Health Care Sector Earnings: Major Companies Open The Books On Q3 Results In Weeks Ahead

Photo Credit: Shutterstock
The health care sector has been one of the better-performing sectors in 2017, bouncing back after being the only sector in the S&P 500 to finish last year in the red. So far this year, the S&P Health Care Select Sector Index is outperforming the S&P 500 by 5.75% as of October 6.
The sector got a bump recently when Republicans’ released an initial framework for tax reform, with CNBC pointing out that some of the largest companies in the health care sector could be primary beneficiaries of the proposed repatriation tax break. For the sector’s upcoming earnings, analyst estimates are calling for low to mid-single-digit growth for both earnings and revenue.
Within the S&P 500, the health care sector is expected to report year-over-year revenue growth of 4.8% and earnings growth of 2.5%, according to FactSet, with profit margins estimated to decline from 10.3% to 10.1% across the sector. Those estimates are slightly below the sector’s estimated revenue and earnings growth rates expected for the full year.
Beyond the proposed tax reform, below we’ll take a look at what’s been happening in the sector as companies prepare to report earnings in the upcoming weeks.
 thinkorswim
thinkorswimAfter underperforming by a large margin in 2016, the health care sector has been recovering in 2017. The S&P Health Care Select Sector Index, charted above, is up 18.49% year-to-date, compared to a 12.74% increase in the S&P 500, the teal line. The Nasdaq Biotechnology Index, the purple line, has outperformed both and climbed 25.6% year-to-date. Chart source: thinkorswim® by TD Ameritrade. Data source: Standard & Poor’s. Not a recommendation. For illustrative purposes only. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Biotech Industry Outperforming
So far this year, the biotechnology industry has outpaced the broader health care sector, with the Nasdaq Biotechnology Index up 25.6% versus a 18.49% increase in the S&P Health Care Select Sector Index. However, looking at 2016, the Nasdaq Biotechnology Index fared far worse than the S&P Health Care Select Sector Index, declining 22.01% when the latter only declined 4.37%.
Stocks in the biotech industry are notoriously volatile and it can take many years, even decades, for a company to undergo research and development, and the clinical trial process. A 2014 study by Tufts University’s Center for the Study of Drug Development found that only 11.8% of drugs that enter clinical trials end up being approved by the FDA.
Washington on Health Care
Drug pricing scrutiny has been an ongoing focus in Congress, but there’s yet to be concrete legislation pushed forward to address the issue. Dr. Scott Gottlieb, the head of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), recently said high drug prices are a “public health concern” and in a post on the FDA’s official blog, outlined several steps the agency is taking to make the generic approval process for complex drugs easier.
On October 17, the Senate Health Committee is scheduled to hold a second hearing as part of its investigation into high drug prices. Representatives from drug company and pharmacy benefit managers—essentially middle men between pharmacies and drug companies—have been invited to speak before the panel. Depending on how that hearing goes, there could be heightened volatility in healthcare stocks.
Due to the costly process of developing drugs, companies often go to great lengths to protect patents. Those practices have also started to come into scrutiny in Congress as well. Allergan announced last month it had transferred the patent rights for its drug Restasis to the St. Regis Mohawk Indian Nation, which would license them back to Allergan in exchange for ongoing payments to the tribe.
The tribe’s sovereign immunity would potentially shield the drug from certain patent reviews. “Allergan has argued that the legal maneuver is aimed at removing administrative patent challenges through inter partes review by the U.S. Patent Trial and Appeal Board, and not challenges in federal court”, according to Reuters.Shortly after Allergan transferred the patent rights, U.S. Senator Claire McCaskill quickly announced she had drafted a bill to prevent tribal sovereign immunity from being used to block U.S. Patent and Trademark Office review of a patent in response to the move.
Aging Demographics and More Disease as Population Grows
There are some trends that analysts anticipate to be tailwinds for the sector for years to come. One of them is aging demographics and the other is growth of certain diseases. Approximately 10,000 baby boomers turn 65 every day, according to Pew Research, and that trend is expected to continue until 2030, when the last of the boomers reach retirement age and roughly 18% of the U.S. population is projected to be 65 and older.
As world populations grow and age, certain diseases are expected to have a greater prevalence than others and a large portion of health care spending is likely to go towards them. By 2020, Deloitte projects that 50% of global health care expenditures, about $4 trillion, will be spent on cardiovascular diseases, cancer and respiratory diseases.
These trends could be a tailwind for healthcare companies, but at the same time a lot could change in the regulatory environment as well as with the treatments available in the years ahead.
Looking Ahead to Earnings
The first major company in the sector to report earnings is Johnson & Johnson, which will release results before market open on Tuesday, October 17. The following companies report later in the month: Eli Lilly & Co. before market open on Tuesday, October 24, Gilead Sciences after market close on Thursday, October 26, Merck before market open on Friday, October 27 and Pfizer before market open on Tuesday, October 31.
You can read the original article here.
Source:
Kinahan J. (10 October 2017). "Health Care Sector Earnings: Major Companies Open The Books On Q3 Results In Weeks Ahead" [Web Blog Post]. Retrieved from address https://www.forbes.com/sites/jjkinahan/2017/10/10/health-care-sector-earnings-major-companies-open-the-books-on-q3-results-in-weeks-ahead/#417bef6a44bb
Saxon Welcomes a New Senior Solutions Specialist
Saxon is excited and proud to announce a new employee added to our team, Leigh Rathje!

Leigh’s background in group health insurance has led her to a new path with Saxon as a Senior Advisor. She helps her clients in the day to day needs when it comes to Medicare questions, enrollments, claims issues, and billing concerns.
Self funded health care – a big business advantage
Check out this article from Business Insurance by one of their staff writers. In this article, Business Insurance dives into the awesome advantages of self-funding for big businesses.
You can read the original article here.
Health insurance benefits are expensive. The rising costs of health care has driven up insurance premiums to levels where many businesses have been forced to reduce these benefits or drop them altogether. There is, however another option that is less regulated, taxed less and typically results in cost savings: self funded health insurance. The problem is, it's not always the best option for all employers, particularly the smaller ones. And there's a number of reasons for this:
What is self funded health care a.k.a. self-insurance?
Self-insurance is a method of providing health care to employees by taking on the financial liabilities of the care instead of paying premiums to an insurance agency to do the same. In other words: when a person covered under a self-funded plan needs medical care, the company is financially responsible for paying the medical bill (minus deductibles). It's an alternative risk transfer strategy that assumes the risk and liability of medical bills for those covered instead of outsourcing it to a third party. It's a surprisingly common practice:
In 2008, 55% of workers with health benefits were covered by a self-insured plan….and 89% of workers in firms of 5,000 or more employees.
Most (but not all) self-insurance plans are administered by a third party, usually a health insurance company, in order to process claims. The bills are simply paid for by the employer. Health insurance companies act as a third party administrators in what are called ASO contracts (Administrative Services Only)
Another common component of self insurance plans is stop-loss insurance. This is a separate insurance plan that the employer can purchase to reduce the overall liability of claims. With this type of insurance, if claims exceed a certain dollar amount, stop-loss kicks in paying the rest. There are two kinds of stop-loss insurance:
Specific – covers the excess costs from larger claims made by individuals in the group
Aggregate – kicks in when total claims by the group exceed a set amount
For example, a company who self-insures their $1000 employees projects $100,000 in medical care claims for the year. If they purchase aggregate stop-loss insurance for claims that exceed 120% of the expected amount or $120,000, the insurance will pick up the bill for the remaining claims. If the company purchases specific stop-loss insurance at 200%, if any single claim exceeds $2,000, the stop-loss pays the remainder.
Typically, self-funded insurance providers will purchase both specific and aggregate stop-loss insurance unless the conditions are such that specific stop-loss provides enough financial protection.
Benefits of self-insurance
There are a number of financial and administrative advantages to using self-funded health insurance plans for employers. According to the Self-Insurance Institute of America (SIIA) these include:
- The employer can customize the plan to meet the specific health care needs of its workforce, as opposed to purchasing a 'one-size-fits-all' insurance policy.
- The employer maintains control over the health plan reserves, enabling maximization of interest income – income that would be otherwise generated by an insurance carrier through the investment of premium dollars.
- The employer does not have to pre-pay for coverage, thereby providing for improved cash flow.
- The employer is not subject to conflicting state health insurance regulations/benefit mandates, as self-insured health plans are regulated under federal law (ERISA).
- The employer is not subject to state health insurance premium taxes, which are generally 2-3 percent of the premium's dollar value.
- The employer is free to contract with the providers or provider network best suited to meet the health care needs of its employees.
There are, however, some drawbacks to self-insurance policies:
Health care can be costly, so heavy claims years can be extremely expensive
Self insurance isn't tax deductible the same way the costs of providing health insurance is.
Financial benefits are long-term, particularly with an investment component.
Small businesses at a disadvantage
Self insurance is much more prevalent for larger companies mostly because it is easier to predict health care costs from a larger group. The more people in the group, the less potentially damaging a single expensive claim will be to the plan overall. That's why less than 10% of companies with less than 50 employees use self-insurance.
Because risk is more difficult to predict with smaller groups, stop-loss insurance is also more expensive for smaller businesses. The practice of “lasering”, or increasing deductibles for specific higher risk employees can also be much tougher on small firms. As a result, self-insurance tends to be a less cost effective option than it is for larger companies.
Another roadblock for small businesses is a lack of cash-flow that is necessary to finance self-insurance. This doesn't mean, however, that small businesses can't benefit from a self-insurance plan. In fact, an increasing number of small businesses still are. But fully understanding the risks and rewards for doing so can sometimes be difficult.
Regulations
Because the only 3rd party administration of insurance (stop-loss) is between the employer and the insurance company directly, it is not subject to state level regulation the way traditional insurance policies are. Instead, they're regulated by the department of labor under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act – ERISA. Benefit administrators must still comply with federal standards despite the lack of state regulation.
California SB 1431
California is considering a proposed legislation to regulate the sale of stop-loss policies to smaller businesses. On the surface, the regulation looks as though it is an attempt to prevent small businesses from taking on too much risk. But the true intentions of the legislation may be to prevent cherry-picking of generally healthier small businesses (effectively removing them from the health insurance pool). This cherry-picking would theoretically cause traditional insurance premiums to become more expensive.
According to the SIIA, SB 1431 would prohibit the sale of stop-loss policies to employers with fewer than 50 employees that does any of the following:
- Contains a specific attachment point that is lower than $95,000;
- Contains an aggregate attachment point that is lower than the greater of one of the following:
- $19,000 times the total number of covered employees and dependents;
- 120% of expected claims;
- $95,000
This legislation would effectively limit the options of small businesses as it would force them to purchase a more expensive low deductible stop-loss policies. And according to the SIIA, with this legislation, almost no small business under 50 employees would (nor should they) consider self-insurance as an option.
If the legislation is passed in California, it has been suggested that it is only time before other states follow suit and/or enact even stricter regulations on small businesses. The SIIA even has a facebook page dedicated to defeating the bill they say is:
“…unnecessary and will only exasperate the problem that small employers in California face in being able to afford the rising cost of providing quality health benefits to their employees.”
So while self insurance can be a relatively risky option for small businesses, with legislation like this, it could no longer be a realistic option at all… And, in effect: another competitive advantage big businesses will have over their smaller counterparts.
You can read the original article here.
Source:
Staff Writer. (Date Unlisted). "Self funded health care – a big business advantage" [Web Blog Post]. Retrieved from address https://www.businessinsurance.org/self-funded-health-care-a-big-business-advantage/
The Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Benefit
Below we have an article from the Kaiser Family Foundation providing detailed information and graphics on the benefit of the Medicare Prescription Drug Plan.
You can read the original article here.
Medicare Part D is a voluntary outpatient prescription drug benefit for people on Medicare that went into effect in 2006. All 59 million people on Medicare, including those ages 65 and older and those under age 65 with permanent disabilities, have access to the Part D drug benefit through private plans approved by the federal government; in 2017, more than 42 million Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Part D plans. During the Medicare Part D open enrollment period, which runs from October 15 to December 7 each year, beneficiaries can choose to enroll in either stand-alone prescription drug plans (PDPs) to supplement traditional Medicare or Medicare Advantage prescription drug (MA-PD) plans (mainly HMOs and PPOs) that cover all Medicare benefits including drugs. Beneficiaries with low incomes and modest assets are eligible for assistance with Part D plan premiums and cost sharing. This fact sheet provides an overview of the Medicare Part D program and information about 2018 plan offerings, based on data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and other sources.
Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Availability in 2018
In 2018, 782 PDPs will be offered across the 34 PDP regions nationwide (excluding the territories). This represents an increase of 36 PDPs, or 5%, since 2017, but a reduction of 104 plans, or 12%, since 2016 (Figure 1).
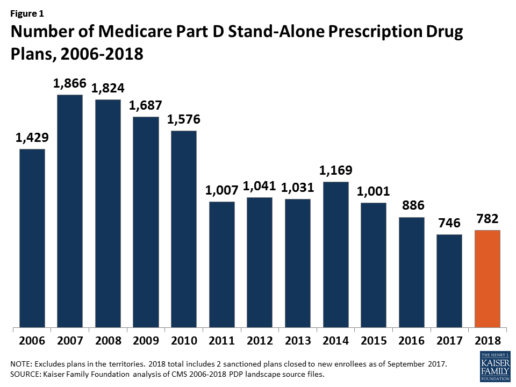
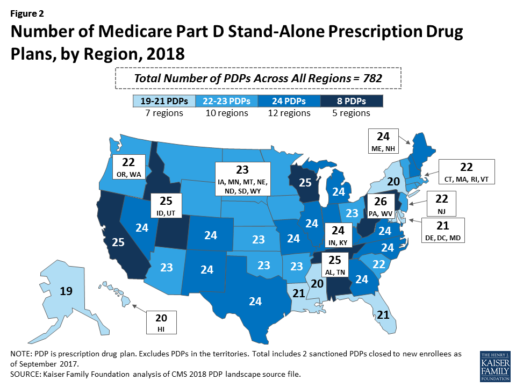
Beneficiaries in each state will continue to have a choice of multiple stand-alone PDPs in 2018, ranging from 19 PDPs in Alaska to 26 PDPs in Pennsylvania/West Virginia (in addition to multiple MA-PD plans offered at the local level) (Figure 2).
Low-Income Subsidy Plan Availability in 2018
Through the Part D Low-Income Subsidy (LIS) program, additional premium and cost-sharing assistance is available for Part D enrollees with low incomes (less than 150% of poverty, or $18,090 for individuals/$24,360 for married couples in 2017) and modest assets (less than $13,820 for individuals/$27,600 for couples in 2017).1
In 2018, 216 plans will be available for enrollment of LIS beneficiaries for no premium, a 6% decrease in premium-free (“benchmark”) plans from 2017 and the lowest number of benchmark plans available since the start of the Part D program in 2006. Roughly 3 in 10 PDPs in 2018 (28%) are benchmark plans (Figure 3).
Low-Income Subsidy Plan Availability in 2018
Through the Part D Low-Income Subsidy (LIS) program, additional premium and cost-sharing assistance is available for Part D enrollees with low incomes (less than 150% of poverty, or $18,090 for individuals/$24,360 for married couples in 2017) and modest assets (less than $13,820 for individuals/$27,600 for couples in 2017).1
In 2018, 216 plans will be available for enrollment of LIS beneficiaries for no premium, a 6% decrease in premium-free (“benchmark”) plans from 2017 and the lowest number of benchmark plans available since the start of the Part D program in 2006. Roughly 3 in 10 PDPs in 2018 (28%) are benchmark plans (Figure 3).
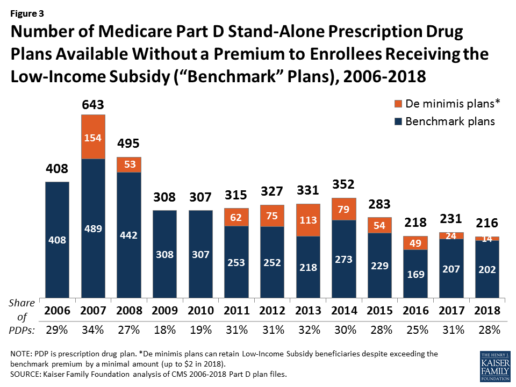
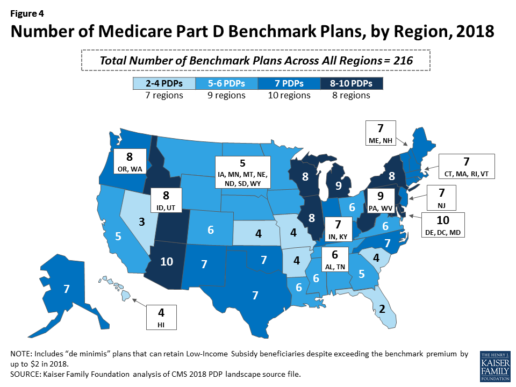
Benchmark plan availability varies at the Part D region level, with most regions seeing a reduction of 1 benchmark plan for 2018 (Figure 4). The number of premium-free plans in 2018 ranges from a low of 2 plans in Florida to 10 plans in Arizona and Delaware/Maryland/Washington D.C.
Part D Plan Premiums and Benefits in 2018
Premiums. According to CMS, the 2018 Part D base beneficiary premium is $35.02, a modest decline of 2% from 2017.2 Actual (unweighted) PDP monthly premiums for 2018 vary across plans and regions, ranging from a low of $12.60 for a PDP available in 12 out of 34 regions to a high of $197 for a PDP in Texas.
Part D enrollees with higher incomes ($85,000/individual; $170,000/couple) pay an income-related monthly premium surcharge, ranging from $13.00 to $74.80 in 2018 (depending on their income level), in addition to the monthly premium for their specific plan.3 According to CMS projections, an estimated 3.3 million Part D enrollees (7%) will pay income-related Part D premiums in 2018.
Benefits. In 2018, the Part D standard benefit has a $405 deductible and 25% coinsurance up to an initial coverage limit of $3,750 in total drug costs, followed by a coverage gap. During the gap, enrollees are responsible for a larger share of their total drug costs than in the initial coverage period, until their total out-of-pocket spending in 2018 reaches $5,000 (Figure 5).
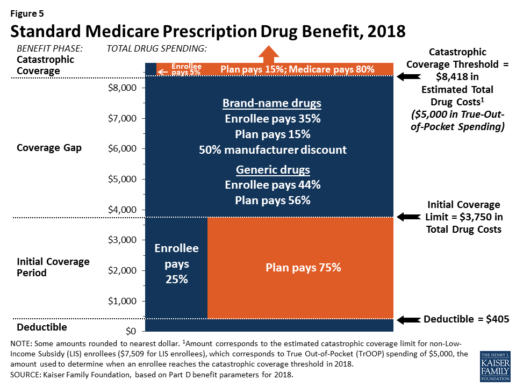
After enrollees reach the catastrophic coverage threshold, Medicare pays for most (80%) of their drug costs, plans pay 15%, and enrollees pay either 5% of total drug costs or $3.35/$8.35 for each generic and brand-name drug, respectively.
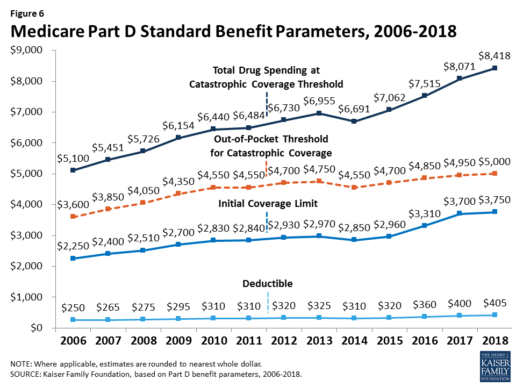
The standard benefit amounts are indexed to change annually by rate of Part D per capita spending growth, and, with the exception of 2014, have increased each year since 2006 (Figure 6).
Part D plans must offer either the defined standard benefit or an alternative equal in value (“actuarially equivalent”), and can also provide enhanced benefits. But plans can (and do) vary in terms of their specific benefit design, cost-sharing amounts, utilization management tools (i.e., prior authorization, quantity limits, and step therapy), and formularies (i.e., covered drugs). Plan formularies must include drug classes covering all disease states, and a minimum of two chemically distinct drugs in each class. Part D plans are required to cover all drugs in six so-called “protected” classes: immunosuppressants, antidepressants, antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, antiretrovirals, and antineoplastics.
In 2018, almost half (46%) of plans will offer basic Part D benefits (although no plans will offer the defined standard benefit), while 54% will offer enhanced benefits, similar to 2017. Most PDPs (63%) will charge a deductible, with 52% of all PDPs charging the full amount ($405). Most plans have shifted to charging tiered copayments or varying coinsurance amounts for covered drugs rather than a uniform 25% coinsurance rate, and a substantial majority of PDPs use specialty tiers for high-cost medications. Two-thirds of PDPs (65%) will not offer additional gap coverage in 2018 beyond what is required under the standard benefit. Additional gap coverage, when offered, has been typically limited to generic drugs only (not brands).
The 2010 Affordable Care Act gradually lowers out-of-pocket costs in the coverage gap by providing enrollees with a 50% manufacturer discount on the total cost of their brand-name drugs filled in the gap and additional plan payments for brands and generics. In 2018, Part D enrollees in plans with no additional gap coverage will pay 35% of the total cost of brands and 44% of the total cost of generics in the gap until they reach the catastrophic coverage threshold. Medicare will phase in additional subsidies for brands and generic drugs, ultimately reducing the beneficiary coinsurance rate in the gap to 25% by 2020.
Part D and Low-Income Subsidy Enrollment
Enrollment in Medicare drug plans is voluntary, with the exception of beneficiaries who are dually eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid and certain other low-income beneficiaries who are automatically enrolled in a PDP if they do not choose a plan on their own. Unless beneficiaries have drug coverage from another source that is at least as good as standard Part D coverage (“creditable coverage”), they face a penalty equal to 1% of the national average premium for each month they delay enrollment.
In 2017, more than 42 million Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Part D plans, including employer-only group plans.4 Of this total, 6 in 10 (60%) are enrolled in stand-alone PDPs and 4 in 10 (40%) are enrolled in Medicare Advantage drug plans. Medicare’s actuaries estimate that around 2 million other beneficiaries in 2017 have drug coverage through employer-sponsored retiree plans where the employer receives subsidies equal to 28% of drug expenses between $405 and $8,350 per retiree in 2018 (up from $400 and $8,250 in 2017).5 Several million beneficiaries are estimated to have other sources of drug coverage, including employer plans for active workers, FEHBP, TRICARE, and Veterans Affairs (VA). Yet an estimated 12% of Medicare beneficiaries lack creditable drug coverage.
Twelve million Part D enrollees are currently receiving the Low-Income Subsidy. Beneficiaries who are dually eligible, QMBs, SLMBs, QIs, and SSI-onlys automatically qualify for the additional assistance, and Medicare automatically enrolls them into PDPs with premiums at or below the regional average (the Low-Income Subsidy benchmark) if they do not choose a plan on their own. Other beneficiaries are subject to both an income and asset test and need to apply for the Low-Income Subsidy through either the Social Security Administration or Medicaid.
Part D Spending and Financing in 2018
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates that spending on Part D benefits will total $92 billion in 2018, representing 15.5% of net Medicare outlays in 2018 (net of offsetting receipts from premiums and state transfers). Part D spending depends on several factors, including the number of Part D enrollees, their health status and drug use, the number of enrollees receiving the Low-Income Subsidy, and plans’ ability to negotiate discounts (rebates) with drug companies and preferred pricing arrangements with pharmacies, and manage use (e.g., promoting use of generic drugs, prior authorization, step therapy, quantity limits, and mail order). Federal law prohibits the Secretary of Health and Human Services from interfering in drug price negotiations between Part D plan sponsors and drug manufacturers.6
Financing for Part D comes from general revenues (78%), beneficiary premiums (13%), and state contributions (9%). The monthly premium paid by enrollees is set to cover 25.5% of the cost of standard drug coverage. Medicare subsidizes the remaining 74.5%, based on bids submitted by plans for their expected benefit payments. Part D enrollees with higher incomes ($85,000/individual; $170,000/couple) pay a greater share of standard Part D costs, ranging from 35% to 80%, depending on income.
According to Medicare’s actuaries, in 2018, Part D plans are projected to receive average annual direct subsidy payments of $353 per enrollee overall and $2,353 for enrollees receiving the LIS; employers are expected to receive, on average, $623 for retirees in employer-subsidy plans.7 Part D plans’ potential total losses or gains are limited by risk-sharing arrangements with the federal government (“risk corridors”). Plans also receive additional risk-adjusted payments based on the health status of their enrollees and reinsurance payments for very high-cost enrollees.
Under reinsurance, Medicare subsidizes 80% of drug spending incurred by Part D enrollees above the catastrophic coverage threshold. In 2018, average reinsurance payments per enrollee are estimated to be $941; this represents a 7% increase from 2017. Medicare’s reinsurance payments to plans have represented a growing share of total Part D spending, increasing from 16% in 2007 to an estimated 41% in 2018.8 This is due in part to a growing number of Part D enrollees with spending above the catastrophic threshold, resulting from several factors, including the introduction of high-cost specialty drugs, increases in the cost of prescriptions, and a change made by the ACA to count the 50% manufacturer discount in enrollees’ out-of-pocket spending that qualifies them for catastrophic coverage. Analysis from MedPAC also suggests that in recent years, plans have underestimated their enrollees’ expected costs above the catastrophic coverage threshold, resulting in higher reinsurance payments from Medicare to plans over time.
Issues for the Future
After several years of relatively low growth in prescription drug spending, spending has risen more steeply since 2013. The average annual rate of growth in Part D costs per beneficiary was 2.4% between 2007 and 2013, but it increased to 4.4% between 2013 and 2016, and is projected to increase by 4.7% between 2016 and 2026
(Figure 7).9
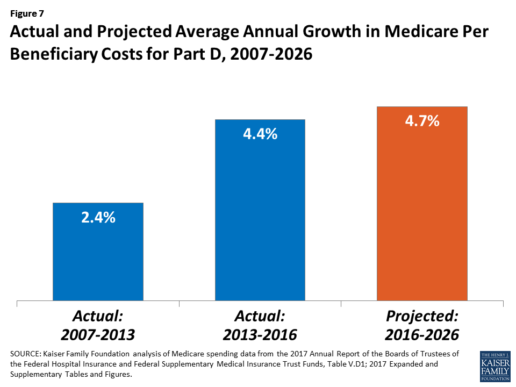
Medicare’s actuaries have projected that the Part D per capita growth rate will be comparatively higher in the coming years than in the program’s initial years due to higher costs associated with expensive specialty drugs, which is expected to be reflected in higher reinsurance payments to plans. Between 2017 and 2027, spending on Part D benefits is projected to increase from 15.9% to 17.5% of total Medicare spending (net of offsetting receipts).10 Understanding whether and to what extent private plans are able to negotiate price discounts and rebates will be an important part of ongoing efforts to assess how well plans are able to contain rising drug costs. However, drug-specific rebate information is not disclosed by CMS.
The Medicare drug benefit helps to reduce out-of-pocket drug spending for enrollees, which is especially important to those with modest incomes or very high drug costs. Closing the coverage gap by 2020 will bring additional relief to millions of enrollees with high costs. But with drug spending on the rise and more plans charging coinsurance rather than flat copayments for covered brand-name drugs, enrollees could face higher out-of-pocket costs for their Part D coverage. These trends highlight the importance of comparing plans during the annual enrollment period. Research shows, however, that relatively few people on Medicare have used the annual opportunity to switch Part D plans voluntarily—even though those who do switch often lower their out-of-pocket costs as a result of changing plans.
Understanding how well Part D is working and how well it is meeting the needs of people on Medicare will be informed by ongoing monitoring of the Part D plan marketplace and plan enrollment; assessing coverage and costs for high-cost biologics and other specialty drugs; exploring the relationship between Part D spending and spending on other Medicare-covered services; and evaluating the impact of the drug benefit on Medicare beneficiaries’ out-of-pocket spending and health outcomes.
Endnotes
- Poverty and resource levels for 2018 are not yet available (as of September 2017).
- The base beneficiary premium is equal to the product of the beneficiary premium percentage and the national average monthly bid amount (which is an enrollment-weighted average of bids submitted by both PDPs and MA-PD plans). Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, “Annual Release of Part D National Average Bid Amount and Other Part C & D Bid Information,” July 31, 2017, available at https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Health-Plans/MedicareAdvtgSpecRateStats/Downloads/PartDandMABenchmarks2018.pdf.
- Higher-income Part D enrollees also pay higher monthly Part B premiums.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Medicare Advantage, Cost, PACE, Demo, and Prescription Drug Plan Contract Report – Monthly Summary Report (Data as of August 2017).
- Board of Trustees, 2017 Annual Report of the Boards of Trustees of the Federal Hospital Insurance and Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Funds, Table IV.B7, available at https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/ReportsTrustFunds/Downloads/TR2017.pdf.
- Social Security Act, Section 1860D-11(i).
- 2017 Annual Report of the Boards of Trustees of the Federal Hospital Insurance and Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Funds; Table IV.B9.
- Kaiser Family Foundation analysis of aggregate Part D reimbursement amounts from Table IV.B10, 2017 Annual Report of the Boards of Trustees of the Federal Hospital Insurance and Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Funds.
- Kaiser Family Foundation analysis of Part D average per beneficiary costs from Table V.D1, 2017 Annual Report of the Boards of Trustees of the Federal Hospital Insurance and Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Funds.
- Kaiser Family Foundation analysis of Part D benefits spending as a share of net Medicare outlays (total mandatory and discretionary outlays minus offsetting receipts) from CBO, Medicare-Congressional Budget Office’s June 2017 Baseline.
Read the full article here.
Source:
Kaiser Family Foundation (2 October 2017). “The Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Benefit” [Web Blog Post]. Retrieved from address https://www.kff.org/medicare/fact-sheet/the-medicare-prescription-drug-benefit-fact-sheet/#26740
15 Most Expensive States for Long-Term Care: 2017
Are you reaching retirement? Then, perhaps, you've already looked into the affordability of long-term care, and - well - it's not as affordable as you thought. If you're looking to get the most out of your retirement budget, then you may want to stray away from these 15 most expensive states for long-term care, as of 2017.
This article is brought to you by Think Advisor, and it was written by Marlene Y. Satter. You can read the full article here.
Genworth’s annual study on the cost of care nationwide, which includes home care, assisted living facilities, etc., is not reassuring

The price of long-term care insurance is high—for everyone involved. Not just the patient but also the caregivers pay in more than money to make sure that the person in need of care is given the best care they can manage.
In this year’s version of Genworth Financial’s annual study on the cost of care nationwide—not just in nursing homes, which are less and less on the forefront, but also care provided at home, adult day care and assisted living facilities—the news is not reassuring. Costs have risen steadily, with those for licensed homemakers—those who provide what the study calls “hands-on personal care” for patients still in their homes—rising the fastest, increasing 6.17% just since last year.
And of course since people would prefer to stay in their homes, that’s going to hit a lot of people hard.
Less-skilled “homemaker care,” such as cooking, cleaning and running errands (not included in the breakdown that follows) has risen pretty quickly as well, increasing by 4.75% since last year. But both versions of homemaker assistance are at the low end on the price scale, coming in at $21 for homemaker care and $22 for licensed homemaker care. The big bucks are elsewhere.
They may not have risen as quickly percentage-wise as the two already mentioned, but adult day care increased by 2.94% since last year to a national median rate of $70 per day. Assisted living facilities now average a median monthly rate of $3,750, an increase of 3.36% from last year, while nursing homes, at an increase of 5.50% for a private room, now run a median daily rate of $267. No matter how you look at it, that’s a lot of money.
And caregivers often sacrifice their own financial well-being to care for their family members, forking over an average of $10,000 out of their own pockets for expenses that range from household expenses, personal items, or transportation services to payment of informal caregivers or LTC facilities.
A whopping 62% are paying for these expenses out of their own retirement funds; 45% have seen those costs cut their basic quality of living; and 38% have cut the amount they devote to savings and retirement to meet the costs of care.
And another sad side effect of all this stress is that 27% say it’s had a negative impact on their relationship with the person they’re caring for.
The penalty for all this devotion is that absences, reduced hours and chronic tardiness can end up cutting a caregiver’s pay. About a half of caregivers estimate that they lost approximately a third of their income.
Check out the 15 most expensive states for LTC.

15. Maryland
Average Annual LTC Cost: $60,305
- Adult day care: $2,150
- Licensed home care: $52,281
- Assisted living: $49,800
- Nursing home (private room): $118,990

14. Rhode Island
Average Annual LTC Cost: $60,789
- Adult day care: $19,500
- Licensed home care: $57,772
- Assisted living: $61,860
- Nursing home (private room): $104,025

13. California
Average Annual LTC Cost: $61,239
- Adult day care: $20,020
- Licensed home care: $57,200
- Assisted living: $51,300
- Nursing home (private room): $116,435

12. Washington
Average Annual LTC Cost: $61,704
- Adult day care: $16,900
- Licensed home care: $60,632
- Assisted living: $55,920
- Nursing home (private room): $113,362

11. Vermont
Average Annual LTC Cost: $63,139
- Adult day care: $34,320
- Licensed home care: $57,200
- Assisted living: $49,527
- Nursing home (private room): $111,508

10. North Dakota
Average Annual LTC Cost: $64,010
- Adult day care: $25,480
- Licensed home care: $63,972
- Assisted living: $36,219
- Nursing home (private room): $130,367

9. Maine
Average Annual LTC Cost: $64,423
- Adult day care: $28,080
- Licensed home care: $53,768
- Assisted living: $58,680
- Nursing home (private room): $117,165

8. New York
Average Annual LTC Cost: $65,852
- Adult day care: $20,800
- Licensed home care: $54,340
- Assisted living: $47,850
- Nursing home (private room): $140,416

7. New Hampshire
Average Annual LTC Cost: $66,044
- Adult day care: $18,720
- Licensed home care: $60,357
- Assisted living: $58,260
- Nursing home (private room): $126,838

6. Delaware
Average Annual LTC Cost: $68,472
- Adult day care: $18,850
- Licensed home care: $50,908
- Assisted living: $72,180
- Nursing home (private room): $131,948

5. New Jersey
Average Annual LTC Cost: $68,833
- Adult day care: $23,400
- Licensed home care: $52,624
- Assisted living: $69,732
- Nursing home (private room): $129,575

4. Hawaii
Average Annual LTC Cost: $71,820
- Adult day care: $18,200
- Licensed home care: $59,488
- Assisted living: $51,000
- Nursing home (private room): $158,593

3. Connecticut
Average Annual LTC Cost: $72,671
- Adult day care: $20,800
- Licensed home care: $52,624
- Assisted living: $55,200
- Nursing home (private room): $162,060
![]()
2. Massachusetts
Average Annual LTC Cost: $73,307
- Adult day care: $16,900
- Licensed home care: $59,488
- Assisted living: $67,188
- Nursing home (private room): $149,650

1. Alaska
Average Annual LTC Cost: $117,800
- Adult day care: $43,709
- Licensed home care: $63,492
- Assisted living: $72,000
- Nursing home (private room): $292,000
You can read the full article here.
Source:
Satter M. (2 October 2017). "15 Most Expensive States for Long-Term Care: 2017" [Web Blog Post]. Retrieved from address https://www.thinkadvisor.com/2017/10/02/15-most-expensive-states-for-long-term-care-2017
Apple, Fitbit to join FDA program to speed health tech
Wondering how technology can speed the process of developing health tech? In this article from BenefitsPro written by Anna Edney, gain a close insight on how Apple and Fitbit are working together with the FDA to make your health of vital importance.
You can read the original article here.
A federal agency that regulates apples wants to make regulations on Apple Inc. a little easier.
The Food and Drug Administration, which oversees new drugs, medical devices and much of the U.S. food supply, said Tuesday that it had selected nine major tech companies for a pilot program that may let them avoid some regulations that have tied up developers working on health software and products.
“We need to modernize our regulatory framework so that it matches the kind of innovation we’re being asked to evaluate,” FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb said in a statement.
The program is meant to let the companies get products pre-cleared rather than going through the agency’s standard application and approval process that can take months. Along with Apple, Fitbit Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Verily Life Sciences, Johnson & Johnson and Roche Holding AG will participate.
A new report and video from the Health Enhancement Research Organization (HERO) identifies six promising practices for effectively integrating wearables...
The FDA program is meant to help the companies more rapidly develop new products while maintaining some government oversight of technology that may be used by patients or their doctors to prevent, diagnose and treat conditions.
Apple is studying whether its watch can detect heart abnormalities. The process it will go through to make sure it’s using sound quality metrics and other measures won’t be as costly and time-consuming as when the government clears a new pacemaker, for example. Verily, the life sciences arm of Google parent Alphabet Inc., is working with Novartis AG to develop a contact lens that could continuously monitor the body’s blood sugar.
Faster Pace
“Historically, health care has been slow to implement disruptive technology tools that have transformed other areas of commerce and daily life,” Gottlieb said in July when he announced that digital health manufacturers could apply for the pilot program.
Officially dubbed the Pre-Cert for Software Pilot, Gottlieb at the time called it “a new and pragmatic approach to digital health technology.”
The other companies included in the pilot are Pear Therapeutics Inc., Phosphorus Inc. and Tidepool.
The program is part of a broader move at the FDA, particularly since Gottlieb took over in May, to streamline regulation and get medical products to patients faster. The commissioner said last week the agency will clarify how drugmakers might use data from treatments already approved in some disease to gain approvals for more conditions. In July, he delayed oversight of electronic cigarettes while the agency decides what information it will need from makers of the products.
Rules Uncertainty
As Silicon Valley developers have pushed into health care, the industry has been at times uncertain about when it needed the FDA’s approval. In 2013, the consumer gene-testing company 23andMe Inc. was ordered by the agency to temporarily stop selling its health analysis product until it was cleared by regulators, for example.
Under the pilot, the FDA will scrutinize digital health companies’ software and will inspect their facilities to ensure they meet quality standards and can adequately track their products once they’re on the market. If they pass the agency’s audits, the companies would be pre-certified and may face a less stringent approval process or not have to go through FDA approval at all.
More than 100 companies were interested in the pilot, according to the FDA. The agency plans to hold a public workshop on the program in January to help developers not in the pilot understand the process and four months of initial findings.
You can read the original article here.
Source:
Edeny A. (27 September 2017). "Apple, Fitbit to join FDA program to speed health tech" [Web Blog Post]. Retrieved from address https://www.benefitspro.com/2017/09/27/apple-fitbit-to-join-fda-program-to-speed-health-t
Absent federal action, states take the lead on curbing drug costs
What's your state's stance on the cost of prescription drugs? See how Maryland has moved forward in their decision making for drug prices, giving themselves the ability to say "no" in this article from Benefits Pro written by Shefali Luthra.
You can read the original article here.
Lawmakers in Maryland are daring to legislate where their federal counterparts have not: As of Oct. 1, the state will be able to say “no” to some pharmaceutical price spikes.
A new law, which focuses on generic and off-patent drugs, empowers the state’s attorney general to step in if a drug’s price climbs 50 percent or more in a single year. The company must justify the hike. If the attorney general still finds the increase unwarranted, he or she can file suit in state court. Manufacturers face a fine of up to $10,000 for price gouging.
As Congress stalls on what voters say is a top health concern — high pharmaceutical costs — states increasingly are tackling the issue. Despite often-fierce industry opposition, a variety of bills are working their way through state governments. California, Nevada and New York are among those joining Maryland in passing legislation meant to undercut skyrocketing drug prices.
Maryland, though, is the first to penalize drugmakers for price hikes. Its law passed May 26 without the governor’s signature.
The state-level momentum raises the possibility that — as happened with hot-button issues such as gay marriage and smoke-free buildings — a patchwork of bills across the country could pave the way for more comprehensive national action. States feel the squeeze of these steep price tags in Medicaid and state employee benefit programs, and that applies pressure to find solutions.
“There is a noticeable uptick among state legislatures and state governments in terms of what kind of role states can play in addressing the cost of prescription drugs and access,” said Richard Cauchi, health program director at the National Conference of State Legislatures.
Many experts frame Maryland’s law as a test case that could help define what powers states have and what limits they face in doing battle with the pharmaceutical industry.
The generic-drug industry has already filed a lawsuit to block the law, arguing it’s unconstitutionally vague and an overreach of state powers. A district court is expected to rule soon.
The state-level actions focus on a variety of tactics:
“Transparency bills” would require pharmaceutical companies to detail a drug’s production and advertising costs when they raise prices over certain thresholds. Cost-limit measures would cap drug prices charged by drugmakers to Medicaid or other state-run programs, or limit what the state will pay for drugs. Supply-chain restrictions include regulating the roles of pharmacy benefit managers or limiting a consumer’s out-of-pocket costs.
A New York law on the books since spring allows officials to cap what its Medicaid program will pay for medications. If companies don’t sufficiently discount a drug, a state review will assess whether the price is out of step with medical value.
Maryland’s measure goes further — treating price gouging as a civil offense and taking alleged violators to court.
“It’s a really innovative approach. States are looking at how to replicate it, and how to expand on it,” said Ellen Albritton, a senior policy analyst at the left-leaning Families USA, which has consulted with states including Maryland on such policies.
Lawmakers have introduced similar legislation in states such as Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Tennessee and Montana. And in Ohio voters are weighing a ballot initiative in November that would limit what the state pays for prescription drugs in its Medicaid program and other state health plans.
Meanwhile, the California legislature passed a bill earlier in September that would require drugmakers to disclose when they are about to raise a price more than 16 percent over two years and justify the hike. It awaits Democratic Gov. Jerry Brown’s signature.
In June, Nevada lawmakers approved a law similar to California’s but limited to insulin prices. Vermont passed a transparency law in 2016 that would scrutinize up to 15 drugs for which the state spends “significant health care dollars” and prices had climbed by set amounts in recent years.
But states face a steep uphill climb in passing pricing legislation given the deep-pocketed pharmaceutical industry, which can finance strong opposition, whether through lobbying, legal action or advertising campaigns.
Last fall, voters rejected a California initiative that would have capped what the state pays for drugs — much like the Ohio measure under consideration. Industry groups spent more than $100 million to defeat it, putting it among California’s all-time most expensive ballot fights. Ohio’s measure is attracting similar heat, with drug companies outspending opponents about 5-to-1.
States also face policy challenges and limits to their statutory authority, which is why several have focused their efforts on specific parts of the drug-pricing pipeline.
Critics see these tailored initiatives as falling short or opening other loopholes. Requiring companies to report prices past a certain threshold, for example, might encourage them to consistently set prices just below that level.
Maryland’s law is noteworthy because it includes a fine for drugmakers if price increases are deemed excessive — though in the industry that $10,000 fine is likely nominal, suggested Rachel Sachs, an associate law professor at Washington University in St. Louis who researches drug regulations.
This law also doesn’t address the trickier policy question: a drug’s initial price tag, noted Rena Conti, an assistant professor in the University of Chicago who studies pharmaceutical economics.
And its focus on generics means that branded drugs, such as Mylan’s Epi-Pen or Kaleo’s overdose-reversing Evzio, wouldn’t be affected.
Yet there’s a good reason for this, noted Jeremy Greene, a professor of medicine and the history of medicine at Johns Hopkins University who is in favor of Maryland’s law.
Current interpretation of federal patent law suggests that the issues related to the development and affordability of on-patent drugs are under federal jurisdiction, outside the purview of states, he explained.
In Maryland, “the law was drafted narrowly to address specifically a problem we’ve only become aware of in recent years,” he said. That’s the high cost of older, off-patent drugs that face little market competition. “Here’s where the state of Maryland is trying to do something,” he said.
Still, a ruling against the state in the pending court case could have a chilling effect for other states, Sachs said, although it would be unlikely to quash their efforts.
“This is continuing to be a topic of discussion, and a problem for consumers,” said Sachs.
“At some point, some of these laws are going to go into effect — or the federal government is going to do something,” she added.
Kaiser Health News, a nonprofit health newsroom whose stories appear in news outlets nationwide, is an editorially independent part of the Kaiser Family Foundation. KHN’s coverage of prescription drug development, costs and pricing is supported in part by the Laura and John Arnold Foundation.
Source:
Luther S. (29 September 2017). "Absent federal action, states take the lead on curbing drug costs" [Web Blog Post]. Retrieved from address https://www.benefitspro.com/2017/09/29/absent-federal-action-states-take-the-lead-on-curb?page=2
How data analytics is changing employee benefit strategies
As technology continues to grow and expand, more employers are turning to digital platforms when it comes to managing their employee benefits program. With more access to technology, employers can use data accumulated from their employees to better personalize their employee benefits package to fit each individual's needs. Take a look at this column by Eric Helman from Employee Benefit Advisor and find out some more tips on how you can better leverage the data from an employee benefits program to fit your employees'es needs.
In the realm of employee benefits, surveys, focus groups and anecdotes about specific employee encounters with the benefits program typically drive the discussions about how that program should evolve in the future. Unlike the situation at Outback, it is difficult to “observe” how people actually consume benefits and tailor a program that is attractive to them.
Fortunately, recent developments in data analytics have unlocked the potential of using consumer behavior insights to drive employee benefits strategy.
Leading practitioners are beginning to leverage these developments to change the annual renewal process. The technologies that support data aggregation, normalization and reporting have been aggressively developed to support the provider and payer communities. Only now have these advancements been made available to employers and their advisers.
The most successful practitioners point to the value of standardized claims reporting based upon credible data. By combining current claims data with industry benchmarks and predictive analytics, employers gain insight into the ongoing performance of their benefit plans. They “see” for themselves what industry professionals have been telling them for years. Plan performance is based upon claims, both in terms of the number of units of healthcare consumed and the price of those units. In recent surveys, benefit professionals report the difficulty they have in convincing CFOs and CEOs to make the necessary changes to benefit programs. Standardized reporting from a credible analytics platform can greatly enhance the ability for benefit professionals to communicate their agenda.
But standardized reporting is not the panacea. Benefits are complex. And the relationship between risk and consumption of healthcare add to the complexity. Even in the best reporting environments where executives are well informed about the performance of their plans and how the key metrics compare to industry norms, they are often perplexed about what to do with the information. Advancements in the realm of “actionable analytics” are beginning to address this problem as well.
While artificial intelligence or AI is all the rage, the underlying concept of having a computer suggest a course of action based upon data is not a new idea. The new application to employee benefits is the ability to provide “suggestions” in the context of standardized financial reporting. The number of ideas to bend the cost curve are numerous. The challenge is matching these ideas with the appropriate populations, convincing decision makers to invest and engaging the appropriate cohorts of employees to take specific actions necessary to realize the return on investment for these initiatives.
New systems are now available to close the gaps on this execution continuum. The foundation for these new systems is a robust analytics platform. But actionable analytics build upon this foundation by evaluating the employer’s data to discern whether a specific cost-saving initiative might generate savings worthy of the investment. These new systems present the output of that analysis in an easy to understand graphical format for benefit consultants and HR professionals to effectively communicate the potential of cost savings initiatives to decision makers.
Targeted engagement maximizes compliance and ROI
Getting executives to commit to intentional actions to affect the rising costs of benefits solves one half of the problem. The second half of the problem is one of focus. Rather than attempting to engage all employees with generalized messaging, these new systems use analytics to focus their engagement on a specific cohort of individuals in order to drive the greatest impact. This focus allows for a concentration of resources on the targeted populations, resulting in increased compliance and larger return on investment. The best implementations are integrated with benefits administration platforms and can incorporate multiple initiatives simultaneously. Point solutions, from an engagement perspective, have been proven to result in single-digit compliance. The power of an integrated engagement solution allows for initiatives that, because they are both focused and automated, can be executed simultaneously.
Advancements in technology have created a new era in which the democratization of big data allows for non-technical professionals to access detailed information and convert that information into intelligence. According to a recent survey, more than 65% of employers confess they are not strategic when it comes to benefits cost management. In spite of the many cost savings ideas available, more than 40% say they are not engaging in any new initiatives in the upcoming year. While the future of healthcare reform is in doubt, the potential for actionable analytics to significantly change the trajectory of the employer’s benefits costs is certain.
See the original article Here.
Source:
Helman E. (2017 September 5). How data analytics is changing employee benefit strategies [Web blog post]. Retrieved from address https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/opinion/closing-the-execution-continuum-on-employee-benefit-cost-savings
Avoid these 12 Common Open Enrollment Mistakes
Open enrollment season is right around the corner. Check out this great column by Alan Goforth from Benefits Pro and find out the top mistakes employers and HR have made during open enrollment and what you can do to avoid them.
Every employer or human resources professional has made mistakes during open enrollment.
Trying to accommodate the diverse needs of the workforce in a short timeframe against the backdrop of increasing options and often bewildering regulations, can be a challenge even in the best-run companies.
Avoiding mistakes is impossible, but learning from them is not. Although the list may be limitless, here are a dozen of the most common pratfalls during open enrollmentand how to avoid tripping over them.
1. Failing to communicate
"What we've got here… is failure to communicate." – Cool Hand Luke
This mistake likely has topped the list since open enrollment first came into existence, and it will probably continue to do so. That's because enrollment is a complex procedure, and few challenges are greater that making sure employers, employees, brokers and carriers are on the same page.
Employers have both a stick and a carrot to encourage them to communicate as well as possible. The stick is the Affordable Care Act, which requires all employers subject to the Fair Labor Standards Act to communicate with employees about their health-care coverage, regardless of whether they offer benefits.
As a carrot, an Aflac study found that 80 percent of employees agree that a well-communicated benefits package would make them less likely to leave their jobs
2. Neglecting technology
The integration of new technology is arguably the most significant innovation in the enrollment process in recent years.
This is especially important as younger people enter the workforce. Millennials repeatedly express a preference for receiving and analyzing benefits information by computer, phone or other electronic devices.
The challenge is to make the use of technology as seamless as possible, both for employees who are tech-savvy and for those who are not.
Carriers and brokers are making this an emphasis, and employers should lean on them for practical advice.
See the original article Here.
3. Over-reliance on technology
At the other end of the spectrum is the temptation to rely on technology to do things it never was meant to do.
"Technology is so prevalent in the enrollment space today, but watch out for relying on technology as the one thing that will make or break enrollment," says Kathy O'Brien, vice president of voluntary benefits and nation client group services for Unum in Chattanooga, Tennessee. "Technology is great for capturing data, but it won't solve every problem and doesn't change the importance of the other work you need to do."
4. Succumbing to inertia
It can be frustrating to invest substantial time and effort into employee benefit education, only to have most of the staff do nothing.
Yet that is what happens most of the time. Just 36 percent of workers make any changes from the previous enrollment, and 53 percent spend less than one hour making their selections, according to a LIMRA study.
One reason may be that employees don’t feel assured they are making the right decisions.
Only 10 percent felt confident in their enrollment choices when they were done, according to a VSP Vision Care study. One good strategy for overcoming inertia is to attach dollar values to their choices and show where their existing selections may be leaving money on the table.
5. Cutting too many corners
One of the most difficult financial decisions employers make each year is deciding how much money to allocate to employee benefits.
Spending too much goes straight to the bottom line and could result in having to lay off the very employees they are trying to help. Spending too little, however, can hurt employee retention and recruiting.
Voluntary benefits offer a win-win solution. Employees, who pick up the costs, have more options to tailor a program that meets their own needs.
In a recent study of small businesses, 85 percent of workers consider voluntary benefits to be part of a comprehensive benefits package, and 62 percent see a need for voluntary benefits.
6. Not taking a holistic approach
"Holistic" is not just a description of an employee wellness program; it also describes how employers should think about employee benefit packages.
The bread-and-butter benefits of life and health insurance now may include such voluntary options as dental, vision and critical illness. Employers and workers alike need to understand how all of the benefits mesh for each individual.
Businesses also need to think broadly about their approach to enrollment
"Overall, we take a holistic approach to the customer’s enrollment program, from benefits communication to personalized benefits education and counseling, as well as ongoing, dedicated service," says Heather Lozynski, assistant vice president of premier client management for Colonial Life in Columbia, South Carolina. "This allows the employer to then focus on other aspects of their benefits process."
7. Unbalanced benefits mix
Employee benefits have evolved from plain vanilla to 31 (or more) flavors.
As the job market rebounds and competition for talented employees increases, workers will demand more from their employers.
Benefits that were once considered add-ons are now considered mandatory.
Round out the benefits package with an appealing mix of standard features and voluntary options with the objective of attracting, retaining and protecting top-tier employees.
8. Incomplete documentation
Employee satisfaction is a worthy objective — and so is keeping government regulators happy.
The Affordable Care Act requires employers who self-fund employee health care to report information about minimum essential coverage to the IRS, at the risk of penalties.
Even if a company is not required by law to offer compliant coverage to part-time employees, it still is responsible for keeping detailed records of their employment status and hours worked.
As the old saying goes, the job is not over until the paperwork is done.
9. Forgetting the family
The Affordable Care Act has affected the options available to employers, workers and their families.
Many businesses are dropping spousal health insurance coverage or adding surcharges for spouses who have access to employer-provided insurance at their own jobs.
Also, adult children can now remain on their parents' health policies until they are 26.
Clearly communicate company policies regarding family coverage, and try to include affected family members in informational meetings.
Get to know more about employees' families — it will pay dividends long after open enrollment.
10. Limiting enrollment options
Carriers make no secret about their emphasis on electronic benefits education and enrollment.
All things considered, it is simpler and less prone to copying and data-entry errors.
It would be a mistake, however, to believe that the high-tech option is the first choice of every employee.
Be sure to offer the options of old-fashioned paper documents, phone registration and face-to-face meetings. One good compromise is an on-site enrollment kiosk where a real person provides electronic enrollment assistance.
11. Letting benefits go unused
A benefit is beneficial only if the employee uses it. Too many employees will sign up for benefits this fall, forget about them and miss out on the advantages they offer.
Periodically remind employees to review and evaluate their available benefits throughout the year so they can take advantage of ones that work and drop those that do not.
In addition to health and wellness benefits, also make sure they are taking advantage of accrued vacation and personal days.
Besides maximizing the return on their benefit investment, it will periodically remind them that the employer is looking out for their best interests.
12. Prematurely closing the 'OODA' loop
Col. John Boyd of the U.S. Air Force was an ace fighter pilot. He summarized his success with the acronym OODA: Observe, Orient, Decide and Act. Many successful businesses are adopting his approach.
After the stress of open enrollment, it's tempting to breathe a sigh of relief and focus on something else until next fall.
However, the close of enrollment is a critical time to observe by soliciting feedback from employees, brokers and carriers.
What worked this year, and what didn't? What types of communications were most effective? And how can the process be improves in 2017?
"Make sure you know what is working and what is not," said Linda Garcia, vice president for human resources at Rooms to Go, a furniture retailer based just outside Tampa. "We are doing a communications survey right now to find out the best way to reach each of our 7,500 employees. We also conduct quarterly benefits surveys and ask for their actual comments instead of just checking a box."
Source:
Goforth A. (2017 Aug 22). Avoid these 12 common open enrollment mistakes [Web blog post]. Retrieved from address https://www.benefitspro.com/2017/08/22/avoid-these-12-common-open-enrollment-mistakes?ref=hp-in-depth&page_all=1
6 employee benefits trends in 2017
2018 is almost upon us. More employers are beginning to start their search for new talent next year. If you are in the process of hiring check out this great article put together by Marlene Y. Satter from Benefits Pro and find out the top employee benefit trends for attracting new talent in 2017.
Employers looking to attract the best new employees need to look closely at their benefits offerings.
That’s according to a CBS report that highlights the six trends in benefits that are of the most interest to prospective employees. With millennials having outpaced GenXers as the largest demographic in the workplace, the report says, “it has become abundantly clear over the course of the last half decade that millennials have very different career priorities than their predecessors.”
With that in mind, here are six types of benefits employers might want to consider, if they’re not already on offer.
Flex hours are high on the list for millennials, who regard life/work balance as very important. In fact, according to a PwC study, it’s more important to them than financial compensation. Flexible schedules provide a way for employers to give that balance to employees, allowing them to work hours other than 9-to-5, or from home part of the week. As a result, the report says, employees will have better job satisfaction and be more likely to stay.
Workplace wellness programs are another way to provide a perk that pays off for both employer and employee — and not necessarily at a high cost, the report says. Not only do such programs foster a strong sense of team unity that will help drive job satisfaction and productivity, they also cut health care costs.
Continuing education not only gives employees a leg up, but also provides employers with better-trained staff who are able to cope with modern challenges and less likely to jump ship in search of a more congenial workplace. While the report concedes that most small and midsize businesses don’t have the budget to provide postgrad tuition to employees, that doesn’t mean that companies can’t focus on such investments in language and software certification classes.
Digital health care solutions enable masters of the cyber world in the workforce to reach out to health practitioners via mobile devices and computers, resulting in faster and more personalized treatment. In addition, the report says, “digital health programs are also incredibly cost effective and are estimated to save billions in medical costs over the next four years.”
Fringe benefits and perks — even if not on the scale of big-budget Silicon Valley companies — are another way to woo millennial employees. Public transportation passes, reimbursing employees for yoga classes and massage sessions and providing free lunches or snacks, can give recruiting an edge over companies that do nothing along these lines, the report points out.
Last but not least, there’s a bigger budget of vacation days. Employers may think that’s too expensive, but employee burnout is responsible for 50 percent of employee churn— and the cost of replacing even an entry-level employee can cost a company up to 50 percent of his or her annual salary. The money spent on extra vacation to avoid burnout could be more than offset by the losses of not doing so. Plus, the knowledge that well-rested employees are more productive will also help to counter the down time that might be caused by those additional days off.
See the original article Here.
Source:
Satter M. (2017 September 5 ). 6 employee benefits trends in 2017 [Web blog post]. Retrieved from address https://www.benefitspro.com/2017/09/05/6-employee-benefits-trends-in-2017?page=2&page_all=1









