IRS increases 2020 HSA limits
Recently, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) announced an increase in the annual limit on deductible contributions to HSAs. The annual limit will increase by $50 for individuals and $100 for families in 2020. Continue reading this blog post for more on this increase to HSA limits.
Employees will be able to sock away some extra money into their health savings accounts next year.
The annual limit on deductible contributions to an HSA will jump by $50 for individuals and $100 for families next year, the IRS announced Tuesday.
For 2020, the annual limit on deductible contributions will be $3,550 for individuals with self-only coverage, a $50 increase from 2019, and $7,100 for family coverage, a $100 increase from 2019.
The minimum deductible for a qualifying high-deductible health plan also will increase to $1,400 for self-only coverage and $2,800 for family coverage.
Annual out-of-pocket expenses will see an even bigger jump next year. Deductibles, copayments and other amounts that do not include premiums will have a maximum limit of $6,900 for individual coverage next year, up from $6,750 in 2019, and $13,800 for family coverage, up from $13,500 in 2019.
HSA enrollment continues to grow, especially as employees look at the accounts as a way to save for medical expenses in retirement. The number of HSAs grew 13% over the past year to top 25 million, according to research firm Devenir, while assets grew 19% to $53.8 billion. Devenir projects the number of HSAs to hit 30 million by 2020, with $75 billion in total assets and $16.7 billion in investment assets.
More employers are also offering employees contributions to their accounts. Indeed, the average HSA employer contribution rose to $839 last year, up 39% from $604 in 2017, according to Devenir. All told, employer contributions totaled almost $9 billion last year.
HSAs also saw a boon this year with Amazon’s decision to allow consumers to use the accounts to buy thousands of items on its site, a move that was ballyhooed as a positive for HSA customers, as well as Amazon. Items will be listed on Amazon as “FSA or HSA eligible” on the individual product pages; a full list of items can also be browsed on Amazon’s website.
“By accepting HSA dollars, Amazon is finally giving this untapped savings tool its moment to shine,” David Vivero, co-founder and CEO at Amino, an employee financial wellness platform, wrote recently in an Employee Benefit News blog. “Every payment method or currency — whether it’s dollars, airline miles, bitcoins or credit cards — depends on reliable large-scale merchant acceptance to become truly mainstream.”
Amazon’s chief competitor, Walmart, allows consumers to use HSA and FSA cards to purchase medical items, as well.
HSA contribution limits are updated annually to reflect cost-of-living adjustments. The increases are detailed in Revenue Procedure 2019-25 and take effect in January.
SOURCE: Mayer, K. (28 May 2019) "IRS increases 2020 HSA limits" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/news/irs-announces-2020-hsa-limits
Insuring the Times of Your Life
Do you have life insurance? According to the 2019 Insurance Barometer Study, by Life Happens and LIMRA, 43 percent of adult Americans do not have life insurance. Read this blog post to learn more.
Preston Newby was a youth minister. He and his wife, Tara, were driving with their son to visit family—excited to announce a new baby on the way. In the keeping with the kind of person Preston was, he stopped to help at the scene of an accident. That’s when he was struck by another car and killed. He was only 24.
Fortunately, this young couple had done their planning and had bought life insurance. So despite the emotional upheaval that Preston’s death caused, Tara, a stay-at-home mom, and her two sons were able to carry on financially as they had before. You can watch their story here.
How many other people have prepared like this for the unexpected? Unfortunately, not enough: 43% of adult Americans don’t have life insurance, according to the 2019 Insurance Barometer Study, by Life Happens and LIMRA.
Many people think, “I’m young. That won’t happen to me.” Statistically, they may be right. However, they could be up being one of the statistics. You just don’t know—and that’s the problem. The solution is life insurance.
If you have people you love and who depend on you, or you have financial obligations to meet, you need life insurance to protect against the “what ifs”—at every stage in life. Here are just a few reasons you may need life insurance, or more of it, throughout your life.
Single with no children: You may think you don’t need life insurance since you have no dependents, but if you owe money, you need it. It ensures that your debts, including student loans and funeral expenses, won’t be passed on to your family. Additionally, if you are taking care of aging parents or a special-needs sibling, or know you will in the future, life insurance is a smart way to make sure that care can continue uninterrupted.
Married or partnered: As you begin your lives together, you’ll likely incur joint financial obligations like buying a home, in addition to monthly bills. It makes sense to protect your spouse or partner with adequate life insurance. It’s also a smart move to get coverage in place now if you plan on having a family in the future.
Parents with children: If you’re in the midst of this stage, financial obligations abound. Many couples rely on two incomes to make ends meet and single parents may be their children’s one-and-only. Life insurance is critical at this point. When figuring out how much you need, remember that the economic impact you have on your family can be measured not just by how much you earn now, but by how much you’ll earn over the course of your working life. Life Happens’ Human Life Value Calculator can help you figure out what that will be.
Empty-nesters/retirees: Your kids are on their own and your mortgage is paid off, so you may think you don’t need life insurance. However, if you are still building your retirement nest egg, life insurance ensures that if something happens to you that your spouse or partner can still live comfortably in retirement, despite any shortfalls.
Keep in mind, life insurance is a simple answer to an important question: Would anyone suffer financially if I were to die. If the answer is yes, it’s time to sit down with an insurance professional.
SOURCE: Leyes, M. (13 May 2019) "Insuring the Times of Your Life" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://lifehappens.org/blog/insuring-the-times-of-your-life/
Working from home for medical reasons poses challenges for employers
Did you know: There has been an 11 percent increase in remote work since 2014, according to SHRM. This increase in remote work is posing new challenges for HR teams when the request is due to medical reasons. Continue reading to learn more.
While working from home has become much more popular in recent years – an 11% increase just since 2014, according to SHRM – this can pose challenges for HR teams when the request is due to medical reasons.
Even if your workplace has guidelines for remote workers, requests to telecommute as an accommodation must be carefully reviewed to assure you’re in compliance with ADA regulations
The ADA prohibits discrimination in employment based on disability, and requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations to applicants and employees. A reasonable accommodation entails any changes in the work environment, or in the way things are customarily done, which enables an individual with a disability to enjoy equal employment opportunities.
In these cases, it’s important for both the HR rep and a physician to gather information about the accommodation request to gauge if telecommuting is medically necessary or simply a personal preference.
The HR rep needs to gather specific information from the employee, including the following:
- Explanation of why it’s medically necessary to work from home
- The essential job functions the employee finds challenging to perform in the office
- The duration of the request to work from home
- Whether telecommuting for a period of time enables the employee to return to work in the office and perform essential functions of the job
- Confirmation that they have a dedicated workspace with phone, Wi-Fi and other essential technology
Meanwhile, the physician should gather certain information from the HR rep, including:
- A description of the medical condition
- How working from home will help the employee better manage that medical condition and perform the essential job functions
- The restrictions (things the employee cannot do) and limitations (things the employee should not do)
- Why the employee can work from home but not in the office
- How long the employee will require the accommodation (short or long term)
- Likelihood that the employee will ever be able to perform their essential job functions from the office
With more offices adopting an agile model with open workspaces, employees now have more natural lighting, feel less cramped and have more opportunity for collaboration with their colleagues. However, these advantages to many people can be challenges for others.
Light and odor sensitivity, as well as distractions, are some of the most frequent triggers of medical conditions that drive the need for accommodations. In many cases, some simple modifications to the workplace can help solve or alleviate some of the employee’s challenges.
Light sensitivity, or photophobia, is intolerance to light, which can cause a painful reaction to strong lighting. Adjustments can be made to help alleviate this, including head lighting modifications, window shading, cubicle shields for fluorescent lights, polarized glasses and/or prescription eyewear.
Odor sensitivity is another common issue in open workspaces – especially for employees who previously were in a contained space with infrequent interaction with colleagues. Consider workplace signage prohibiting perfume or cologne in the office, enforcing a fragrance policy, air purifiers throughout or in select areas, a transition to scent-free cleaning products, or upgrading the ventilation system in the office to allow more air flow. For food smells, ask employees to eat in a designated area and not bring food to their workspace.
Distractibility is the inability to sustain attention or attentiveness to one task. With agile workspaces often involving moving around frequently or being positioned in a high-traffic area, this can be challenging to some employees. Consider providing noise-canceling headphones, white noise machines, cubicle shields, noise barriers or an adjustment to the office configuration. Consider allocating space within the open work plan that’s off-limits for meetings and away from heavy foot traffic.
While agile workspaces have many benefits, they can pose challenges to your workforce. It’s your responsibility to work with employees to accommodate medical requests which may result from light sensitivity, distractions or even odors. Following these simple tips can help assure a healthy, happy and productive workplace for your team.
SOURCE: Holliday-Schiavon, K. (23 May 2019) "Working from home for medical reasons poses challenges for employers" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/remote-work-for-medical-reasons-challenging-for-employers
3 summer workplace legal issues and how to handle them
Issues such as hiring interns, dress code compliance and handling time off requests can cause legal issues for employers during the summer months. Continue reading this blog post for how to handle these three summer workplace legal issues.
Summer is almost here and with that comes a set of seasonal employment law issues. Top of the list for many employers includes hiring interns, dress code compliance and handling time off requests.
Here’s how employers can navigate any legal issues that may arise.
Summer interns
Employers looking to hire interns to work during the summer season or beyond should know that the U.S. Department of Labor recently changed the criteria to determine if an internship must be paid. In certain circumstances, internships are considered employment subject to federal minimum wage and overtime rules.
Under the previous primary beneficiary test, employers were required to meet all of the six criteria outlined by the DOL for determining whether interns are employees. The new seven-factor test is designed to be more flexible and does not require all factors to be met. Rather, employers are asked to determine the extent to which each factor is met. For example, how clear is it that the intern and the employer understand that the internship is unpaid, and that there is no promise of a paid job at the end of the program? The non-monetary benefits of the intern-employer relationship, such as training, are also taken into consideration.
Though no single factor is deemed determinative, a review of the whole internship program is important to ensure that an intern is not considered an employee under FLSA rules and to avoid any liabilities for misclassification claims.
Companies also should be aware of state laws that may impact internship programs. For example, California, the District of Columbia, Illinois, Maryland and New York consider interns to be employees and offer some protections under various state anti-discrimination and sexual harassment statutes.
All employers should be clear about the scope of their internship opportunities, including expectations for the relationship, anticipated duties and hours, compensation, if any, and whether an intern will become entitled to a paid job at the end of the program.
Summer dress codes
Warmer temperatures mean more casual clothing. This could mean the line between professional and casual dress in the workplace is blurred. The following are some tips when crafting a new or revisiting an existing dress code policy this summer.
If the dress code is new or being revised, the policy should be clearly communicated. Sending a reminder out to employees may be helpful in some workplaces. In all cases, the policy should be unambiguous. List examples to make sure there is no confusion about what is considered appropriate and explain the reasoning behind the policy and the consequences for any violations.
To serve their business or customer needs, companies may apply dress code policies to all employees or to specific departments. They should also make sure the dress code does not have an adverse impact on any religious groups, women, people of color or people with disabilities. Company policies may not violate state or federal anti-discrimination laws. If the policy is likely to have a disparate impact on one or more of these groups, employers should be prepared to show a legitimate business reason for the policy. Also, reasonable accommodations should be provided for employees who request one based on their protected status. For example, reasonable modifications may be required for ethnic, religious or disability reasons.
Finally, failure to consistently enforce a neutral dress code policy or provide reasonable accommodations can expose a company to potential claims. As always, dress codes and any discipline for code violations should be implemented equitably to avoid claims of discrimination.
Time off requests
Summer time tends to prompt an influx of requests for time off. Now is a good time to review policies governing time off, as well as the implementation of those policies to ensure consistency. Written time off policies should explicitly inform employees of the process for handling time off requests and help employers consistently apply the rules.
An ideal policy will explain how much time off employees receive and how that time accrues. It also will include reasonable restrictions on how time off is administered such as requiring advance approval from management, and how to handle scheduling so that business needs and staffing levels are in sync.
Most importantly, time off policies and procedures must not be discriminatory. For instance, if a policy denies time off or permits discipline for an employee who needs to be out of the office on a protected medical leave, the policy could be seen as discriminating against employees with disabilities. Companies should train their managers on how to administer time off requests in a non-discriminatory manner. Employers generally have the right to manage vacation requests, however protected leave available to employees under federal, state and local laws adds another layer of complexity that employers should consider when reviewing time off requests.
To minimize employment issues this summer and all year around: plan ahead, know the relevant employment laws and train managers and supervisors to apply HR best practices consistently throughout the organization.
SOURCE: Starkman, J.; Rochester, A. (23 May 2019) "3 summer workplace legal issues and how to handle them" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/how-employers-can-handle-summer-workplace-legal-issues
Netflix exec: To boost diversity, employers must improve benefits
Are you implementing specific employee benefits in an effort to boost diversity and inclusion at work? According to Vice President of Inclusion Strategy at Netflix, Verna Myers, Implementing the right employee benefits could help employers boost workplace diversity and inclusion.
NEW YORK — Employers still have a long way to go when it comes to fostering diversity and inclusion at work — but implementing the right benefits could be a step in a positive direction.
That’s according to Vernā Myers, vice president of inclusion strategy at Netflix, who said companies should focus on rolling out new benefits that help employees at different life stages. While perks like free lunch are nice, they aren’t going to keep workers around long term, she said at a meeting with reporters Wednesday.
“It’s more about [having] a kind of system that acknowledges real life and what people’s needs are,” she said. “That builds a certain kind of loyalty and trust.”
So what should employers focus on? Myers said employees want holistic benefits that address life changes, including starting out careers and parenthood. Mental health and financial benefits also should be a priority.
So far, tech companies, startups and other progressive employers are doing this well. “Companies have realized they’re part of a life ecosystem, and that makes a big difference,” she added.
But employers may still have a long way to go. Myers, who is a Harvard trained lawyer, said she has heard of instances where male employees faced discrimination for taking advantage of benefits like paternity leave. Meanwhile, offerings like maternity leave have not always been industry standard, she said.
“People still don’t remember that we did not have maternity leave,” Myers said, recalling a conversation with a partner at a law firm who used three weeks of vacation time when she had her baby.
Myers said she has overwhelmingly found that while organizations are interested in bringing in more diverse workers, they often won’t make adjustments to benefits and culture in order to better accommodate these employees. Employers “were unwilling to do much of anything to adjust to the fact that they were inviting difference,” she said.
Survey data from PwC suggests that diversity and inclusion is a high priority for employers, but many can still do more to improve their programs. A full 74% of employers said diversity and inclusion is a priority at their company. But the consulting firm found that only 5% of the programs were reaching their full maturity when assessed against PwC’s model, which reviews factors including strategy and engagement.
But employers have shown interest in adding more inclusive benefits. Some — like Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Hilton — have invested in family-friendly offerings like expanded paid parental leave and breast milk shipping. Others are adding student loan repayment programs and coaching benefits.
Susan Eandi, the head of Baker McKenzie’s global employment and labor law practice in North America, said employers need to focus on employee engagement in benefits if they want to improve diversity and inclusion. As Generation Z enters the workforce, companies may see a shift toward stability. Unlike their millennial counterparts, who spearheaded flexible schedules and gig work, Gen Z workers are more cautious and want security in their jobs and benefits.
“They’re very cautious, concerned individuals who want financial security,” she said. “It will be a big shift for employers.”
Regardless, Myers said companies should continue to create safe spaces for all perspectives and backgrounds to influence decision making. “If employers allow for more opportunity and for people be treated more fairly, then everyone is going to benefit,” she said.
SOURCE: Hroncich, C. (15 May 2019) "Netflix exec: To boost diversity, employers must improve benefits" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/news/netflix-to-boost-diversity-employers-must-improve-benefits
Taking the first steps to a long-term benefits strategy
A common struggle for many companies that are searching for a cost-effective, successful employee benefits strategy is that HR professionals and finance professionals have conflicting objectives. Continue reading this blog post to learn more.
The quest for a cost-effective and successful employee benefits program can feel like a search for the Holy Grail. To most, it’s an elusive goal within the context of rising and unsustainable costs.
Unlike “Monty Python and the Holy Grail,” in which a comedy of errors made for a hilarious movie, nonsensical benefits strategies can have serious consequences.
One major challenge is that many HR and finance professionals have conflicting objectives. HR’s mission is to design a program that is competitive in the marketplace for human capital needs while supporting the organization’s culture. Finance, on the other hand, is charged with managing to a budget by controlling expenses to mitigate year-over-year increases. The result, in spite of best intentions, leaves organizations unable to commit to a multi-year plan and opt in favor of living year-to-year.
So, how do you overcome this challenge?
Step 1: Key HR and finance stakeholders need to align on goals and objectives. They also need to remain engaged in the process throughout the year (not just at renewal). Once you achieve alignment, these objectives should be memorialized into a benefits philosophy. Why? So the collective team has guiding principles for future decisions.
Step 2: Identify the cost drivers of the program. Many employers have little line of sight into how their plan is performing until it’s too late. Once you are staring down the barrel of a 25% increase, an organization may be forced to make swift changes to soften the blow to their bottom line rather than follow a strategic approach that comes with preparation. Unfortunately, this type of knee-jerk reaction only temporarily relieves the pressure and may create unintended consequences to the employee value proposition.

Step 3: Understand where you were, where you are and where you want to be. After 25 years in the consulting industry, one thing I know for certain is there are only so many levers you can pull to rein in escalating benefit costs. Identify the levers and how far you want to pull them.
Step 4: Determine success metrics. I’ve seen many organizations implement new tactics, such as a health savings account. When I ask them if it was successful, they can’t answer because they didn’t set an internal bar for success. That barometer will help you gauge success and determine what changes need to be made to your approach to achieve your goal.
Step 5: Commit the plan to writing and review it periodically. Just like your company’s overall business plan, you will need to make adjustments along the way as your business changes.
Regardless of strategy, I recommend employers take steps toward a self-funding benefits model. Historically, self-funding was for groups with 1,000 lives and above. But that’s no longer the case. Self-funding provides that all-important line of sight into cost drivers because of access to claims data. Having a deeper understanding of the “why” behind costs allows an organization to implement a data-driven approach to the overarching benefits strategy. Self-funding also provides more plan design flexibility and eliminates the internal costs that an insurance carrier builds into a plan for profit.
It’s more effective to create a benefits strategy that is sustainable over time, so when you inevitably endure a higher-than-normal renewal cycle, typically every three to five years, you are prepared to stay the course.
Consider timing. When you make changes to a benefit plan is just as important as what changes you make. Evaluate the timing of benefit changes, how they are implemented and how adjustments will impact your workforce now and in the future.
For example, if you plan to add new voluntary benefits, such as indemnity plans, it may make sense to run them “off cycle” from the core medical benefits open enrollment season. This gives employees more time to conduct research about the new product option and make an educated decision.
Strive for simplicity. I can’t stress this enough. The Affordable Care Act, an increase in voluntary benefit options, new funding models and benefit trends have created an enormous amount of noise in the insurance industry. Tune it out and simplify your process as much as you can. Your HR and Finance teams are overwhelmed and so are your employees. Instead of throwing new benefits at them each year, focus on educating them and making choices simple. In fact, any long-term benefits plan worth its weight always includes an education and communications component.
Benefit illiteracy is rampant, and confusion over options at open enrollment can have consequences for the employee throughout the plan year. If your employees choose their benefits online, spend the open enrollment meeting educating them on how to buy and consume insurance, rather than just what the benefit choices are for the plan year, or how to use the online enrollment tool. You should also communicate throughout the year, rather than just at open enrollment to support employees’ understanding of their benefits program.
Identify other areas where employees might struggle. One trend is to offer transparency tools to help them choose a doctor or specialist. But be aware that the sheer number of doctors in a given list can be overwhelming. Rather than offering employees a choice of 50 doctors, narrow it down to five providers with the best healthcare outcomes.
Making it simpler for employees to be better consumers of healthcare will help you cut costs and get on the right path to a long-term benefit strategy. Of course, you’ll have to check in each year and consider making small adjustments to the program, and data will help guide these changes. Adjustments should all be in service of a long-term plan. If you begin your long-term plan by asking the question, “Where were we, where are we now and where do we want to be in the future?” you’re halfway there. You may eventually find that your Holy Grail is within reach.
SOURCE: Bloom, A. (14 May 2019) "Taking the first steps to a long-term benefits strategy" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/taking-the-first-steps-to-a-long-term-benefits-strategy
Are you offering the right benefits? Look to benchmarking, surveys for answers
Are you offering the right employee benefits? With unemployment at historic lows, benefits have become a big differentiator for employers. Read this blog post for more on offering competitive benefits.
With unemployment at a 50-year low, benefits have become a big differentiator for employers, which means they need to be competitive to attract and retain employees. What are competitive benefits? Ask 100 employers and you’ll get 100 answers.
It’s no longer affordable to offer Cadillac plans with low employee contributions. How do employers offer attractive yet affordable benefits that will draw potential employees in? They turn to benchmarking and employee surveys to build and validate benefit plans.
“High cost” has become so synonymous with “healthcare benefits” that it’s hard to separate one from the other. As benefits become more costly, they also become more complicated to manage. Add today’s shift to the need for competitive programs and the whole thing begins to look like a slog through quicksand.
Here’s the thing: The employer must strike a balance between what employees want and what they’ll use. That means zeroing in on what they find valuable. While it may be tempting to follow benefit trends by offering pet insurance or creating in-office perks like beer and pizza, research suggests that most employees value more traditional coverages and benefits. What gets them in the door — and keeps them engaged — is likely going to be paid leave, flexible/remote work options and professional development.
To determine what your employees want and what peer employers are offering in your industry, look to benchmarking and employee surveys as two of the sharpest arrows in your plan design quiver.
Benchmarking tells you what you’re competing against. While certain employee benefits are more popular in some industries than others, it’s vital to know who you’re competing against to attract and retain employees. For example, nonprofit organizations historically provide modest employee salaries but rich benefits. While that benefits model may work for most of your workforce, it’s important not to overlook other industry standards. A large nonprofit hiring employees for its IT department is not only competing against other nonprofits for talent, but they’re also competing against tech-industry talent, which may put more of a focus on salary and bonuses than rich benefits.
The best way to identify who you’re competing against and what types of benefits they’re offering is to undertake a benchmarking study. Benchmarking your benefits package can provide insight into what your competition offers across industries, regions and company size so you can ensure your plan design stands up against the competition. Benchmarking studies yield details like:
- Medical plan type
- Employee premium cost
- Employee premium contribution
- Medical copay
- Prescription drug copay
- Office visit copay
- Emergency room copay
- Voluntary benefits offerings
- Salary ranges
- Paid sick leave
Armed with that data, you can decide where you should aim your focus and whether you’re offering a competitive benefits package.
Surveys tell you what employees value. The best way to understand what your employees value is to ask them. Employee surveys can help you find out which benefits your employees love, which ones they don’t like and where you can make improvements.
When developing an employee benefits survey, pay close attention to how questions are written in order to elicit the best responses from employees. It might make sense to reach out to a survey organization to ensure it’s done right. Benefit brokers often have experience with surveys, too.
When the survey is complete, put together a communications plan so you can get the highest number of responses about what your employees love and what needs improvement. It’s a best practice to survey employees every plan year to stay on top of changes across the workforce. (Just not at open enrollment time).
It’s an inexpensive undertaking that could lead to serious cost savings from changes to the plan and increased employee retention. So basically, a survey is worth the time and effort.
Benchmarking and surveys are important components of a benefits strategy. They can put you on a more direct path to a plan design with options that are right for your culture and workforce.
SOURCE: Newman, H. (17 May 2019) "Are you offering the right benefits? Look to benchmarking, surveys for answers" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/hr-review-surveys-for-employee-benefits-trends
What to consider before adding a genetic testing benefit
According to recent statistics from the Society of Human Resource Management (SHRM), 18 percent of employers provide health-related genetic testing benefits. Read this blog post for what employers should consider before adding a genetic testing benefit to their benefits package.
As employers look for new voluntary benefits to help attract and retain employees, a growing number are turning to direct-to-consumer genetic testing for all employees to their benefits plans. According to the latest statistics from the Society for Human Resource Management, 18% of employers provide a health-related genetic testing benefit, an increase of 6% over the previous year.
For the most part, it can be a smart move: Not only can the benefit differentiate one employer from others vying to hire from the same employee pool, genetic testing providers market the benefit as a way to potentially lower healthcare costs and increase employee wellness.
This type of testing can be valuable for employees at an increased risk for certain types of cancer, such as breast and ovarian cancer related to mutations of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, those considering having a child who have risk factors for genetic conditions such as cystic fibrosis and Tay Sachs disease, those who have a family history of conditions like high cholesterol, and those who take medications such as blood thinners and anti-depressants. There also are tests that look for genes associated with conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and celiac disease.
But employers also have to realize that genetic testing for all employees, regardless of family history and risk factors, comes with potential downsides. In fact, some physicians believe that widespread genetic testing of this type may even present a risk of harm. There’s also the issue of regulation and oversight of direct-to-consumer genetic testing. The industry is not currently regulated, which, some researchers have found, can lead to inaccurate or varying results. One study found that when the same genetic variant was provided to nine different labs for analysis, the answers provided were different 22% of the time, highlighting the risk of false positive and false negative results.
So for employers who offer — or are considering adding — a genetic benefit, make sure to think about the potential outcomes that can occur by doing so.
The potential for lower costs as well as unnecessary healthcare spending
If an employee’s genetic test is positive for a mutation that’s associated with cancer or another disease, he or she may be more proactive about screening for the disease and may make lifestyle changes that may lower the risk of developing the disease. There are potential healthcare cost savings to early detection of some conditions. For example, by some estimates, the cost for treating early-stage breast cancer is more than 50% less than the cost to treat the same cancer at an advanced stage.
For employees who undergo testing related to how effective a blood thinner or antidepressant will be, there can be better health outcomes as well as cost savings. One study found that when physicians prescribed the blood thinner Warfarin based on pharmacogenomic testing, adverse events decreased by 27%. Avoiding adverse events and making sure employees are taking the medications that can most effectively treat their conditions can help keep them healthy, out of the hospital and productively on the job, all of which has a positive financial impact.
But when you’re screening people who don’t have risk factors or a family history of these conditions, a positive test result can lead to unnecessary testing and medical procedures, potential complications from those procedures and the costs associated with that testing and care.
Before and after testing, education
Employers who offer genetic testing without a physician referral need to take steps to ensure that employees understand the risks and benefits of these tests upfront and that they know what a genetic test can and cannot tell them about their health now and in the future. The first step is for any employer offering genetic testing to provide education for employees.
Many employees don’t realize that having a gene mutation that’s associated with a disease does not mean that he or she will ever develop that disease. The risk associated with most genetic variations is, in fact, relatively small. Because of that misunderstanding, employees may experience needless worry or, if the test is negative for mutations related to a disease, may forgo screenings like mammograms, colonoscopies and cholesterol tests that can help detect health problems earlier when they are often more treatable. In the case of genetic testing for mutations associated with cancer, employees may not be aware that most cancers are not caused by a mutation in the single gene that the test screens for.
For some of the conditions that genetic tests screen for, like Alzheimer’s disease, there are currently no treatments. This can again cause anxiety for employees and their families. Genetic tests also have implications that reach beyond the specific employee who is tested. A positive test can affect siblings and children as well, opening the question of whether the employee wants or feels compelled to share the results with other family members who may also be at risk.
Employers who offer employees genetic testing should ensure that all employees who choose to undergo testing are guided by experienced genetic counselors who can help them interpret and understand the results of their test and can connect them with other healthcare providers for additional testing or treatment as needed.
SOURCE: Varn, M. (3 May 2019) "What to consider before adding a genetic testing benefit" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/what-to-consider-before-adding-a-genetic-testing-benefit
4 benefits messages to send employees in May
Tax season has come and gone, and summer is right around the corner, making it a great time of year for employers to beef up communications about certain employee benefits. Read this blog post for four benefits messages employers should send their employees this May.
With tax season behind us, summer right around the corner and the second half of the year coming up, now is a great time of year for employers to beef up communications about certain benefits.
That’s because there are a number of important messages that are specific to this time of year, including saving money for summer vacations and putting more money into a health savings account so employees can plan for healthcare expenses for the remainder of the year.
Here are four messages employers should share with their employers this month.
1. Think about putting more money in your HSA.
May is a great time for your employees to take stock of their healthcare costs from January to April, and plan ahead for the second half of the year. Here’s a breakdown you can send to help them save money and have more cash available through December to pay their bills.
- Add up this year’s out-of-pocket health care costs thus far.
- Make a new estimate of your upcoming expenses (padding that estimate for unexpected expenses that may pop up.).
- Add your estimated costs to what you’ve already spent.
- Compare that total with how much you’ll have in your HSA account at the end of the year as it is now.
- If there’s a gap, you can increase your contribution rate now to make up the difference.
2. Adjust your W-4s.
Tax season has passed, which means it’s an excellent time to…think a little more about taxes.
The tax law changes that went into effect at the start of 2018 might have made your employees’ existing W-4s less accurate. If they didn’t update their withholding amount last year, they might have been surprised by a smaller refund, a balance due, or even by a penalty owed — and chances are, they don’t feel too happy about it.
Let your employees know that they can prevent unexpected surprises like this next tax season with a visit to this IRS tax withholding calculator. There, they can estimate their 2019 taxes and get instructions on how to update their W-4 withholdings to try and avoid any surprises next year. If they can update their W-4 online, send them the link along with clear step-by-step instructions. And if they need to fill out a paper form, explain where to find it and how to submit it.
3. Revisit your budgeting tools.
Summer is almost here, and your employees are likely starting to think about hitting the beach, road-tripping across the country or eating their weight in ice cream. Since having fun costs money, May is a good time to serve up some ideas on how to squirrel away a little extra cash in the next few months.
Employers should share tips for saving money on benefits-related expenses, like encouraging high-deductible health plan employees to use sites like GoodRx.com for cheaper prescription costs, or visiting urgent care instead of the emergency room for non-life-threatening issues. Also, consider making employees aware of apps like Acorns, Robinhood, Stash, Digits and Tally, which round up credit or bank card expenses to the next dollar, and automatically deposit the extra money into different types of savings accounts.
4. Double-check out-of-network coverage.
While you’re on the subject of summer fun, remind your employees to take a quick peek at their health plan’s out-of-network care policies before they head out of town. If they need a doctor (or ice cream headache cure) while they’re away, they’ll know where to go, how to pay, and how to get reimbursed.
Employers should remind employees that their HSA funds never expire, and they’re theirs for life. So if they put in more than they need this year, it will be there for them next year.
SOURCE: Calvin, H. (1 May 2019) "4 benefits messages to send employees in May" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/list/4-benefits-messages-to-send-employees-in-may
Can Employers Require Measles Vaccines?
Can employers require that their employees get the measles vaccine? The recent measles outbreak is raising the question of whether employers can require that their workers get the vaccine. Read this blog post from SHRM to learn more.
The recent measles outbreak, resulting in mandatory vaccinations in parts of New York City, raises the question of whether employers can require that workers get the vaccine to protect against measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) or prove immunity from the illness.
The answer generally is no, but there are exceptions.
Offices and manufacturers probably can't require vaccination or proof of immunity because the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) generally prohibits medical examinations—unless the employer is in a location like Williamsburg, the neighborhood in Brooklyn where vaccinations are now mandatory. Health care providers, schools and nursing homes, however, probably can require them because their employees work with patients, children and people with weak immune systems who risk health complications from measles.
But even these employers must try to find accommodations for workers who object to vaccines for a religious reason or because of a disability that puts them at risk if they're vaccinated, such as having a weak immune system.
Proof of Immunity
Proof of immunity includes one of the following:
- Written documentation of adequate vaccination.
- Laboratory evidence of immunity.
- Laboratory confirmation of measles.
- Birth before 1957. The measles vaccine first became available in 1963, so those who were children before the late 1950s are presumed to have been exposed to measles and be immune.
Measles, which is contagious, typically causes a high fever, cough and watery eyes, and then spreads as a rash. Measles can lead to serious health complications, especially among children younger than age 5. One or two out of 1,000 people who contract measles die, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
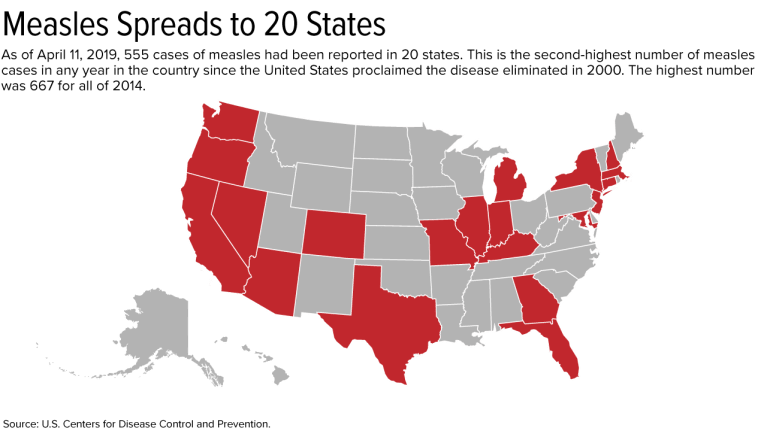
Outbreak Has Spread to 20 States
As of April 11, 555 cases have been reported in the United States this year. This is the second-greatest number in any year since the United States proclaimed measles eliminated in 2000; 667 cases were reported in all of 2014.
On April 9, New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio declared a public health emergency in Williamsburg, requiring the MMR vaccine in that neighborhood. Those who have not received the MMR vaccine or do not have evidence of immunity may be fined $1,000.
Since the outbreak started, 285 cases have been confirmed in Williamsburg, including 21 hospitalizations and five admissions to intensive care units.
If a city requires vaccinations, an employer's case for requiring them is much stronger, said Robin Shea, an attorney with Constangy, Brooks, Smith & Prophete in Winston-Salem, N.C. But employers usually should not involve themselves in employees' health care unless they are making an inquiry related to a voluntary wellness program, or the health issue is job-related, she cautioned.
The measles outbreak has spread this year to 20 states—outbreaks linked to travelers who brought measles to the U.S. from other countries, such as Israel, Ukraine and the Philippines, where there have been large outbreaks.
Strike the Right Balance
Health care employers typically require vaccinations or proof of immunity as a condition of employment, said Howard Mavity, an attorney with Fisher Phillips in Atlanta. He noted that most schoolchildren must be immunized, so many employees can show proof of immunity years later.
If an employee provides current vaccination records when an employer asks, the ADA requires that those records be kept in separate, confidential medical files, noted Meredith Shoop, an attorney with Littler in Cleveland.
All employers must balance their health and safety concerns with the right of employees with disabilities to reasonable accommodations under the ADA and the duty to accommodate religious workers under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
Under the ADA, a reasonable accommodation is required unless it would result in an undue hardship or direct threat to the safety of the employee or the public. The direct-threat analysis will be different for a registered nurse than for someone in a health care provider's billing department, for example, who might not work around patients.
Even if the ADA permitted mandatory vaccines in a manufacturing setting in limited circumstances, such as in Williamsburg now, any vaccination orders may need to be the subject of collective bargaining if the factory is unionized. Shoop has seen manufacturers shut down because employees were reluctant to come to work when their co-workers were sick on the job.
An employer does not have to accommodate someone who objects to a vaccine merely because he or she thinks it might do more harm than good but doesn't have an ADA disability or religious objection, said Kara Shea, an attorney with Butler Snow in Nashville, Tenn.
If someone claims to have a health condition that makes getting vaccinated a health risk, the employer does not have to take the person's word for it. The employer instead should ask the person to sign a consent form allowing the employer to learn about the condition and get documentation from the employee's doctor, she said. Before accommodating someone without an obvious impairment, the ADA allows employers to require medical documentation of the disability.
Courts don't closely scrutinize religious objections to immunizations, Mavity remarked.
"Some people have extremely strong beliefs that they don't want a vaccine in their body," said Kathy Dudley Helms, an attorney with Ogletree Deakins in Columbia, S.C. If the employer works with vulnerable people but can't find an accommodation for a worker who refuses vaccination, the employee may have to work elsewhere, she said.
SOURCE: SHRM (17 April 2019) "Can Employers Require Measles Vaccines?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/legal-and-compliance/employment-law/pages/measles-outbreak-2019-vaccinations.aspx