
Employers that decide to pay such workers for a full eight-hour shift are not required under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) to include that extra hour of pay in calculating employees' regular rate of pay for overtime purposes. In addition, the FLSA prohibits employers from crediting that extra hour of pay towards any overtime compensation due to the employee.
Employers, however, should ensure that they do not have any additional obligations under a collective bargaining agreement or state law.
Hera Arsen, J.D., Ph.D., is managing editor of Ogletree Deakins' publications in Torrance, Calif. Ogletree Deakins is a national labor and employment law firm. © Ogletree Deakins. All rights reserved. Reposted with permission. Updated from an article originally posted on 11/1/2017.
SOURCE: Arsen, H. ( 2 October 2019) "As Daylight-Saving Time Ends, Wages & Hour Problems Begin" (Web Blog Post) https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/hr-topics/compensation/pages/daylight-saving-time-wage-hour-problems.aspx
Key elements to consider when researching financial wellness programs
With financial wellness programs becoming a staple employee benefit, organizations find themselves implementing programs that only offer a few tools or resources. Read the following blog post from Employee Benefit Advisor for key elements to consider when researching financial wellness programs.
Financial wellness programs are becoming a staple in the employee benefit universe. But what should a successful financial wellness program encompass? As a rapidly growing industry, we often lack a consistent definition for financial wellness. This leads to organizations believing they have implemented a financial wellness program, when they may only be offering a few tools like education or counseling.
I define financial wellness as the process by which an individual can efficiently and accurately assess their financial posture, identify personal goals, and be motivated to gain the necessary knowledge and resources to create behavioral change. Behavioral change will result in improved emotional and mental well-being, along with short- and long-term financial stability.
As the administrator of your company’s benefits, you are responsible for bringing the best possible solution to your employees. That’s a tough ask, given the growing number of service providers. So, what is the most efficient and effective way to assess financial wellness services to determine which solution best fits your organizational needs? Ask yourself these questions:
Does the platform offer a personal assessment of each employee’s current financial situation and help them identify their financial goals? If the answer is yes: Does the assessment return quantifiable and qualifiable data unique to each individual employee?
Does the platform address 100% of your employee base, including the least sophisticated employees at various levels of employment? Much of your ROI from a financial wellness program does not come from your top performers. It comes from creating behavioral changes within your employees who need the most financial guidance.
Does the platform integrate the various components to provide a personalized roadmap for each employee? It should connect program elements like personal assessments, educational resources, tools, feedback and solutions to ensure the employee is presented with a cohesive, comprehensive plan to attack and improve their financial situation.
Does the platform offer solutions for short-term financial challenges like cash flow issues, as well as long-term financial challenges associated with saving and planning? A major return on your investment comes from reduced employee stress, which is substantially driven by short-term needs versus long-term objectives. The program must help employees deal with current financial challenges before they can focus on their longer-term vision.
About 78% of U.S. workers live paycheck to paycheck to make ends meet, according to data from CareerBuilder.com. The need for financial wellness is clear, but there are consistent pillars that must be addressed in any successful financial wellness program to affect change: spend, save, borrow and plan. When evaluating financial wellness programs, it’s important that these dots all connect if you are truly going to motivate behavioral change and recognize the ROI of a comprehensive financial wellness program.
SOURCE: Kilby, D. (13 September 2019) "Key elements to consider when researching financial wellness programs" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/opinion/key-considerations-for-employee-financial-wellness-programs
4 pitfalls of paid leave and how clients can avoid them
Employers are using paid leave options to help boost their employee benefits packages in efforts to better attract and retain talent. Read the following blog post from Employee Benefit Advisor for 4 common pitfalls of paid leave and how employers can avoid them.
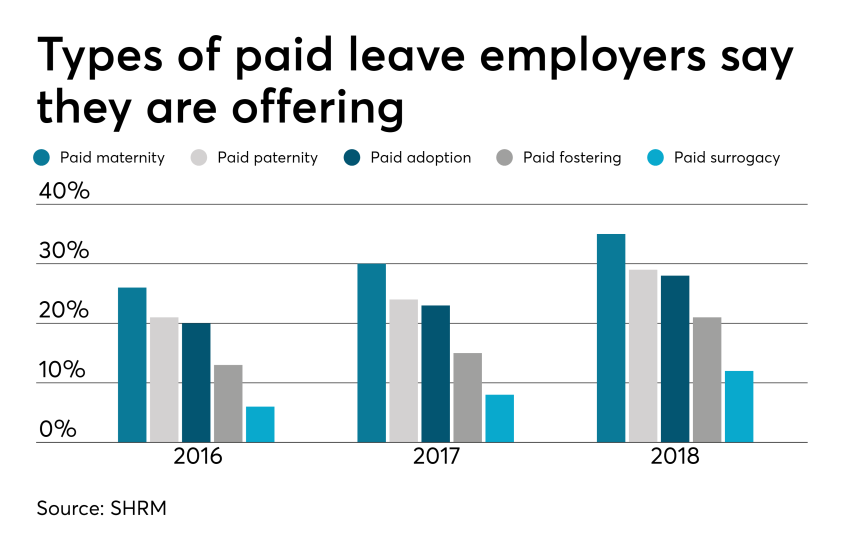 Smart employers are boosting their benefits packages with paid family leave — the most coveted work perk among all generations. In today’s low unemployment environment, paid leave benefits can be a huge differentiator in attracting and retaining talent.
Smart employers are boosting their benefits packages with paid family leave — the most coveted work perk among all generations. In today’s low unemployment environment, paid leave benefits can be a huge differentiator in attracting and retaining talent.
But some employers are getting themselves into trouble in the process, facing accusations of gender discrimination or improper use of leave.
Here are four potential pitfalls of paid leave, and how employers can avoid them.
1. Be careful what you call “maternity leave.”
Employers have long been granting leave for new moms in the form of disability coverage. In fact, the top cause of short term disability is pregnancy. Disability insurance usually grants new moms six to eight weeks of paid leave to recover from childbirth.
Because this coverage applies to the medical condition of recovering from childbirth, it shouldn’t be lumped in with bonding leave.
Guidance from the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission says leave granted for new moms for bonding must also be extended to new dads, so separating disability leave from bonding leave is crucial to avoiding gender discrimination.
2. Don’t make gender assumptions.
The amount of bonding time for new parents after birth, adoption or fostering must be granted equally for men and women. Companies that don’t provide the same amount of paid leave for men and women may find themselves in a discrimination lawsuit.
It’s not just the time away from work that matters, but also the return-to-work support provided. If new moms are granted temporary or modified work schedules to ease the transition back to work, new dads must also have access to this.
Some companies may choose to differentiate the amount of leave and return-to-work support for primary or secondary caregivers. That’s compliant as long as assumptions aren’t made on which gender is the primary or secondary caregiver.
The best way to avoid potential gender discrimination pitfalls is to keep all parental bonding and related return-to-work policies gender neutral.
3. Avoid assuming the length of disability.
Be careful about assuming the length of time a new mom is disabled, or recovering medically, after birth. Typical coverage policies allot six to eight weeks of recovery for a normal pregnancy, so assuming a new mom may be out for 10 weeks might be overestimating the medical recovery time, and under-representing the bonding time, which must be gender neutral.
4. Keep up with federal, state and local laws.
Mandated leave laws are ever-evolving, so employers should consistently cross-check their policies with state and local laws. For instance, do local paid leave laws treat adoption the same as birth? Are multistate employers compliant? What if an employee lives in one state but works in another: Which state’s leave policies take precedence?
Partnering with a paid leave service provider can mitigate the risk of improperly administering leave. Paid leave experts can help answer questions, review guidelines and provide information regarding job-protecting medical or family leave.
They can also help flag potential pitfalls, ensuring leave requests from all areas of your company are managed uniformly and in accordance with state and federal laws, including the EEOC.
SOURCE: Bennett, A. (12 September 2019) "4 pitfalls of paid leave and how clients can avoid them" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/list/4-pitfalls-of-paid-leave-and-how-clients-can-avoid-them
U.S. Jobs Increase by 130,000 in August
According to a recent report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), U.S. employers added 130,000 jobs this past August and the unemployment rate stayed unchanged at 3.7 percent for the third month in a row. Read this article from SHRM to learn more.
U.S. employers added 130,000 jobs in August, coming in below economists' expectations, and the unemployment rate held at 3.7 percent for the third straight month, according to the latest Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) report.
July's employment total was revised down from 164,000 new jobs to 159,000. In the past three months, job gains averaged 156,000 a month after revisions.
"Today's jobs report shows slowing private-sector job growth and slowing wage growth, which—while expected this late in the recovery—is somewhat disappointing after the rapid gains of the past two years," said Julia Pollak, a labor economist at employment marketplace ZipRecruiter.
On Sept. 5, the ADP Research Institute and Moody's Analytics reported private-sector growth of 195,000 new jobs, better than economists' expectations of about 160,000 jobs.
"Despite the slower growth in jobs added, labor force participation did perk up, a sign that the healthy labor market is still drawing in workers from the sidelines," said Glassdoor senior economist Daniel Zhao.
The labor force participation rate—which includes people who are working and those looking for work—ticked up to 63.2 percent, one of its highest readings in years. The proportion of the population currently employed is at 60.9 percent, its highest point since December 2008. And the employment-to-population ratio for workers aged 25-54 reached 80 percent for the first time since January 2008.
Zhao said that the increases signal that the tightness of the labor market is putting upward pressure on labor force participation despite an aging population pulling it down.
Michael Stull, senior vice president at the staffing and recruiting firm Manpower North America, said other positive takeaways from the report are better than expected wage growth and strong hiring in the professional and business, financial and health care sectors.
Job gains in August were led by professional and business services (37,000 new jobs), which includes many technology jobs and the nation's booming health care industry (23,900). Other industries showing gains include finance (15,000) and construction (14,000).
"Health care and professional services have both grown strongly across 2019, carrying the labor market despite weakness in the goods-producing sectors," Zhao said. "Additionally, the increase in temporary help services [15,400 jobs] is a good sign that employers are not cutting back on the most flexible parts of their workforces in the face of recession chatter."
However, Pollak noted that the BLS reported that the private sector only added 96,000 jobs, marking a slowdown from the pace of job growth over the last two years.
Industries like mining and manufacturing are struggling. Mining employment fell by 5,600 jobs and manufacturers have seen a marked slowdown in job creation, with only 3,000 jobs added in August. "In 2018, manufacturing job growth exceeded 10,000 jobs in 11 of 12 months, but this year job growth has been below 10,000 or even negative in six of eight months," Pollak said. "Trade policy uncertainty and a global manufacturing slowdown seem to have brought the 2017-2018 manufacturing boom to a halt."
The retail sector lost 11,000 jobs in August, continuing a trend of month-over-month declines for the seventh consecutive month. "Despite strong consumer spending, increasing labor costs and the rise of e-commerce are keeping retail hiring down even as we begin to enter the holiday hiring season," Zhao said. "We'll be watching the next few reports for signs that the holiday retail hiring season has slowed or that the latest round of tariffs are having a larger effect on the retail industry."
Juiced by Census Hires
U.S. jobs data is now—and will for some time be—inflated by a temporary spike in government hiring for 2020 Census workers. The federal government added 28,000 workers (excluding U.S. Post Office hires) to its payrolls in August. The majority of those—25,000 temporary workers—will go door-to-door over the next several weeks to verify addresses ahead of the 2020 count.
The Census Bureau expects to hire about 40,000 people for this preliminary duty and about 500,000 workers next year for the actual canvassing.
Unemployment Stays Low
The BLS data showed that the national unemployment rate remained below 4 percent for the 18th consecutive month. The number of unemployed people held at 6 million.
"The unemployment rate remains near its lowest level in 50 years, again signaling the strength of the labor market for workers as the number of job openings continues to exceed the number of unemployed workers," Zhao said.
The number of long-term unemployed (those jobless for 27 weeks or more) rose from 1.1 million to 1.2 million in August and accounted for 20.6 percent of the unemployed.
The U-6 unemployment rate—a broader measure capturing both the unemployed, underemployed and those too discouraged to seek work—continued its long decline and held at 7.3 percent for the second month in a row. There were 467,000 discouraged workers in August, about the same as a year ago.
"There are still more discouraged workers than we would expect, given the low unemployment rate," Pollak said. "Discouraged workers are those who are out of work but have not applied for a job in the past four weeks because they think there are none available or none for which they qualify," she explained. "If there were fewer discouraged workers, labor force participation and employment rates would be higher, and more vacancies would be filled."
Wages Inch Up
Average hourly earnings increased 11 cents to $28.11, following 9-cent gains in both June and July. Over the past 12 months, average hourly earnings have increased by 3.2 percent.
"At this point in the expansion, we'd expect wage growth to pick up, but it is continuing to stall," said Nick Bunker, a Washington, D.C.-based economist at the Indeed Hiring Lab. "Wage growth continues to be strongest for workers in lower-wage industries."
SOURCE: Maurer, R. (06 September 2019) "US Jobs increase by 130,000 in August" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/hr-topics/talent-acquisition/pages/bls-hr-jobs-unemployment-august-2019.aspx
What would change if your employees were CEO for a day?
How is your workplace culture? New data shows that employees are 4.6 times more likely to contribute their best work when they feel like their voices are being heard. Read this blog post from Employee Benefits News to learn more about building a strong workplace culture.
When employees feel like their voices are being heard, they are reportedly 4.6 times more likely to contribute their best work, according to SalesForce data. Ultimately, knowing that the company is interested in what employees have to say builds trust and encourages loyalty among members of the workforce.
Respect is the most important leadership behavior, according to a Georgetown University survey of nearly 20,000 employees. More than merely listening, making employees a part of a two-way conversation shows that the company values their opinions.
With this in mind, we set out to develop a process to help Nearmap increase workplace communication. Along the way, we found that creating opportunities for interaction, encouraging honest participation and involving executive participation were all keys to building a stronger corporate culture.
Invite employee interaction
We recognized that we needed a conversation starter to open the lines of communication and spark a little enthusiasm. We discovered that engagement surveys work the best for our circumstances because they’re quick and easy to take, which results in high completion rates.
We like to include thought-provoking questions like “if you were CEO for a day, what is the one thing you would change?” to keep the employees engaged. At first, that particular question provided some of our most entertaining suggestions, including “free umbrellas for all,” “I would like the CEO’s paycheck,” “change my LinkedIn profile,” and “put margarita slushy machines in the kitchen.” When employees saw that the CEO responded to every answer, they realized that we were taking the feedback seriously, and that changed the tone of their responses.
Anonymity invites honest responses
It was essential to Nearmap that we collect unfiltered, honest feedback from our employees. This meant reassuring participants that their responses were completely anonymous. We believe this confidentiality encouraged authentic and candid submissions from employees that otherwise would have remained silent for fear of reprimand or judgment.
For instance, we’ve received excellent insights about driving the strategy and growth of the business, giving Nearmap valuable concepts that we’ve been able to embed into the business.
In addition, we present the survey results back to the employees so they can see how their thoughts align with those of their co-workers. We believe this commitment to being open is an excellent way to motivate honest dialog.
Executive participation leads by example
When the survey concludes, we group all of the responses under different headings, such as collaboration and communication, marketing, mission, planning, product, compensation, recognition, and general. Then, our CEO, Rob Newman, gets together with other executives to provide answers and comments on many of the submissions. In turn, those responses are shared with the employees via the HR newsletter and on our company collaboration app.
In reply to an inquiry about creating a green initiative for the company, our CEO shared a list of active programs that Nearmap was involved in to reduce not only our carbon footprint but also that of our customers as well.
While we may not know what we would change if we were the CEO for a day, we are convinced that employee interaction, honest responses and executive participation are reliable and important ways to make impactful connections with our employees and build a stronger corporate culture in our company.
SOURCE: Steel, S. (13 September 2019) "What would change if your employees were CEO for a day?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/what-would-change-if-your-employees-were-ceo-for-a-day









