Motivating employees to higher performance
Building and sustaining an energized, motivated workforce take initiative and requires that employers develop an inspiring workplace culture. Continue reading this blog post for more on motivating employees to increase performance.
Building and sustaining an energized workforce that takes initiative requires creating an inspiring atmosphere.
Some of the key features of such a workplace are:
- A creative work environment where employees are able to express themselves openly.
- A work environment not stifled by unnecessary process and policy hurdles.
- A challenging and constructive work environment featuring constant feedback.
- Leadership that listens and responds to employees.
- A collaborative and cross-functional workforce where diversity is cherished.
Employees recognize the difference between empty slogans and real commitment and will respond to an organization that walks the walk in creating a great place to work.
Happiness equals productivity
A recent study found that employees who are happy are 12 percent more productive than those who aren’t.
Whether or not the specific percentage is totally accurate, we can all confirm the general point from our own work experiences.
Happy employees get to work on time, work hard, and take responsibility.
So how to keep a happy workplace? Here are some ideas:
- Make humor part of the agenda – work is stressful. Find ways to lighten things up occasionally
- Within the constraints of your particular process, don’t insist on rigid schedules. Give employees some control over how they use their time during the day.
- Respect, and encourage respect for, differences
- Fewer managers and official leaders
- Make fitness and physical activity part of a normal day
- Create a bright atmosphere and encourage interaction
SOURCE: McElgunn, T. (2 May 2019) "Motivating employees to higher performance" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrmorning.com/performance-management-motivating-employees/
How do you know when learning programs are working?
How do employers measure the success of employee learning programs? The demand for employee learning programs is increasing, as well as the spend that employers are allocating for these programs. Continue reading to learn more.
Demand for learning is up and the spend that employers allocate to it is climbing — but as employers spend more money, they may also need to increase expectations for learning's success.
What outcomes do employers expect from learning programs? Whenever a company initiates training, that company must also ensure it has clear, definable results in mind, experts told HR Dive. Training to increase practical knowledge — how to utilize equipment, for example — should be task-oriented and measurable. Other training goals, like developing soft skills, may be more intangible, but success metrics can still be necessary.
Quantifying learning and finding success
The classic Kirkpatrick Model to evaluate training is widely used, Tom Griffiths, CEO and co-founder of Hone, explained to HR Dive. It covers four measurements:
- Reaction. Were workers actively engaged and participating in the program? Observation and reaction surveys can help with this metric.
- Actual learning. Did they come away from the session knowing more than they went in knowing? Baseline quizzes before and after give a snapshot of whether or not the session met objectives.
- Behavioral change. Are you seeing a change in the way people perform their work? If training isn't directly relatable and usable, this might be more difficult to quantify.
- Results. What is the final impact on the business overall following the training? Have errors decreased? Has productivity increased? Is customer satisfaction up? These measurements may take longer to quantify, but they're worthwhile metrics to obtain.
Ultimately, employers should keep an eye out for true measures of performance improvement, Anna Robinson, CEO of Ceresa, told HR Dive in an email. Sales growth, unit cost reductions and improved throughput are all examples of potential results. "If business performance improves, that means the right person is receiving the right content, and it is having an impact on their performance," she added.
But there are other ways to measure success, Ujjwal Gupta, co-founder and COO of BenchPrep, told HR Dive in an email. A learner getting that long-sought promotion or spreading knowledge in their department are key ways to witness a development program's success, Gupta said.
Changing minds and habits
What is the goal of training — changing minds or changing behaviors? Griffiths believes both are needed for a growth mindset, but one can lead to another.
"We can inspire change by giving learners the mental models, evidence and ways of thinking to start shifting their mindset, which can have a huge effect on behavior," he said. "For example, how differently do I behave if I believe I know everything and have nothing to learn from others, versus the mindset that I have something to learn from everyone?"
Employers should do more than just encourage learning, but should aspire to have a culture of learning, which enables employees to actively look for growth because learning is readily available and development is rewarded. For Griffiths, a successful learning culture is one that is open, aware and flexible. Ideally, there is a balance between dictating what the organization wants people to learn and giving the learners choice and control over what they learn to foster an employee-driven culture of learning, he noted.
Robinson said to look for engagement and buy-in. To gauge success of their mentoring program, for example, Ceresa looks at the number of women who are interested in continuing the relationship as well as the number who begin to mentor others. "This both extends and expands the learning culture," she said.
Has it made an impact?
Employees may be participating in learning exercises, but that doesn't necessarily translate to impact, experts warned. Knowledge can keep employees on track for what they need to be doing today, but it isn't enough on its own to ready them for new challenges or spark innovation. Seeing strong numbers on employee engagement surveys and significant changes in the way people work are key indicators, but the real goal is for employees to be hungry for more. Experts have noted that offering training outside workers' current areas of expertise and comfort zones can help push them further. Training that regards growth as the goal, whether or not it's of use at work today, can have the most impact on the employee and organization.
For Gupta, the numbers are important; evaluating retention and growth are leading indicators for those seemingly outside opportunities. "Seeing that you are not only keeping your employees happy, but that you are also expanding the business leads to a win-win situation by having a great learning culture that drives ROI," he said.
SOURCE: O'Donnell, R. (7 May 2019) "How do you know when learning programs are working?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrdive.com/news/how-do-you-know-when-learning-programs-are-working/554099/
Workforce Planning Will Help You Understand the Needs of Your Organization
How are you managing your workforce? Workforce planning is one of HR's most important priorities, but many HR professionals shy away from the task. Continue reading this post from SHRM to learn how workforce planning will help HR departments understand the needs of their organization.
Managing headcount—and workforce planning overall—is one of HR's most important priorities, yet so many HR and talent acquisition (TA) leaders shy away from it.
"Very few TA organizations do it, because it's a very analytical process that scares HR," said Jeremy Eskenazi, SHRM-SCP, managing principal of Riviera Advisors, a Long Beach, Calif.-based talent acquisition consulting and training company. "It's perceived to be outside of HR's expertise, and it involves inputs that come from outside HR's ownership."
In many organizations, headcount forecasting is understood to be a financial and budgeting exercise owned by finance, Eskenazi said. "But because the function of headcount is not perceived to be owned by HR, and finance doesn't make it a priority, nobody owns it in the end."
The TA function's failure to successfully predict talent gaps and prepare for hiring needs can be chalked up to a lack of experience with workforce planning, a lack of capacity to undertake it and not understanding its benefits, said John Vlastelica, founder and managing director of Recruiting Toolbox, a global management consulting and training firm in Seattle.
"Most TA leaders operate in a transactional environment and unfortunately see their jobs as purely a fulfillment function," he said. "TA is dealing with so much need that it can't help but be reactive. There's not enough time spent with the business, outlining hiring goals, conducting quarterly business reviews, updating turnover forecasts, reviewing talent composition, going over succession planning, or starting proactive sourcing conversations."
The organizations that win at talent acquisition are those that have a pipeline of talent ready to choose from when they need it, Eskenazi said. "The only way to have that ability is to know what is coming up. If you don't know what's coming up, you're operating on assumptions."
Workforce planning connects recruiting, hiring, employee development and talent management by identifying needed skills, helping recruiters target the right candidates with those skills and assisting managers in charting the internal pathways for employee growth.
"Workforce planning is not just about hiring new people; it's [also] about the gaps between what you currently have and what you need," Eskenazi said. "If you do it right, you can discover who is capable of stepping into new roles with training and development, and who may not be able to stay on in a job because the required skill sets are changing. Workforce planning is about all movement—up, down, in, out or across the organization."
Creating a Workforce Plan
The process begins with information gathering. "You simply need to interview managers of individual workgroups inside your organization and then consolidate and analyze that data," Eskenazi said. HR should be the facilitator of the process and everyone who leads people should participate, he said.
Vlastelica outlined a top-to-bottom approach to collect the information. He advised HR to sit in on executive-level discussions on overall growth and industry challenges. "At the middle level there is a lot of work to be done on forecasting for expected growth and backfills and which job families and roles are most critical," he said. To represent the bottom, "HR should talk with individual hiring managers and department leaders about their talent priorities and workforce composition," he said.
Eskenazi explained that HR should ask department heads a series of standard questions:
- How will the business impact you over the next six months? Twelve months? Twenty-four months?
- What skills do you need to meet your goals and how does current staff meet that need?
- Who is expected to be let go? Who is expected to remain? Who is getting promoted?
After gathering and tracking information about each department's talent inventory and their future talent requirements—using a spreadsheet or a workforce planning platform—it's time to conduct a gap analysis. Estimate what types of positions, people and competencies will be needed in the future to help the organization address talent gaps and then align necessary resources.
When presenting a final analysis to leadership, don't just repeat what you heard. Categorize the findings in a way that makes sense for talent acquisition, Vlastelica said.
"Forecasting is a little bit of science and a lot of art," he added. "It's a good opportunity to teach the business about how to think about talent acquisition, the ramp up time and resource cost to meet business need."
Be Flexible
Organizations looking to be more agile in a rapidly changing environment should engage in regular workforce planning updates, Eskenazi said. "All you have to do is create the framework once, then update it every six months. Once you do it one time in a comprehensive way, it's far easier than having to start from scratch."
The workforce planning team should reach out routinely for insights from department and business line leaders to update and modify the plan based on hiring needs.
"It needs to be very flexible, because oftentimes the business's priorities change, even in a short time," Eskenazi said. "The business is constantly resetting—and faster than ever before."
SOURCE: Maurer, R. (13 May 2019) "Workforce Planning Will Help You Understand the Needs of Your Organization" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/hr-topics/talent-acquisition/pages/workforce-planning-will-help-you-understand-organization-need.aspx
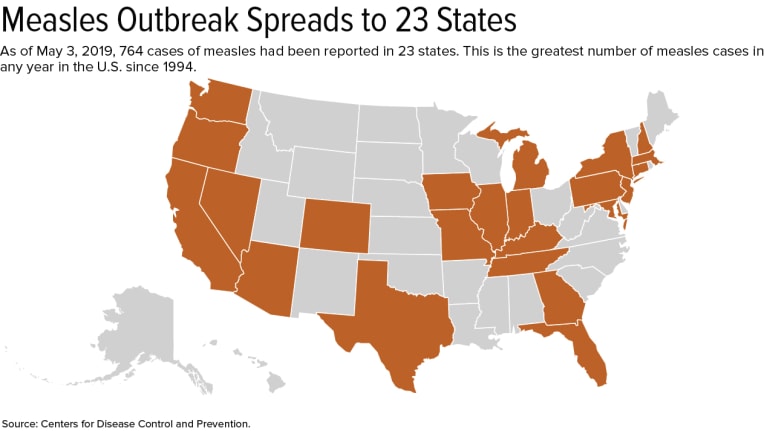
How to Respond to the Spread of Measles in the Workplace
How should employers respond to the spread of measles? With measles now at its highest number of cases in one year since 1994, employers are having to cooperate with health departments to fight the spread. Read this blog post from SHRM to learn more.
Employers and educators are cooperating with health departments to fight the spread of measles, now at its highest number of cases in one year since 1994: 764.
Two California universities—California State University, Los Angeles (Cal State LA) and the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA)—recently quarantined staff and students at the request of local health departments.
In April at Cal State LA, the health department told more than 600 students and employees to stay home after a student with measles entered a university library.
Also last month, UCLA identified and notified more than 500 students, faculty and staff who may have crossed paths with a student who attended class when contagious. The county health department quarantined 119 students and eight faculty members until their immunity was established.
The quarantines ended April 30 at UCLA and May 2 at Cal State LA.
Measles is one of the most contagious viruses; one measles-infected person can give the virus to 18 others. In fact, 90 percent of unvaccinated people exposed to the virus become infected, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes.
Action Steps for Employers
Once an employer learns someone in the workplace has measles, it should immediately send the worker home and tell him or her not to return until cleared by a physician or other qualified health care provider, said Robin Shea, an attorney with Constangy, Brooks, Smith & Prophete in Winston-Salem, N.C.
The employer should then notify the local health department and follow its recommended actions, said Howard Mavity, an attorney with Fisher Phillips in Atlanta. The company may want to inform workers where and when employees might have been exposed. If employees were possibly exposed, the employer may wish to encourage them to verify vaccination or past-exposure status, directing those who are pregnant or immunocompromised to consult with their physicians, he said.
Do not name the person who has measles, cautioned Katherine Dudley Helms, an attorney with Ogletree Deakins in Columbia, S.C. "Even if it is not a disability—and we cannot assume that, as a general rule, it is not—I believe the ADA [Americans with Disabilities Act] confidentiality provisions cover these medical situations, or there are situations where individuals would be covered by HIPAA [Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act]."
The employer shouldn't identify the person even if he or she has self-identified as having measles, Mavity noted.
Shea said that once the person is at home, the employer should:
- Inform workers about measles, such as symptoms (e.g., dry cough, inflamed eyes, tiny white spots with bluish-white centers on a red background in the mouth, and a skin rash) and incubation period—usually 10 to 12 days, but sometimes as short as seven days or as long as 21 days, according to the CDC.
- Inform employees about how and where to get vaccinations.
- Remind workers that relatives may have been indirectly exposed.
- Explain that measles exposure to employees who are pregnant or who might be pregnant can be harmful or even fatal to an unborn child.
- Explain that anyone born before 1957 is not at risk. The measles vaccine first became available in 1963, so those who were children before the late 1950s are presumed to have been exposed to measles and be immune.
Employers may also want to bring a health care provider onsite to administer vaccines to employees who want or need them, Shea said.
"Be compassionate to the sick employee by offering FMLA [Family and Medical Leave Act] leave and paid-leave benefit options as applicable," she said.
When a Sick Employee Comes to Work Anyway
What if an employee insists on returning to work despite still having the measles?
Mavity said an employer should inform the worker as soon as it learns he or she has the measles to not return until cleared by a physician, and violating this directive could result in discipline, including discharge. A business nevertheless may be reluctant to discipline someone who is overly conscientious, he said. It may opt instead to send the employee home if he or she returns before being given a medical clearance.
The employer shouldn't make someone stay out longer than is required, Helms said. Rely instead on the health care provider's release.
SOURCE: Smith, A. (9 May 2019) "How to Respond to the Spread of Measles in the Workplace" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/legal-and-compliance/employment-law/pages/how-to-respond-spread-measles-workplace.aspx
What to consider before adding a genetic testing benefit
According to recent statistics from the Society of Human Resource Management (SHRM), 18 percent of employers provide health-related genetic testing benefits. Read this blog post for what employers should consider before adding a genetic testing benefit to their benefits package.
As employers look for new voluntary benefits to help attract and retain employees, a growing number are turning to direct-to-consumer genetic testing for all employees to their benefits plans. According to the latest statistics from the Society for Human Resource Management, 18% of employers provide a health-related genetic testing benefit, an increase of 6% over the previous year.
For the most part, it can be a smart move: Not only can the benefit differentiate one employer from others vying to hire from the same employee pool, genetic testing providers market the benefit as a way to potentially lower healthcare costs and increase employee wellness.
This type of testing can be valuable for employees at an increased risk for certain types of cancer, such as breast and ovarian cancer related to mutations of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, those considering having a child who have risk factors for genetic conditions such as cystic fibrosis and Tay Sachs disease, those who have a family history of conditions like high cholesterol, and those who take medications such as blood thinners and anti-depressants. There also are tests that look for genes associated with conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and celiac disease.
But employers also have to realize that genetic testing for all employees, regardless of family history and risk factors, comes with potential downsides. In fact, some physicians believe that widespread genetic testing of this type may even present a risk of harm. There’s also the issue of regulation and oversight of direct-to-consumer genetic testing. The industry is not currently regulated, which, some researchers have found, can lead to inaccurate or varying results. One study found that when the same genetic variant was provided to nine different labs for analysis, the answers provided were different 22% of the time, highlighting the risk of false positive and false negative results.
So for employers who offer — or are considering adding — a genetic benefit, make sure to think about the potential outcomes that can occur by doing so.
The potential for lower costs as well as unnecessary healthcare spending
If an employee’s genetic test is positive for a mutation that’s associated with cancer or another disease, he or she may be more proactive about screening for the disease and may make lifestyle changes that may lower the risk of developing the disease. There are potential healthcare cost savings to early detection of some conditions. For example, by some estimates, the cost for treating early-stage breast cancer is more than 50% less than the cost to treat the same cancer at an advanced stage.
For employees who undergo testing related to how effective a blood thinner or antidepressant will be, there can be better health outcomes as well as cost savings. One study found that when physicians prescribed the blood thinner Warfarin based on pharmacogenomic testing, adverse events decreased by 27%. Avoiding adverse events and making sure employees are taking the medications that can most effectively treat their conditions can help keep them healthy, out of the hospital and productively on the job, all of which has a positive financial impact.
But when you’re screening people who don’t have risk factors or a family history of these conditions, a positive test result can lead to unnecessary testing and medical procedures, potential complications from those procedures and the costs associated with that testing and care.
Before and after testing, education
Employers who offer genetic testing without a physician referral need to take steps to ensure that employees understand the risks and benefits of these tests upfront and that they know what a genetic test can and cannot tell them about their health now and in the future. The first step is for any employer offering genetic testing to provide education for employees.
Many employees don’t realize that having a gene mutation that’s associated with a disease does not mean that he or she will ever develop that disease. The risk associated with most genetic variations is, in fact, relatively small. Because of that misunderstanding, employees may experience needless worry or, if the test is negative for mutations related to a disease, may forgo screenings like mammograms, colonoscopies and cholesterol tests that can help detect health problems earlier when they are often more treatable. In the case of genetic testing for mutations associated with cancer, employees may not be aware that most cancers are not caused by a mutation in the single gene that the test screens for.
For some of the conditions that genetic tests screen for, like Alzheimer’s disease, there are currently no treatments. This can again cause anxiety for employees and their families. Genetic tests also have implications that reach beyond the specific employee who is tested. A positive test can affect siblings and children as well, opening the question of whether the employee wants or feels compelled to share the results with other family members who may also be at risk.
Employers who offer employees genetic testing should ensure that all employees who choose to undergo testing are guided by experienced genetic counselors who can help them interpret and understand the results of their test and can connect them with other healthcare providers for additional testing or treatment as needed.
SOURCE: Varn, M. (3 May 2019) "What to consider before adding a genetic testing benefit" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/what-to-consider-before-adding-a-genetic-testing-benefit
Changes are coming to paid leave. Here’s what employers should know
Many states and local governments are enacting their own paid leave policies, making it difficult for employers to navigate employee paid leave. Read this blog post for what employers should know about the coming changes for paid leave.
A growing number of states and local governments are enacting their own paid leave policies. These new changes can be difficult for employers to navigate if they don’t understand the changes that are happening.
Adding to the confusion among employers, paid sick leave and paid family leave are often used interchangeably, when in fact there are some important distinctions. Paid sick leave is for a shorter time frame than paid family leave and allows eligible employees to care for their own or a family member’s health or preventative care. Paid family leave is more extensive and allows eligible employees to care for their own or a family member’s serious health condition, bond with a new child or to relieve family pressures when someone is called to military service.
The best-known type of employee leave is job-protected leave under the Family Medical Leave Act, where employees can request to take family medical leave for their own or a loved one’s illness, or for military caregiver leave. However, leave under FMLA is unpaid, and in most cases, employees may use available PTO or paid leave time in conjunction with family medical leave.
Rules vary by state, which makes it more difficult for multi-state employers to comply. The following is an overview of some new and changing state and local paid leave laws.
Paid sick leave
The states that currently have paid sick leave laws in place are Arizona, California, Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Oregon, Rhode Island, Vermont and Washington. There are also numerous local and city laws coming into effect across the country.
In New Jersey, the Paid Sick Leave Act was enacted late last year. It applies to all New Jersey businesses regardless of size; however, public employees, per diem healthcare employees and construction workers employed pursuant to a collective bargaining agreement are exempt. As of February 26, New Jersey employees could begin using accrued leave time, and employees who started after the law was enacted are eligible to begin using accrued leave 120 days after their hire dates.
Michigan’s Paid Medical Leave Act requires employers with 50 or more employees to provide paid leave for personal or family needs as of March.
Under Vermont’s paid sick leave law, this January, the number of paid sick leave hours employees may accrue rose from 24 to 40 hours per year.
In San Antonio, a local paid sick leave ordinance passed last year, but it may not take effect this August. The ordinance mirrors one passed in Austin that has been derailed by legal challenges from the state. Employers in these cities should watch these, closely.
Paid family leave
The five states that currently have paid family leave policies are California, New Jersey, Rhode Island, New York, Washington and the District of Columbia.

New York, Washington and D.C. all have updates coming to their existing legislation, and Massachusetts will launch a new paid family program for employers in that state. In New York, the state’s paid family leave program went into effect in 2018 and included up to eight weeks of paid family leave for covered employees. This year, the paid leave time jumps to 10 weeks. Payroll deductions to fund the program also increased.
Washington’s paid family leave program will begin on January 1, 2020, but withholding for the program started on January 1 of this year. The program will include 12 weeks of paid family leave, 12 weeks of paid medical leave. If employees face multiple events in a year, they may be receive up to 16 weeks, and up to 18 weeks if they experience complications during pregnancy.
The paid family leave program in Massachusetts launches on January 1, 2021, with up to 12 weeks of paid leave to care for a family member or new child, 20 weeks of paid leave for personal medical issues and 26 weeks of leave for an emergency related to a family member’s military deployment. Payroll deductions for the program start on July 1.
The Paid Leave Act of Washington, D.C. will launch next year with eight weeks of parental leave to bond with a new child, six weeks of leave to care for an ill family member with a serious health condition and two weeks of medical leave to care for one’s own serious health condition. On July 1, the district will begin collecting taxes from employers, and paid leave benefits will be administered as of July 1, 2020.
Challenging times ahead
An employer must comply with all state and local sick and family leave laws, and ignorance of a law is not a defense. Employers must navigate different state guidelines and requirements for eligibility no matter how complex, including multi-state employers and companies with employees working remotely in different jurisdictions.
These state paid leave programs are funded by taxes, but employers must cover the costs of managing the work of employees who are out on leave. While generous paid leave policies can help employers attract talent, they simply don’t make sense for all companies. For example, it can be difficult for low-margin businesses to manage their workforces effectively when employees can take an extended paid leave.
Not only must employers ensure compliance with state and local rules, but they also must make sure that their sick time, family and parental leave policies are non-discriminatory and consistent with federal laws and regulations. That’s a lot to administer.
Employers should expect to see the changes in paid sick leave and family leave laws to continue. In the meantime, companies should make sure they have the people and internal processes in place right now to track these changes and ensure compliance across the board.
SOURCE: Starkman, J.; Johnson, D. (2 May 2019) "Changes are coming to paid leave. Here’s what employers should know" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/what-employers-need-to-know-about-changing-paid-leave-laws?brief=00000152-14a7-d1cc-a5fa-7cffccf00000
Employers Must Report 2017 and 2018 EEO-1 Pay Data
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) is requiring that all employers report their pay data, broken down by race, sex and ethnicity, from 2017 and 2018 by September 30. Continue reading this post from the SHRM to learn more.
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) has announced that employers must report pay data, broken down by race, sex and ethnicity, from 2017 and 2018 payrolls. The pay data reports are due Sept. 30.
Employers had been waiting to learn what pay data they would need to file—if any at all—as litigation on the matter ensued. A federal judge initially ordered the EEOC to collect employee pay data for 2018. The National Women's Law Center (NWLC) and other plaintiffs wanted the EEOC to collect two years of data, as the agency was supposed to under a new regulation before the government halted the collection in 2017.
Judge Tanya Chutkan of the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia sided with the plaintiffs and gave the EEOC the option of collecting 2017 pay data along with the 2018 information by the Sept. 30 deadline or collecting 2019 pay data during the 2020 reporting period. The EEOC opted to collect the 2017 data.
The agency said it could make the collection portal available to employers by mid-July and would provide information and training to employers prior to that date.
Immediate Steps
"We are awaiting confirmation from the EEOC or the contractor it is hiring to facilitate the pay-data collection on how to lay out the data file for a batch upload," said Alissa Horvitz, an attorney with Roffman Horvitz in McLean, Va.
But employers should take some steps immediately. They should reach out to their subject-matter and technical experts and pull together resources to ensure that the required data components can be captured, analyzed and reported by Sept. 30, said Annette Tyman, an attorney with Seyfarth Shaw in Chicago.
Filing the additional reports will impose unanticipated burdens for HR, IT and legal departments, as well as third-party consultants, she noted. "It is unclear whether any further litigation options will impact the Sept. 30 deadline, and we are instructing employers to assume they must comply."
Employers should keep in mind that they still must submit their 2018 data for Component 1 of the EEO-1 form by May 31, unless they request an extension. Note that the EEOC recently shortened the extension period for employers to report Component 1 data from 30 days to two weeks. So the extension deadline is now June 14.
Component 1 asks for the number of employees who work for the business by job category, race, ethnicity and sex. Component 2 data—which includes hours worked and pay information from employees' W-2 forms by race, ethnicity and sex—is the subject of the legal dispute.
Data Collection
Businesses with at least 100 employees and federal contractors with at least 50 employees and a contract with the federal government of $50,000 or more must file the EEO-1 form. The EEOC uses information about the number of women and minorities companies employ to support civil rights enforcement and analyze employment patterns, according to the agency.
The revised EEO-1 form will require employers to report wage information from Box 1 of the W-2 form and total hours worked for all employees by race, ethnicity and sex within 12 proposed pay bands.
The reported hours worked should show actual hours worked by nonexempt employees and an estimated 20 hours per week for part-time exempt employees and 40 hours per week for full-time exempt employees.
"Filling out the added data in the EEO-1 form will present a large amount of work, especially as there's great potential for human error when populating the significantly expanded form," said Arthur Tacchino, J.D., chief innovation officer at SyncStream Solutions, which provides workplace compliance solutions.
Employers should start looking at their data now and conduct an initial assessment of their systems, said Camille Olson, an attorney with Seyfarth Shaw in Chicago. Identify the systems that house the relevant demographic, pay and hours-worked data and determine how to pull the information together, she said.
Pulling EEO-1 data is much simpler for Component 1, she noted, because it only involves reporting the employer's headcount by race, ethnicity and sex—whereas collecting pay information involves more data points. Additionally, employers may use different vendor systems at different locations, some employees may have only worked for part of the year, and other employees may have been reclassified to exempt or nonexempt.
"Employers may want to inquire with their current vendors—payroll or otherwise—or look for outside vendors that may be able to assist them with this reporting requirement," Tacchino said.
Under some circumstances, employers may be able to seek an exemption (at the EEOC's discretion) if filing the information would cause an undue burden. "Mega employers" may not be able to show an undue burden, but this could be an option for smaller businesses, said Jim Paretti, an attorney with Littler in Washington, D.C. But that will depend on how the parties decide to move forward.
The Court Battle
The EEO-1 form was revised during President Barack Obama's administration to add the Component 2 data, but the pay-data provisions were suspended in 2017 by President Donald Trump's administration. The NWLC challenged the Trump administration's hold on the pay-data collection provisions, and on March 4, Chutkan lifted the stay—meaning the federal government needed to start collecting the information.
On March 18, however, the EEOC opened the portal for employers to submit EEO-1 reports without including the pay-data questions. Chutkan subsequently told the government to come up with a plan.
The EEOC proposed the Sept. 30 deadline for employers to submit Component 2 data, claiming that the agency needed more time to address the associated collection challenges. Furthermore, the EEOC's chief data officer warned that rushing the data collection may yield poor quality data. Even with the additional time, the agency said it would need to spend more than $3 million to hire a contractor to provide the appropriate procedures and systems.
Robin Thurston, an attorney with Democracy Forward and counsel for the plaintiffs, said at an April 16 hearing that the plaintiffs don't want the agency to compromise quality. But they also wanted "sufficient assurances" that the EEOC will collect the data by Sept. 30.
On April 25, Chutkan ordered the government to provide the court and the plaintiffs with periodic updates on the EEOC's progress and to continue collection efforts until a certain threshold of employer responses has been received.
SOURCE: Nagele-Piazza, L. (2 May 2019) "Employers Must Report 2017 and 2018 EEO-1 Pay Data" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/legal-and-compliance/employment-law/pages/eeo-1-pay-data-report-2017-2018.aspx
Can Employers Require Measles Vaccines?
Can employers require that their employees get the measles vaccine? The recent measles outbreak is raising the question of whether employers can require that their workers get the vaccine. Read this blog post from SHRM to learn more.
The recent measles outbreak, resulting in mandatory vaccinations in parts of New York City, raises the question of whether employers can require that workers get the vaccine to protect against measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) or prove immunity from the illness.
The answer generally is no, but there are exceptions.
Offices and manufacturers probably can't require vaccination or proof of immunity because the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) generally prohibits medical examinations—unless the employer is in a location like Williamsburg, the neighborhood in Brooklyn where vaccinations are now mandatory. Health care providers, schools and nursing homes, however, probably can require them because their employees work with patients, children and people with weak immune systems who risk health complications from measles.
But even these employers must try to find accommodations for workers who object to vaccines for a religious reason or because of a disability that puts them at risk if they're vaccinated, such as having a weak immune system.
Proof of Immunity
Proof of immunity includes one of the following:
- Written documentation of adequate vaccination.
- Laboratory evidence of immunity.
- Laboratory confirmation of measles.
- Birth before 1957. The measles vaccine first became available in 1963, so those who were children before the late 1950s are presumed to have been exposed to measles and be immune.
Measles, which is contagious, typically causes a high fever, cough and watery eyes, and then spreads as a rash. Measles can lead to serious health complications, especially among children younger than age 5. One or two out of 1,000 people who contract measles die, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
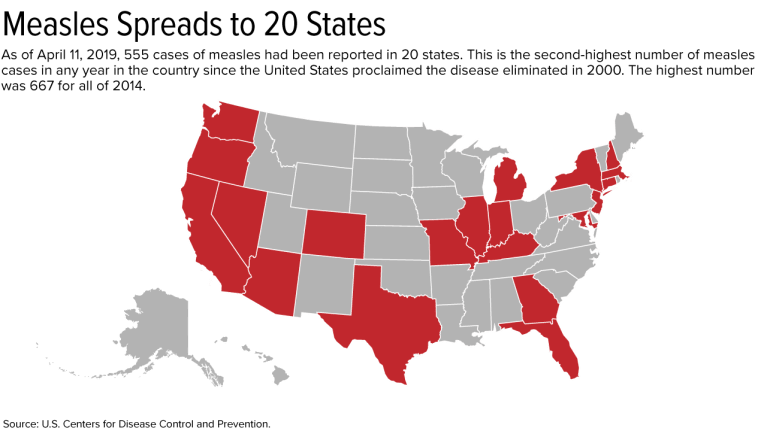
Outbreak Has Spread to 20 States
As of April 11, 555 cases have been reported in the United States this year. This is the second-greatest number in any year since the United States proclaimed measles eliminated in 2000; 667 cases were reported in all of 2014.
On April 9, New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio declared a public health emergency in Williamsburg, requiring the MMR vaccine in that neighborhood. Those who have not received the MMR vaccine or do not have evidence of immunity may be fined $1,000.
Since the outbreak started, 285 cases have been confirmed in Williamsburg, including 21 hospitalizations and five admissions to intensive care units.
If a city requires vaccinations, an employer's case for requiring them is much stronger, said Robin Shea, an attorney with Constangy, Brooks, Smith & Prophete in Winston-Salem, N.C. But employers usually should not involve themselves in employees' health care unless they are making an inquiry related to a voluntary wellness program, or the health issue is job-related, she cautioned.
The measles outbreak has spread this year to 20 states—outbreaks linked to travelers who brought measles to the U.S. from other countries, such as Israel, Ukraine and the Philippines, where there have been large outbreaks.
Strike the Right Balance
Health care employers typically require vaccinations or proof of immunity as a condition of employment, said Howard Mavity, an attorney with Fisher Phillips in Atlanta. He noted that most schoolchildren must be immunized, so many employees can show proof of immunity years later.
If an employee provides current vaccination records when an employer asks, the ADA requires that those records be kept in separate, confidential medical files, noted Meredith Shoop, an attorney with Littler in Cleveland.
All employers must balance their health and safety concerns with the right of employees with disabilities to reasonable accommodations under the ADA and the duty to accommodate religious workers under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
Under the ADA, a reasonable accommodation is required unless it would result in an undue hardship or direct threat to the safety of the employee or the public. The direct-threat analysis will be different for a registered nurse than for someone in a health care provider's billing department, for example, who might not work around patients.
Even if the ADA permitted mandatory vaccines in a manufacturing setting in limited circumstances, such as in Williamsburg now, any vaccination orders may need to be the subject of collective bargaining if the factory is unionized. Shoop has seen manufacturers shut down because employees were reluctant to come to work when their co-workers were sick on the job.
An employer does not have to accommodate someone who objects to a vaccine merely because he or she thinks it might do more harm than good but doesn't have an ADA disability or religious objection, said Kara Shea, an attorney with Butler Snow in Nashville, Tenn.
If someone claims to have a health condition that makes getting vaccinated a health risk, the employer does not have to take the person's word for it. The employer instead should ask the person to sign a consent form allowing the employer to learn about the condition and get documentation from the employee's doctor, she said. Before accommodating someone without an obvious impairment, the ADA allows employers to require medical documentation of the disability.
Courts don't closely scrutinize religious objections to immunizations, Mavity remarked.
"Some people have extremely strong beliefs that they don't want a vaccine in their body," said Kathy Dudley Helms, an attorney with Ogletree Deakins in Columbia, S.C. If the employer works with vulnerable people but can't find an accommodation for a worker who refuses vaccination, the employee may have to work elsewhere, she said.
SOURCE: SHRM (17 April 2019) "Can Employers Require Measles Vaccines?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/legal-and-compliance/employment-law/pages/measles-outbreak-2019-vaccinations.aspx
Getting employees up to speed with health literacy
Do your employees know how much sugar is in a granola bar or how much radiation is in a CT scan? If not, it's most likely because no one is teaching them. Continue reading to learn more on getting your employees up to speed with health literacy.
Your employees probably don’t know how much sugar is in a granola bar or how much radiation is in a CT scan. They may not even know how to reach your employee assistance program.
That’s because no one is teaching them. Which is what happens when wellness program education ends at eat more fruits and vegetables and avoid added sugar.
Sometimes the advice is even wrong. For example, below is a clipping from a popular health risk assessment. Focus on the lower right quadrant.

It isn’t entirely true that low-fat and nonfat dairy is healthier. In fact, full fat dairy does have health benefits, for example some studies suggest it could help protect against diabetes. By comparison, low-fat or nonfat yogurt could be a significant source of sugar.
This is why employee health literacy is so important. With easy access to mis-information, employees need to learn to sift through the noise to determine what is actually good for them.
Plus, there is plenty to learn. Spanning from everyday health, employee medical education and health benefits literacy. I’ve outlined just a few of the ways to employers can better educate their population.
Everyday health education
Sugar is one place where health education could be more impactful — but it should go beyond just telling workers to avoid added sugars. Education starts at work. Chances are your break room is stocked with granola bars, maybe Clif Bars. The first ingredient in a Clif Bar is organic brown rice syrup. That may sound healthy, but it’s really just sugar. In fact, there are almost 60 different sugars disguised with fancy names like turbinado or malted barley extract.
Another example is sleep. We all want employees to get enough of it, but do they know how? They may not know little bits of information that could help them get more shuteye, like there is a night shift setting on their iPhone or that energy-efficient light bulbs contribute to insomnia.
But teaching everyday health is just the beginning of health literacy. The real impact comes with employee medical education.
Employee medical education
U.S. consumers are voracious purchasers of healthcare services and yet our outcomes remain poor. Americans have about 240 CT scans per 1,000 people. To put that in perspective, only about 1 in 1,000 covered people in your employee population was hospitalized for diabetes last year. So 240 times more employees are getting scans than uncontrolled diabetes.
CT scans have risks. They have about 500 times the radiation of an x-ray and are especially concerning for children because their cells are dividing more rapidly than adults and are more sensitive to radiation exposure. The dye used intravenously also carries a risk.
But many employees don’t know about these risks. So it may be important to educate your workforce about these common medical procedures and how to decide whether or not it is right for them.
Health benefit education
Here’s a wild guess: your employees don’t appreciate the health benefits you provide for them. If so, you’ve got company. Most large organizations face the same issue.
Consider the employee assistance program. Do workers know you offer one? Do they know it’s confidential? They know their emails aren’t confidential, so don’t assume they know this. Do they know the URL, username and password? How many free sessions do they get?
Repeat a similar set of questions for all your benefits. You can’t expect that some memos and a website will implant your benefits firmly in their mind.
SOURCE: Lewis, A. (25 April 2019) "Getting employees up to speed with health literacy" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/educating-employees-through-health-literacy
Think your employee is faking sickness? Here’s what you can do
Have your employees misused their FMLA leave before? Navigating FMLA can be tricky, leading to costly lawsuits if a wrong move is taken. Continue reading this blog post to learn more about handling FMLA misuse.
Your employee’s gout flared up, so they took the day off using intermittent medical leave. Later on, a photo of the same employee sliding into home base surfaces on social media that day. How do you find out if the employee was misusing FMLA leave?
Bryon Bass, senior vice president of workforce absence at Sedgwick — a business solution tech company — says navigating FMLA can be tricky, and the wrong move can provoke costly lawsuits. But if an employer has reason to believe the absence isn’t valid, Bass says there’s a process they can follow to investigate.
“I think [a social media photo] casts doubt on the reason for their absence,” Bass said during a recent webinar hosted by the Disability Management Employer Coalition. “It merits a second look, along with some potential code of conduct talks with HR.”
When a questionable situation arises, employers can ask for the worker’s approved medical condition to be recertified, Bass said. This involves having the employee resubmit their original FMLA application. Afterward, employers can send a list of absences to the employee’s healthcare provider to authenticate the dates as valid medical absences. Typically, employers can only request recertification after a 30 day period, unless there’s reason to believe the employee is taking advantage of the system.
“If, for example, you notice two employees — who happen to be dating — are taking off the same days for their different medical conditions, that’s a valid reason for asking for recertification,” Bass said. “Patterns of absence are a common reason to look into it.”
Instead of requesting recertification, some employers make the mistake of contacting the employee’s physician directly — a process called clarification. Employers are only allowed to use clarification during the initial FMLA application, and only after obtaining the employee’s permission. Clarification is used to answer employer questions about the amount of rest an employee’s condition merits.
Employers might not trust the opinion of their employee’s doctor, but they can’t ask for a second opinion until it’s time for the employee to re-submit their annual certification, Bass says. When that time comes, employers can appoint a physician to reexamine the employee at the company’s expense. If the employee objects to the second doctor’s report, a third opinion can be sought.
“With third opinions, both the employer and the employee have to agree on the provider because their decision is final,” Bass said. “Employers are also required to cover this expense.”
Although employers are within their right to file recertification, Bass says it should be done sparingly and in situations where evidence suggests misuse. An employee using slightly more time for recovery isn’t automatically abusing the policy, he said.
“FMLA does not permit healthcare providers to provide an exact schedule of leave, just an estimate of absences necessary for the employee’s treatment and recovery,” Bass said. “Treatments are more predictable, but it’s still only an estimate. If someone takes a little more time than estimated, it doesn’t mean you need to ask for recertification; in fact, the Department of Labor discourages that.”
SOURCE: Webster, K. (24 April 2019) "Think your employee is faking sickness? Here’s what you can do" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/news/how-to-certify-medical-leave-and-handle-pto-requests?feed=00000152-a2fb-d118-ab57-b3ff6e310000