Can Employers Require Measles Vaccines?
Can employers require that their employees get the measles vaccine? The recent measles outbreak is raising the question of whether employers can require that their workers get the vaccine. Read this blog post from SHRM to learn more.
The recent measles outbreak, resulting in mandatory vaccinations in parts of New York City, raises the question of whether employers can require that workers get the vaccine to protect against measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) or prove immunity from the illness.
The answer generally is no, but there are exceptions.
Offices and manufacturers probably can't require vaccination or proof of immunity because the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) generally prohibits medical examinations—unless the employer is in a location like Williamsburg, the neighborhood in Brooklyn where vaccinations are now mandatory. Health care providers, schools and nursing homes, however, probably can require them because their employees work with patients, children and people with weak immune systems who risk health complications from measles.
But even these employers must try to find accommodations for workers who object to vaccines for a religious reason or because of a disability that puts them at risk if they're vaccinated, such as having a weak immune system.
Proof of Immunity
Proof of immunity includes one of the following:
- Written documentation of adequate vaccination.
- Laboratory evidence of immunity.
- Laboratory confirmation of measles.
- Birth before 1957. The measles vaccine first became available in 1963, so those who were children before the late 1950s are presumed to have been exposed to measles and be immune.
Measles, which is contagious, typically causes a high fever, cough and watery eyes, and then spreads as a rash. Measles can lead to serious health complications, especially among children younger than age 5. One or two out of 1,000 people who contract measles die, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
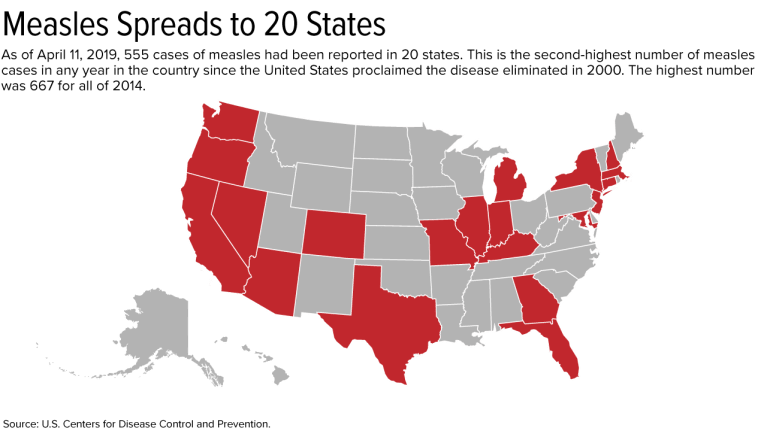
Outbreak Has Spread to 20 States
As of April 11, 555 cases have been reported in the United States this year. This is the second-greatest number in any year since the United States proclaimed measles eliminated in 2000; 667 cases were reported in all of 2014.
On April 9, New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio declared a public health emergency in Williamsburg, requiring the MMR vaccine in that neighborhood. Those who have not received the MMR vaccine or do not have evidence of immunity may be fined $1,000.
Since the outbreak started, 285 cases have been confirmed in Williamsburg, including 21 hospitalizations and five admissions to intensive care units.
If a city requires vaccinations, an employer's case for requiring them is much stronger, said Robin Shea, an attorney with Constangy, Brooks, Smith & Prophete in Winston-Salem, N.C. But employers usually should not involve themselves in employees' health care unless they are making an inquiry related to a voluntary wellness program, or the health issue is job-related, she cautioned.
The measles outbreak has spread this year to 20 states—outbreaks linked to travelers who brought measles to the U.S. from other countries, such as Israel, Ukraine and the Philippines, where there have been large outbreaks.
Strike the Right Balance
Health care employers typically require vaccinations or proof of immunity as a condition of employment, said Howard Mavity, an attorney with Fisher Phillips in Atlanta. He noted that most schoolchildren must be immunized, so many employees can show proof of immunity years later.
If an employee provides current vaccination records when an employer asks, the ADA requires that those records be kept in separate, confidential medical files, noted Meredith Shoop, an attorney with Littler in Cleveland.
All employers must balance their health and safety concerns with the right of employees with disabilities to reasonable accommodations under the ADA and the duty to accommodate religious workers under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
Under the ADA, a reasonable accommodation is required unless it would result in an undue hardship or direct threat to the safety of the employee or the public. The direct-threat analysis will be different for a registered nurse than for someone in a health care provider's billing department, for example, who might not work around patients.
Even if the ADA permitted mandatory vaccines in a manufacturing setting in limited circumstances, such as in Williamsburg now, any vaccination orders may need to be the subject of collective bargaining if the factory is unionized. Shoop has seen manufacturers shut down because employees were reluctant to come to work when their co-workers were sick on the job.
An employer does not have to accommodate someone who objects to a vaccine merely because he or she thinks it might do more harm than good but doesn't have an ADA disability or religious objection, said Kara Shea, an attorney with Butler Snow in Nashville, Tenn.
If someone claims to have a health condition that makes getting vaccinated a health risk, the employer does not have to take the person's word for it. The employer instead should ask the person to sign a consent form allowing the employer to learn about the condition and get documentation from the employee's doctor, she said. Before accommodating someone without an obvious impairment, the ADA allows employers to require medical documentation of the disability.
Courts don't closely scrutinize religious objections to immunizations, Mavity remarked.
"Some people have extremely strong beliefs that they don't want a vaccine in their body," said Kathy Dudley Helms, an attorney with Ogletree Deakins in Columbia, S.C. If the employer works with vulnerable people but can't find an accommodation for a worker who refuses vaccination, the employee may have to work elsewhere, she said.
SOURCE: SHRM (17 April 2019) "Can Employers Require Measles Vaccines?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/legal-and-compliance/employment-law/pages/measles-outbreak-2019-vaccinations.aspx
Think your employee is faking sickness? Here’s what you can do
Have your employees misused their FMLA leave before? Navigating FMLA can be tricky, leading to costly lawsuits if a wrong move is taken. Continue reading this blog post to learn more about handling FMLA misuse.
Your employee’s gout flared up, so they took the day off using intermittent medical leave. Later on, a photo of the same employee sliding into home base surfaces on social media that day. How do you find out if the employee was misusing FMLA leave?
Bryon Bass, senior vice president of workforce absence at Sedgwick — a business solution tech company — says navigating FMLA can be tricky, and the wrong move can provoke costly lawsuits. But if an employer has reason to believe the absence isn’t valid, Bass says there’s a process they can follow to investigate.
“I think [a social media photo] casts doubt on the reason for their absence,” Bass said during a recent webinar hosted by the Disability Management Employer Coalition. “It merits a second look, along with some potential code of conduct talks with HR.”
When a questionable situation arises, employers can ask for the worker’s approved medical condition to be recertified, Bass said. This involves having the employee resubmit their original FMLA application. Afterward, employers can send a list of absences to the employee’s healthcare provider to authenticate the dates as valid medical absences. Typically, employers can only request recertification after a 30 day period, unless there’s reason to believe the employee is taking advantage of the system.
“If, for example, you notice two employees — who happen to be dating — are taking off the same days for their different medical conditions, that’s a valid reason for asking for recertification,” Bass said. “Patterns of absence are a common reason to look into it.”
Instead of requesting recertification, some employers make the mistake of contacting the employee’s physician directly — a process called clarification. Employers are only allowed to use clarification during the initial FMLA application, and only after obtaining the employee’s permission. Clarification is used to answer employer questions about the amount of rest an employee’s condition merits.
Employers might not trust the opinion of their employee’s doctor, but they can’t ask for a second opinion until it’s time for the employee to re-submit their annual certification, Bass says. When that time comes, employers can appoint a physician to reexamine the employee at the company’s expense. If the employee objects to the second doctor’s report, a third opinion can be sought.
“With third opinions, both the employer and the employee have to agree on the provider because their decision is final,” Bass said. “Employers are also required to cover this expense.”
Although employers are within their right to file recertification, Bass says it should be done sparingly and in situations where evidence suggests misuse. An employee using slightly more time for recovery isn’t automatically abusing the policy, he said.
“FMLA does not permit healthcare providers to provide an exact schedule of leave, just an estimate of absences necessary for the employee’s treatment and recovery,” Bass said. “Treatments are more predictable, but it’s still only an estimate. If someone takes a little more time than estimated, it doesn’t mean you need to ask for recertification; in fact, the Department of Labor discourages that.”
SOURCE: Webster, K. (24 April 2019) "Think your employee is faking sickness? Here’s what you can do" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/news/how-to-certify-medical-leave-and-handle-pto-requests?feed=00000152-a2fb-d118-ab57-b3ff6e310000
7 tips for keeping shift workers healthy
Most companies that are open for more than 10 hours a day have some sort of shift work or work pattern. Though shift work can have multiple positives for companies and their workers, it can also have numerous negative impacts on physical and mental health. Read this blog post for seven tips on keeping shift workers healthy.
For companies open for more than 10 hours a day, it’s likely that you have some sort of shift work, or a pattern of work involving rotation through different fixed periods across a working week or month. Employees who work in healthcare, call centers, manufacturing and in a warehouse all regularly work round-the-clock shifts, and these are some of the most common industries utilizing this type of model.
While shift work can have numerous positives for the company and even the workers, it also can have many negative impacts on health — both physical and mental. Beyond the most common health impact — sleep disruption — there are numerous other ways shift work can negatively impact a worker’s health including: mood disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, injuries and accidents, metabolic disorders, cancer, cardiovascular disorders, interference on family live and limited social life.
Shift workers also experience high levels of annual leave requests and short-term disability claims.
For employers in one of these industries, or any industry with non-regular shift hours, there are a few best practices that will help improve worker productivity and minimize leave.
Provide schedules that are as predictable at possible. Allowing an employee to settle into a regular schedule will allow them to establish a routine both at work and at home. Interference with home and social life can be a key trigger for a variety of negative health habits.
Limit the number of nights worked consecutively. Just like a traditional Monday-Friday, 9-5 worker, those working night hours need a weekend of their own, too. While this may not always be Saturday-Sunday, allowing them a couple of consecutive days off will give them time to disconnect and recharge.
Designate areas and times for employees to rest in the workplace. Whether a nurse in a busy ER department or a warehouse worker stocking shelves, everyone needs a break during their workday. Work with the shift manager to map out regular breaks and a calm and quiet place for employees to take a break.
Provide health and wellness programs that are accessible at night and on weekends. Since most HR professionals work office day jobs, they often forget about accessibility of services to employees working different hours. Assure your EAP provider is accessible 24/7 and if you have on-campus programs, be sure to offer them at different times for your shift workers. A factory employee working third shift should have the same level of access as a first-shift office worker.
Give employees more control over their schedules with shift-based hiring. This is an approach of hiring people for individual shifts rather than hiring employees, then scheduling them into shifts. Employees come to companies with a range of responsibilities outside of the workplace. Allowing them to match with the shift that best works with their personal lives will result in greater productivity and fewer health impacts.
For those returning to work following a leave, keep the schedule as close to their normal schedule as possible. While it’s not always possible to perfectly align with their previous schedule, you’ll want to get those returning from a leave back into the routine of their previous shift work. While on leave, many will have transitioned into a different sleep routine, so getting them back to the previous patterns will help with the transition back to work.
Provide resources on good sleep health. For shift workers, a healthy sleep routine can be challenging. However, there are simple and well-proven approaches to establishing sleep patterns regardless of the time of day. Be sure to regularly promote resources in the workplace and through regular communications. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine is a good place to start.
SOURCE: Willett, S. (26 April 2019) "7 tips for keeping shift workers healthy" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/tips-for-keeping-hourly-employees-healthy?brief=00000152-14a5-d1cc-a5fa-7cff48fe0001
Concerned about cybersecurity? Here’s how to protect 401(k) plans
Do you offer a 401(k) retirement plan to your employees? A new emerging cybersecurity risk for plan sponsors is retirement plans. Continue reading this blog post for tips on protecting 401(k) plans from cyberattacks.
All companies that manage personal consumer data are already concerned — or should be concerned — about cybersecurity. The scope and scale of cyberattacks continue to rise worldwide, as demonstrated last year by a breach that compromised data of 50 million Facebook users.
Retirement plans pose a new risk. Lawmakers are keen to protect the personal information of defined contribution plan participants. Recently, Sen. Patty Murray (D.-Wash.) and Rep. Bobby Scott (D.-Va.) asked the U.S. Government Accountability Office to “examine the cybersecurity of the private retirement system.”
Fortunately for plan sponsors, record-keepers and other parties in the retirement services industry, the same solution designed to address the multiple problems stemming from the upsurge in small, stranded 401(k) accounts — auto-portability — can also augment existing practices that protect plan participants’ personal data.
Auto-portability is the routine, standardized and automated transfer of a retirement plan participant’s 401(k) savings account from their former employer’s plan to an active account associated with their current job. This solution is underpinned by paired “locate” and “match” algorithms which work together to locate participants with multiple 401(k) plan accounts, confirm their identities, obtain consent for rolling over their stranded accounts. These accounts can exist in former employer plans or rolled into safe-harbor IRAs before they're moved into active accounts in their current employers’ plans. In addition, consolidation can include a roll-in to the participant’s current employer plan.
The act of consolidating accounts reduces the number of small accounts in the 401(k) system through auto-portability, which makes plan participant data more secure. Consolidating a participant’s multiple 401(k) accounts reduces the number of systems that store a participant’s data, and also encourages participants, sponsors and record-keepers to become more engaged when it comes to keeping track of accounts.
Auto-portability meets cybersecurity best practices
While there is currently no central legal framework regulating cybersecurity in the retirement services industry, the SPARK Institute published a compilation of recommended cybersecurity best practices for retirement plan record-keepers in 2017. Auto-portability, which went live that same year, operates in conformance to the SPARK Institute’s cybersecurity recommendations.
For example, the SPARK Institute, a retirement policy center in Simsbury, Connecticut, issued 16 security control objectives, including the practice of encryption, which requires protection of both “data-in-motion and data at rest.” The institute suggests that the same data protection risk management standards be applied to suppliers. To address cybersecurity, the institute suggests these steps:
- Encrypt all sensitive information subject to auto-portability using Advanced Encryption Standard 256-bit encryption, an industry standard developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. There is no known type of cyberattack that can read AES-encrypted data without having the cryptographic key.
- Never combine a Social Security number with other personally identifiable information in any single file transfer. The objective should be to ensure there is never enough personal data in any single transmission for a hacker to use to steal an identity. In addition, any file with personal information should never include the identity of either the plan’s sponsor or the record keeper. That further thwarts a hacker from accessing an individual participant’s retirement account.
- Know that auto-portability supports multiple methods of exchanging secure data.
- Ensure that any information flagged during the locate-and-match process that doesn’t adhere to certain criteria requires additional verification to confirm an identity.
- Conduct full address-location searches to ensure that the correct participant is found and properly matched to multiple accounts.
When participants strand 401(k) savings accounts in former-employer plans, and nothing is done to transport them to active accounts in their present employers’ plans, there’s a strong chance that the worker may fall victim to a cybercrime. Plan sponsors can protect themselves and their participants from hackers, and strengthen their overall cybersecurity preparedness, by implementing auto-portability to cull small accounts and missing participants.
SOURCE: Williams, S. (25 April 2019) "Concerned about cybersecurity? Here’s how to protect 401(k) plans" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/how-to-protect-401k-plans-from-cybersecurity-risks
Helping a Good Employee Who Hits a Rough Patch
Are any of your top performing employees going through a rough patch? Read this blog post from SHRM for helpful tips and factors to consider when employees are going through rough times.
One of our employees, who has been a steady, solid performer the last two years, suddenly erupted in anger at one of our clients during a company event. Granted, the client is difficult and the event had all of us stressed out, but that’s no excuse to lose one’s temper and get into a shouting match. We immediately suspended him without pay.
Since then we’ve learned from coworkers that he’s dealing with stress by drinking. What should we consider as we try to decide whether to fire him or let him come back?
Suspending him without pay while you’re trying to figure out the situation is a good choice. While emotions run high, I always recommend suspending instead of “firing on the spot”. A suspension allows you to carefully choose a decision after learning all the facts, and avoids you having regrets later for having acted too rashly.
Below are some factors to weigh that will help you decide:
Value - You say he’s been there 2 years, which means he’s probably knowledgeable and you’ve made an investment in his training and development. Does this make him a keeper?
History - Is this his first offense or is this a repeat pattern? Is he well respected? or is he perceived as a hot-head? Does he have good relationships with clients and colleagues? Did you expect this or did it appear to come out of the blue?
Help available. If you were to keep him, what’s the level of support you can provide for him getting some help? For instance, does your company have access to an Employee Assistance Program (EAP) that provides therapy or substance abuse treatment? You can make this a condition of employment. In other words, you can allow him to keep his job as long as he agrees to participate in the EAP.
Note: Be careful here if you make a referral, to do so only for a generic EAP assessment and not for a “substance abuse” program, in other words, stay away from labeling or diagnosing him. Let the pros at EAP determine what he needs. His treatment will remain confidential, you’ll only know whether he’s participating.
Kudos for carefully considering your decision. He may simply be a good employee who is going through a rough time and needs some help.
SOURCE: Del Rio, E. (22 April 2019) "Helping a Good Employee Who Hits a Rough Patch" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://blog.shrm.org/blog/helping-a-good-employee-who-hits-a-rough-patch
Originally posted on HR Box.
Background Screenings and Second Chance Employment - 3 Tips for Success
According to a 2012 SHRM survey, nearly seven out of 10 companies reported that they conduct criminal background checks on all job candidates. Employers today may choose to run background screenings on job applicants for numerous reasons. Continue reading to learn more.
Today’s employers may choose to run background checks on job applicants for variety of reasons. Concerns about negligent hiring, verifying a candidate’s honesty and accountability, and other safety- or performance-related issues may all play a part in this decision. In fact, according to SHRM's 2012 survey, nearly 7 out of 10 companies report that they conduct criminal background checks on all job candidates.
Understandably, employers want to do everything they can to protect their businesses and to ensure (as much as possible) that they’re also protecting their employees. And while an interview is an important opportunity to learn about a job candidate’s character and experience, a background screen provides tangible and practical verification of a candidate’s past, and that is reassuring. What’s important to keep in mind is that background screens are most effective when they’re used judiciously and carefully. Here are a few suggestions to consider.
- Tailor background screens to search for information relevant to the specific responsibilities of the job. While it can be tempting to want to know all the information available about a candidate’s past, the ethical and legal use of background screens means that a motor vehicle report, for example, isn’t relevant for a candidate who won’t be driving as part of their job. Limiting searches to the information that is most relevant to the execution of the job functions will keep you in EEOC compliance and will yield more effective background screens.
- Use a professional background screening company to assist you. There are many excellent and affordable screening companies to choose from, and we at Dave’s Killer Bread Foundation have had great experiences in our work with Occuscreen, GoodHire, and Checkr, among others. A professional background screening company can help you get the most out of your background checks and can work with you to ensure you’re soliciting the right information for the right purpose. Additionally, quality background screening companies are able to verify information through court runners and other means, which improves accuracy and reduces the likelihood that you’ll see or use irrelevant data (arrest records not leading to convictions, for example).
- Remember to be consistent. If you have two or more applicants applying for the same job, you should be requesting the same information about them when you run their backgrounds. Varying types of job responsibilities and roles might require varying levels of inquiry, but if multiple candidates are applying for the same job with the same title, it’s important to keep your process consistent. This will help you avoid the appearance of discrimination or favoritism.
And remember, background screens may involve some level of technological or human error. The information provided from a background screen is a valuable tool to help you in your hiring decision, but it is only one tool. Thoughtfully integrating this information—with your intuition, your experiences with the candidate in the interview, and your willingness to suspend bias or assumptions about an applicant’s character based on their past—can help you to make the best hiring choice every time.
Have questions about how to proceed with a report’s findings? Many employers aren’t criminal code experts, and don’t have to be. Dave’s Killer Bread Foundation is here to help. Get in touch.
SOURCE: Martin, G. (16 April 2019) "Background Screenings and Second Chance Employment - 3 Tips for Success" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://blog.shrm.org/blog/background-screenings-and-second-chance-employment-3-tips-for-success
Dave’s Killer Bread Foundation is the nation’s only nonprofit foundation dedicated to inspiring and equipping employers to embrace Second Chance Employment
This post is part of a series for Second Chance Month, which highlights the need to improve re-entry for citizens returning to society and reduce recidivism. One of the primary ways to do this is by providing an opportunity for gainful employment. To sign the pledge and access the toolkit with information on how to create second chances at your company, visit GettingTalentBacktoWork.org.
4 signs top talent may leave: Best strategies to keep them
Landing new top talent in today's tight labor market is no easy task, making retention an important priority. Read this blog post for four signs that your star employee might be leaving.
There are few things an HR pro dreads more than when a great employee hands in their notice. The challenge of having to replace them can be overwhelming.
And in this tight labor market, landing new top talent is no easy task, making retention an important priority.
Luckily, there are usually signs a valued employee might be thinking about jumping ship, and some proactive steps you can take to try and keep them.
Subtle signs
Experts agree there are a lot of reasons great employees decide they need to move on. Apart from salary, boredom and a lack of recognition and engagement are the biggest issues causing workers to seek employment elsewhere.
While it might seem sudden and jarring when an employee announces their resignation, there were most likely subtle signs it was coming.
Here are the main ones to watch out for, according to Janine Popick, Chief Marketing Officer of Dasheroo:
1. Private calls during work. Everyone needs to take private calls in the office from time to time, but if someone seems to be answering the phone in hushed tones and dashing to the nearest empty office frequently, that’s probably a sign your employee is interviewing somewhere else.
2. Declining work ethic. Many employees mentally check out before they leave a job. While there could be personal issues causing a change in attitude, if an employee seems less enthusiastic and is consistently only doing the bare minimum, they’re most likely ready to move on.
3. Lack of socialization. Someone actively wanting to leave probably won’t go out of their way to make chit chat with co-workers or be overly friendly anymore. Pay attention to any employee who’s suddenly keeping to themselves more than usual.
4. More activity on social networks. If you’re worried an employee may be getting ready to leave, take a peek at their online presence. Is their LinkedIn page completely updated and polished? Are their tweets looking more professional than personal? This kind of online activity could be an indicator an employee is trying to make a good impression on a new employer.
While it may be too late to convince some people to stay, there are still steps you can take to prevent talent from leaving in the future, according to HR Daily Advisor.
Presenting new challenges
Boredom is what’ll disengage your workers the fastest and cause them to seek a new project elsewhere. To get a basic idea of where your employees stand, an engagement survey is a great tool to see who needs a change.
An easy fix is to ask your people if they’d like to tackle different types of assignments. The more you keep things fresh for them, the more likely they are to remain engaged.
Another way to avoid boredom: See who’s due for a promotion. If someone’s been stuck in the same position for so long they’ve grown tired of it, see if there’s a new opportunity for them. The new responsibility could be just what they needed to respark their enthusiasm.
Recognition, feedback
When your people don’t feel appreciated, they’ll have no qualms about leaving the company. To correct this, it’s important to give frequent feedback and let people know when they’ve done a good job.
Gallup research shows employees who are praised are more committed to their work and organizations. Even just quick feedback, positive or negative, can motivate employees and boost their engagement.
Extra communication can only make employees feel more connected to the company.
SOURCE: Mucha, R. (1 February 2019) "4 signs top talent may leave: Best strategies to keep them" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrmorning.com/4-signs-top-talent-may-leave-best-strategies-to-keep-them/
A better place to work: How well-being impacts the bottom line
Did you know: One in 10 employers are skeptical about the value of well-being programs. Health challenges, near stagnant wages, financial stress and more can take a personal toll on your employees, causing their stress levels to rise. Read this blog post to learn more.
Logically, employees bring their “whole selves” to work. Unfortunately, health challenges, relatively stagnant wages, heightened financial pressures, always-on technology and contentious geo-political climates around the world all take a personal toll on employees in the form of rising stress.
Employers recognize that the health and well-being of their workers is vital to engagement, performance and productivity, yet one in ten are skeptical about the value of well-being programs. But by learning from peers’ experiences, employers can take steps to help employees improve their well-being through access to related programs and services. And that contributes strongly to the overall success of the organization.
Survey says
According to the 252 global employers polled in the Working Well: A Global Survey of Workforce Wellbeing Strategies, building a culture of well-being is a higher priority than ever. Fully 40 percent of organizations believe they’ve actually achieved it, up from 33 percent in our 2016 survey. Of those who have not, another 81 percent are making plans to get there.
Top priorities for wellness programs in North America were to reduce stress and boost physical activity. Stress is a bottom-line issue for employers: 96 percent identified employee stress as the biggest challenge to a productive workforce.
Closely related priorities were improving nutrition and work-life issues, addressing depression and anxiety, and getting better access to health care services. On the latter, discussion with many employers confirms this includes sufficient access to mental and behavioral health providers—directly related to the top challenge of stress and its more serious potential debilitative consequences that can include anxiety, depression, addiction and more.
Health
The most frequently offered employee health benefits which respondents also assessed as most effective included the following:
- Employee assistance programs (EAPs): By far the most frequent program, offered by 86 percent of global employers and 96 percent of US respondents. About 7 in 10 of those who offer an EAP said it’s effective in achieving their objectives, although actual experience reveals a wish that many more employees would take full advantage of EAP services. Know your numbers assessments, including health screenings and health risk appraisals, rose in prevalence globally and were considered effective by 86 percent of respondents.
- On-site care: While smaller numbers of employers offer on-site immunizations, delivery of medical care, or fitness centers, they were still rated at just over 80 percent effective – demonstrating that convenience and access can remove barriers and enhance results.
- Flexible working policies: These rose in prevalence over our last survey, consistent with other research demonstrating that multiple generations prize work flexibility to enable balance and help manage life’s stressors.
- Wearables: Sensors and trackers also rose in prevalence. Globally, two-thirds of respondents credited them with effectiveness in monitoring and perhaps motivating healthy activities.
The survey also found health literacy is required to engage and drive behavioral change, and employers need targeted solutions to build it.
Finances
Validated by other research, a majority of employees live paycheck to paycheck today. Of US respondents, 87 percent reported financial distress among employees (the global average was 83 percent). Employers cited negative bottom-line results from financial stress, such as lower morale and engagement, delayed retirement and lower productivity, among other detrimental impacts. Other studies show financially stressed employees spend three hours or more each week distracted by it.
In prior years, this survey showed a top focus on saving for retirement; now, non-retirement-related objectives are rapidly catching up as priorities. It’s hard to focus on retirement when current needs are pressing. As a result, well over 7 in 10 employers also seek ways to ensure adequate insurance protection, help in saving for other future needs, better handling day-to-day expenses, reducing debt, and having emergency savings.
ROI vs. VOI
Just under half of respondents have specific, measurable goals or targets and outcomes for their well-being programs overall. But measurement is tricky, and 45 percent of respondents noted a lack of resources to support measurement as the top barrier to metrics. Nevertheless, only 8 percent perceived “no measurable return.”
Of those measuring the health care cost impact, 54 percent reported their programs were reducing trend by 2 to 5 percentage points per year. Financial well-being ratings were more challenging, with only 4 percent globally saying they have objective data to demonstrate their financial well-being program effectiveness.
Concurrently, many placed their bets on technology tools to inform program design and outreach: 84 percent rated predictive analytics as effective in helping to support well-being, even if just over a quarter offer it today—another half plan to do so in the next 2 to 3 years.
A value-of-investment priority emerges from the data. Employers intuitively pursue programs that build goodwill by providing helpful resources. The top four objectives globally focused on engagement and morale, performance and productivity, attraction and retention, and overall, enhancing the total rewards offering while managing spend. While reducing health care costs was the top objective for the US, it was fifth globally. Other objectives linked the organization’s image or brand and values and mission—if the company has a message to external customers, it needs to “walk the talk” internally with employees.
Holistic strategy
Compared to prior surveys, employers continue to explore new ways to support well-being, in response to employee and business needs. The historically stronger emphasis on health-related well-being continues, but financial well-being efforts are on the rise. For the US/Canada, the recent fast-rising program elements have been spiritual well-being (67 percent), retirement financial security and preparedness (57 percent), social connectedness (57 percent), and financial literacy/skills (63 percent).
In total, survey responses suggest employers understand that these well-being issues are interconnected and cannot be effectively addressed in isolation without a more holistic strategy and delivery solutions.
That’s where value of investment comes in, acknowledging that enhancing physical and emotional, financial, social, and other aspects of employee well-being can help make the organization a better place to work.
SOURCE: Hunt, R. (11 April 2019) "A better place to work: How well-being impacts the bottom line" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitspro.com/2019/04/11/a-better-place-to-work-how-well-being-impacts-the-bottom-line/
How to offboard employees with care
How are your onboarding and offboarding programs? While many employers understand and accept the importance of having a great onboarding program, many lose sight of their offboarding program. Read on for more on how employers can offboard employees with care.
Employers understand the importance of onboarding new employees. A Glassdoor report found a strong onboarding process improved new hire retention by 82% and improved productivity by more than 70%.
Talent professionals place more emphasis than ever on creating positive employee experiences — and that pressure starts from an employee's first day. But should that same attention be given to an employee's last day? In a tight labor market, where referrals from former employees and "boomerang" employees are valuable sources of talent, HR might consider: What are the benefits of creating a strong offboarding process?
Offboarding: part of the employee life cycle
Onboarding has long been an important point in the employee life cycle, while offboarding has always been an afterthought, Jen Stroud, HR evangelist and transformation leader for ServiceNow, told HR Dive. But now, as the entire employee lifecycle is getting attention, offboarding is coming into focus, she said.
"If you have a great onboarding experience and you bring people to work for you and their employee experience and offboarding experience is poor, you spent a lot of money for onboarding that is wasted," she added.
Former employees, particularly those who left voluntarily, are ambassadors of your company's brand, Moses Balian, HR consultant at Justworks, told HR Dive. "A smooth and amiable offboarding is so valuable in maintaining employees beyond active employment," he said. "You never know when you want to rehire someone."
Offboarding may be fundamentally important to keeping potential boomerang employees feeling positive about the organization, maintaining good employer branding, establishing a network of former employees or helping current employees feel engaged despite co-workers' departures. Since offboarding is the final interaction a departing employee may have with an organization, how they're treated — good or bad — during that process can remain top of mind.
Offboarding involuntary separations respectfully
Employers may have a planned-out process for involuntary separations. Even if those employees are not the ones you'd rehire, they still should be treated with compassion, Angela Nino, founder of Empathic Workplace, told HR Dive in an interview.
"Planning for that is important, not just squeezing it into your day," Nino said. From making sure the conversation is done privately, determining if security or police will need to be on site, ensuring the employee has their personal belongings and can get to their car or has transportation home — these are important steps in the offboarding process. It's important that the termination conversation is not a shaming experience for the employee, Nino added. "Treat that person with respect and dignity, respecting the fact that [it is] about to be one of the worst days of their life."
With workplace violence as a concern, handling an involuntary offboarding process carefully is essential. "If you have been in HR, you know that the way that we treat someone on their last day of work or the way that we treat someone during a termination can be [the difference between] whether or not they bring a gun," Nino said.
But mitigating the potential of workplace violence needs to start before the termination meeting, David Moore, partner at Laner Muchin, told HR Dive. "I think it goes all the way back to the process and events leading to an involuntary separation," Muchin said. "Have we treated this person fairly? Have we given them notice of the performance or conduct issues? Have we given them fair opportunity to turn it around? Have we documented that to them so they're not able to say in their mind that 'no one told me that this was going to happen?'"
Offboarding voluntary separations: taking advantage of opportunity
An involuntary offboarding process may be prone to mistakes (i.e. benefits forms filled out and submitted), but a voluntary offboarding process is prone to missed opportunities, Balian said. Exit interviews for voluntary resignations are frequently a formality and employees don't feel their voices are heard. Balian noted that when he worked as in-house HR and conducted exit interviews, he would ask resigning employees, "are you running to or from?," to gauge their reasons for leaving. Combined with additional data gathered through surveys, this information may give HR an opportunity to identify and correct problems. Exit interviews also give employers a chance to show gratitude to the employee and interface with them on a human level, Balian said.
Just as a smooth onboarding process involves ensuring a new employee has a company ID, a workspace and appropriate equipment, a smooth offboarding process, whether for involuntary or voluntary reasons, makes sure those same details are planned for the outgoing employee, Moore said. Will the employee still receive a commission or bonus? When does the next paycheck arrive? Is severance offered? What is the benefits coverage?
Regardless of whether an employee leaves on their own or is terminated, the offboarding process can affect the employee's co-workers as well. If an employee has a poor offboarding experience and tells former co-workers, or if co-workers witness a poor offboarding process, it undermines the value the organization places on talent, Balian said.
It is critical not to think of offboarding as being in a silo or a one-off workflow process, Stroud said. "It is really about the lifecycle of an employee." Organizations that have the greatest impact have added offboarding processes to their considerations of employee experience, Stroud added. To initiate an offboarding process, start by examining the steps in the employee lifecycle and consider what actions are needed to create the best employee experience.
"All it takes is a little bit of time and investment and intention on behalf of your HR team," Balian said. "It doesn't cost anything except effort."
SOURCE: DeLoatch, P. (9 April 2019) "How to offboard employees with care" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrdive.com/news/how-to-offboard-employees-with-care/552053/
The talent textbook: 4 ideas for giving better feedback
Managers enjoy giving good news during a review, but how can reviewers take the sting out of negative feedback or even constructive criticism? Read this blog post from HR Drive for four ideas on giving better feedback.
"You got a promotion! You get a raise!" It's almost as fun for managers to say it as it is for employees to hear. Giving good news during a review is easy, but how can reviewers take the sting out of constructive — or negative — feedback?
Coaching an employee who needs to improve or who isn't quite ready for more responsibility, higher pay or leadership opportunities is perhaps the most difficult aspect of performance management, so in this installment of the Talent Textbook, we'll offer four guiding principles from experts for giving better feedback.
#1: Meet more often
Many talent experts today recommend retiring the annual performance review and replacing it with frequent feedback instead. Unlike annual reviews, continuous feedback sessions can lessen anxiety for managers and workers both, making the conversations less formal and more focused. They can help send the message that the company culture is one of listening and responding to workers' needs — and they help talent pros and managers minimize the risk that workers will be dissatisfied with or surprised by the discussion.
"That feedback should be coming constantly," said Jim Flynn, CHRO at Sitel Group. "Everyone should know where they stand constantly."
Flynn believes that frequency transforms the feedback session into a chance to reflect and recalibrate on priorities and goals. It can also ensure that workers are aware of their progress toward a pay increase, promotion or increased responsibility because their manager has reminded them more recently.
For Jodi Chavez, group president professional staffing group at Randstad Professionals, Randstad Life Sciences, focusing up frequently keeps managers better informed about workers' desires and expectations, potentially preventing turnover and keeping the feedback session from devolving into a bidding war.
"If an employee has a desire and a belief that they want this promotion or to be in that role, there can be instances where you won't be able to undo their desire to leave," she said.
"It can be easier if you catch that earlier on in the process — so constant communication, so they know what you're looking for and you can keep coaching them, is important. It only becomes an issue when no one knows that it's a desire until later in the process."
Just as you wouldn't assess business goals and objectives only once a year, talent pros should expect to assess people often to curb employee disappointment, Flynn said, and this is especially true for employees early on in their careers.
#2: Give a heads up and an open ear
There's still stress for talent pros and managers even when preparing to deliver feedback in a more casual session: Will they feel insulted? Will they disengage afterwards? The fears are relevant, so that's why the way reviewers deliver feedback matters as much as the frequency.
Chavez and Flynn agree that managers and talent pros should begin conversations with what they're going to cover in the session. They can continue to be transparent with workers by providing the reasoning behind the feedback and their expectations for the future, Flynn said.
"I think the old sandwich approach, employees see through that," Flynn said, referring to the tactic of "sandwiching" a criticism between two compliments. "I would rather be more upfront and honest, and that should be the manager's approach to everything."
In that same realm, honest feedback should never come with bias or malice attached. Jeannie Donovan, VP of HR at Velocity Global, wrote in an email to HR Dive that "clear is kind" when it comes to constructive feedback. Whether the manager is discussing goal setting or areas that need improvement, the employee's pay grade or their potential for a future promotion, Chavez said the same principle applies: stick to the facts and strive for objectivity.
"For new talent managers, I think it's important to stay very factual and to hear the employee," she said. "Don't lead with false promises, just very cut and dried — 'The role that you're in and the experience that you have puts you at this level [of pay.]'"
That's not to say that a manager should shut down further discussion, Chavez said. Discussing an employee's strengths and listening to their desires can help them visualize a realistic and reachable future for themselves within the organization.
"It's really important to sit down and talk about the positive things that the employee brings to the table — it's a non-defensive position to put the employee in," Chavez said. "Try to understand what is important to them, and let them tell you. 'I may not be able to be a supervisor, but I'd still like to learn more about how to manage people' — once you know that as a manager, giving them pieces that help fulfill that helps them stay engaged."
#3: Support your managers
Talent pros should focus on workers when they consider their feedback best practices — but managers need their attention and expertise, too. As Flynn put it, "sometimes you have to carry cold water warmly" when delivering feedback, and managers need encouragement, support and guidance from talent pros to pull it off.
"A good HR business partner should understand when those difficult conversations could be occurring," he said, noting that this partnership goes both ways. "If a manager is aware that it might be a tough conversation, it's always a good idea to give your HR business partner a heads up so they can be attuned."
Providing tools or suggestions for approaching reviews can help managers to execute conversations with employees with clarity and mutual understanding. For example, Donovan coaches her managers on the "stoplight exercise," which can be helpful when an employee is making a case for a promotion. She said that managers can take a pen to the job description for the role their charge would like to be promoted into — highlighting current responsibilities in green, responsibilities they have a slight grasp of in yellow and tasks they've never touched in red.
"This is a straightforward way to identify strengths, weaknesses, and gaps to assess readiness for that promotion. Further, if this exercise yields gaps, the results indicate where exactly to focus on growth," she wrote.
Donovan echoed Flynn's belief that managers and talent pros should partner in the feedback process, and that debriefing afterwards is as critical for retention as it is for employee satisfaction.
"Have that second set of eyes to be aware and look for signs of disengagement or other harmful behavior," said Flynn. "Some managers are hands off, so if they've had that difficult conversation make sure you're maintaining that personal connection and increasing your frequency of touch."
#4. Shift the focus forward
The last thing constructive feedback should sound like is a lecture. Reviewers should reiterate that the feedback is in service of plan to get that employee a promotion, salary bump, conference excursion, a chance to lead an internal workshop or whatever the goal is in the future, Chavez said.
"They should feel positive about what they have contributed and what they can continue to contribute," she said. "[It's about] what you can do to help foster that growth for them."
Flynn's approach is similar, keeping the conversation productive and goal-oriented: "I probably spend 25% of the time talking about past performance, and goals reached and past behavior, but I like to focus more on what are the strengths, what are weaknesses and where the potential is."
With the future in mind, Chavez points out that a transparent, frequent and collaborative review process could prevent promising talent from leaving down the road. It can even have ripple effects across an organization, according to Donovan, who saw that workers had a clearer vision of their goals when she transitioned to more continuous feedback.
"As a result of our laser-focus on more frequent performance conversations, our employees have a roadmap of what needs to be done and when, and this approach lends itself to higher productivity and a general sense of purpose across the board," Donovan wrote.
SOURCE: Fecto, M. (10 April 2019) "The talent textbook: 4 ideas for giving better feedback" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrdive.com/news/the-talent-textbook-4-ideas-for-giving-better-feedback/552276/