3 trends and 4 survival tips for managing millennials in 2019
Millennials: America's most diverse and overly stereotyped generation. Whether you like or dislike millennials, it's hard to avoid the fact that they are going to be the prime engine of the workplace for years to come. Continue reading to learn more.
anyone knows more about millennials than an actual millennial, it’s Brian Weed, CEO of Avenica. Founded in 1998, Avenica’s personnel services are focused exclusively on recent college graduates and the companies who are looking for such talent.
“Our goal is to place recent college graduates on the right career-track, finding entry-level positions for them at companies offering strong professional growth,” Weed says.
Millennials have been given “kind of a bad rap” by being overly stereotyped and studied. “Millennials are America’s most diverse generation. They hold more college degrees than any other generation, and they’ve experienced economic and political turmoil. They’re savvy, educated, skeptical, and on top of it all, they’re idealists. All of this has led to vast changes in the ways today’s workforce views business, engages with their organizations and leaders and makes decisions about their careers,” he says. And yet, just as with any generation, one must be cautious about assuming one profile fits all.
However one feels about this generation, there’s the fact that millennials are going to be the prime engine of the workplace for years to come. “The truth is that companies have to adapt to them, not the other way around,” he says.
Given the company’s focus and its tenure of service, BenefitsPRO asked Weed to identify three top millennial worker trends for 2019. Here’s his list:
1. Shifting motivations
Salary and culture continue to rank high on the list for attracting millennial and Gen Z candidates, but the following factors are increasingly important:
Flexibility: They expect more control over where and when they can work, with the ability (enough PTO and work-life balance) to travel and have other life experiences.
Mission driven: They are more in touch with the environment, society, and the future of both. They feel they are not only representative of their organization, but their organization also represent who they are as individuals and want to be a part of organizations that share similar views. They look for leaders who will make decisions that will better the world, not just their organizations, and solve the problems of the world through their work.
Development and training opportunities: Because millennials have seen such dramatic shifts in the economy, they seek to have more control over the future of their careers. Not only to “recession proof” but also to “future proof” their careers by constantly learning and developing.
2. Declining levels of loyalty and increased job hopping
These phenomena, well-known to employers or millennials, are largely due to:
Shifting motivations (outlined above): The key to managing this group is understanding the shifting motivations and finding ways to meet those needs/wants will help organizations attract and retain top talent.
Higher value placed on experiences, constantly wanting to try and learn new things: Managers need to give these employees opportunities to grow and develop in their roles is essential, but also opportunities to explore different fields and disciplines is also key. Keeping the work and the environment interesting and diverse will keep millennial employees engaged for longer.
Less patience, with a desire for frequent indicators of career progress (higher pay and/or promotions): Job hopping often allows the quickest opportunity to make more money and climb the career ladder. As a result, organizations are building in a quicker cadence for promotions and pay raises.
3. An increasing lack of basic professional skills/awareness
Many of these talented young people lack essential knowledge about what to wear, how to act and how to/engage in an office setting. Here’s how to respond:
Managers need to be ready to guide these new workforce entries into the professional skills areas. They often don’t have a network of older (parents/relatives) professionals around them to set an example and advise on what “professionalism” looks like and means. And colleges often don’t provide education in professionalism in an office setting: aside from business schools, many colleges don’t prepare students—especially those in the liberal arts—on meeting etiquette, business apps and technology, and other everyday professional practices.
Corporate onboarding of new entry-level employees often excludes the “basics” (meeting protocols, MS Office skills, etc.). While companies typically have some type of job-specific training programs, they often assume these basic office skills are there and aren’t able to see a candidate’s potential when lack of professional skills/awareness is present. This can create a barrier for highly qualified but more “green” candidates, especially first-generation graduates. Effective companies will develop training, coaching, and mentorship programs can help once on the job.
Weed’s 4 survival tips to managers of millennials
1. Create clear and fast-moving career tracks.
- Create distinct career tracks with clear direction on how to advance to each level.
- Restructure promotion and incentive programs that give smaller, more incremental promotions and salary raises, giving more consistent positive reinforcement and closer goals that make it more enticing to stay.
- Create professional development opportunities that help them advance in those career tracks and build other skills they need and want.
- Create ways young employees can explore other career tracks without leaving the company. Millennials and Gen Z’s have a higher propensity for changing their minds and/or wanting different experiences, so consider ways that enable employees to make lateral moves, or create rotational programs that allow inexperienced professionals to get experience in a variety of business capacities and are then more prepared to choose a track.
2. Alongside competitive compensation packages that include 401k matching programs and comprehensive insurance offerings, provide benefits that allow them to have a sense of flexibility when it comes to how they work.
- Working remotely, flex schedules/hours
- Floating holidays–especially beneficial as the workforce becomes more and more diverse
- Restructure PTO that gives employees more autonomy and responsibility for their work
- Tuition reimbursement programs to increase retention and build leaders internally
3. Create a strong company culture: company culture is one of the strongest recruiting and retention tools. Go beyond the flashy tactics of having an on-site game room and fun company outings and bring more focus to the company’s mission. Create and live/work by a set of core values that represents your company’s mission. People will be more engaged and move beyond just being their role or position when they feel connected to the mission.
4. Challenge without overworking. Boredom and stress are equally common as factors for driving millennials out of a workplace. Allow involvement in bigger, higher-level projects and discussions to provide meaningful learning opportunities, and create goals that stretch their capabilities but are attainable.
SOURCE: Cook, D. "3 trends and 4 survival tips for managing millennials in 2019" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitspro.com/2018/11/13/3-trends-and-4-survival-tips-for-managing-millenni/
5 critical elements to consider when choosing an HSA administrator
The Employee Benefit Research Institute recently reported that 83 percent of today’s workforce said health insurance was very or extremely important in deciding whether they would change jobs or not. Read on to learn more.
If anyone needed any reminding, health insurance is still an urgent matter to today’s employees. According to Employee Benefit Research Institute’s 2017 Health and Workplace Benefits Survey, 83% of the workforce said that health insurance was very or extremely important in deciding whether to stay in or change jobs. Yet research has uncovered that employees tend to delay or disengage from retirement and healthcare decisions, which they view as difficult and complex.
Fortunately, with consumer-driven healthcare plans and health savings accounts on the rise, benefits managers have a real opportunity to turn this frustrating situation into a positive one for their workforce. A critical step in doing so is choosing the right health savings administrator.
Employers should consider the following five elements when choosing a health savings administrator, or for evaluating the one with which you’re currently working.
1. Minimize risk by ensuring business alignment. Look for a health savings administrator that aligns with your company’s mission and business goals. Lack of business alignment can create real risks to your organization and employees and can damage your company brand and employee experience. For example, if your account administrator nickels-and-dimes you and your employees with added fees, you’ll experience higher costs and reduced employee satisfaction.
2. Service, support are key to employee satisfaction. It’s a fact: Employees will have HSA-related questions — probably a lot of them. Their questions may range from pharmacy networks and claims to the details of IRS rules. That’s why account management and customer service support from your health savings administrator are vital. Having first-class customer service means that employees will be better educated on their savings accounts, which can result in HSA adoption and use to their fullest potential.

3. Education, communication drive adoption. Educating employees about health savings accounts using various methods is critical, especially in the first year of adoption. This ensures your employees understand the true benefits and how to maximize their account. As CDHPs require more “skin in the game,” consumers show a higher likelihood to investigate costs, look for care alternatives, use virtual care options, and negotiate payments with providers. These are all positive outcomes of HSA adoption, and an HSA administrator oftentimes can offer shopping, price and quality transparency tools to enable your employees to make these healthcare decisions.
4. Understand the HSA admin’s technology. Because most spending and savings account transactions are conducted electronically, it’s critical that your administrator’s technology platform be configured to deliver a positive user experience that aligns with your expectations. It should allow for flexibility to add or adjust offerings and enable personalization and differentiation appropriate for your brand.
Be aware that some vendors have separate technology platforms, each running separate products (i.e., HSAs versus FSAs) and only integrate through simple programming interfaces. Because the accounts are not truly integrated, consumers may need to play a bigger role in choosing which accounts their dollars come from and how they’re paid, leading to consumer frustration and an increase in customer service call volume. With a fully integrated platform, claims flow seamlessly between accounts over multiple plan years, products and payment rules.
5. Evaluate your financial investment. Transparent pricing and fees from your health savings administrator is important. Administrators can provide value in a variety of ways including tiered product offerings, no traditional banking fees or hidden costs, and dedicated customer service. It’s important to know what these costs are up front.
Evaluate your financial investment by knowing whether or not your health savings administrator charges for program upgrades, multiple debit cards, unique data integration requirements, ad-hoc reports and more. These fees can add up and result in a final investment for which your company didn’t plan. And, it’s best to know in advance if your account holders will be charged any additional fees. Not communicating these potential fees at adoption can lead to dissatisfaction, which can then hurt your employee satisfaction ratings and complete adoption of the savings account products.
Choosing a health savings administer is a critical decision that affects not only employee satisfaction but the entire company. With eight in 10 employees ranking their benefits satisfaction as extremely or very important in terms of job satisfaction, according to EBRI, taking the time to fully vet your health savings administrator will pay dividends.
SOURCE: Santino, S. (5 November 2018) "5 critical elements to consider when choosing an HSA administrator" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/opinion/what-to-consider-when-choosing-an-hsa-administrator
How to create a strong communication plan for open enrollment
What is your communication plan for open enrollment? Now that you have your plan changes locked in, it's time to focus on communicating those changes to your employees. Read this blog post to learn more.
Ready or not… the Benefits Super Bowl is here! Whether you are a broker, benefits manager or anywhere in between, you have been knee-deep on plan updates, rate reviews and benefit changes for months. Now that the plan changes are locked, it’s go-time! The focus is now on communicating and educating employees about their benefit options.
It takes an enormous amount of planning and execution to provide a productive open enrollment experience for employees. But, it is well worth it as this is often the only time during the year that employees stop to consider their benefit options.
Learn from past wins and misses
Consider previous years’ open enrollment communications and ask yourself the following:
- What is the feedback you received from employees (the good, the bad and the ugly)?
- What were the most common questions?
- Were there key pieces of information employees had difficulty finding?
Learn from the answers to these questions and then craft your content in a clear and concise manner that is easier for employees to digest.
The communication medium is key to your success
Now that you’ve developed the content to communicate, the next equally important step is determining how, when and where you deliver this information. Is there a centralized location where employees can find information for both core and voluntary benefits? Is the information in a format that the employee can easily share with his or her significant other?
It is critical to have multi-channel communications to reach your audience. Some employees may naturally gravitate to a company-wide email and the company intranet, while others lean on more interactive mediums like E-books, text messages, webinars or lunch and learns. Providing a variety of communication avenues ensures you are reaching employees where they want to receive information.
Make sure your communications campaign provides educational materials at each of the key milestones during the open enrollment journey–such as prior to enrollment, midway through enrollment, and right before enrollment closes. Wherever possible, always support employees through the process and give them options to reach out for help.
How to communicate the same benefits to a diverse workforce
You are likely communicating to a group of employees with diverse needs and wants. What may be appealing to an entry-level recent grad may not resonate with a senior-level employee nearing retirement. For example, employees with young children may be especially interested in accident insurance or pet owners might look to pet insurance to help offset the costs of well-visits and routine care. If possible, tailor your communications to different segments of the employee population.
Communicating voluntary health-related benefits
Core medical benefits are what employees gravitate to during the enrollment period. Are you offering voluntary benefits to employees? The most successful voluntary benefit programs are positioned next to core medical plans on the enrollment platform. This shows employees how those voluntary benefits (critical illness, accident insurance and hospital indemnity) complement the core offerings with extended protection.
When voluntary benefit programs are positioned as an integral part of the employee benefits experience, employees are more likely to understand the value and appreciate the support provided by their employer. For example, a critical illness program can help to bridge the gap of a high-deductible health plan in the case of a covered critical condition. Communicate that voluntary benefits can be an integral part of a “Total Rewards Package” and can contribute to overall financial wellness.
Review and refine
Finally, don’t miss your opportunity at the end of enrollment to review how your communication campaign performed. Pull stats and analyze your communication campaign for next year’s open enrollment… it is never too early to start! HR managers can glean valuable information and metrics from the employee experience.
SOURCE: Marcia, P. (1 November 2018) "How to create a strong communication plan for open enrollment" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitspro.com/2018/11/01/how-to-create-a-strong-communication-plan-for-open/
Predictive Analytics Will Be The Silent Game-Changer In Employee Benefits
Employers can now use their own data to help fine-tune their employer-sponsored benefits packages. Continue reading to learn how this technology could be used to help fine-tune employee benefits offerings.
Last year’s World Series between the Houston Astros and the Los Angeles Dodgers came down to a seven-game battle based not only on talent, athleticism and coaching but also on data. Just as Sports Illustrated suggested back in 2014 via predictive data, the Astros were the victors.
The publication of Moneyball: The Art of Winning an Unfair Game spurred not only Major League Baseball teams to deploy predictive analytics, but also businesses to take a harder look at what their data means. It's no longer part of the hype cycle: Statista forecasts (paywall) that the predictive analytics market worldwide will reach $6.2 billion in 2018 and $10.95 billion in 2022.
I believe we are also at a transformational point in improving corporate employee benefits and our employees’ lives by embracing predictive analytics. HR is swimming in rich data. Instead of guesstimating needs across multiple generations of employees, employers can turn to their own data to fine-tune what they are offering as benefits solutions. Companies spend 25-40% of an employee’s salary on benefits. It simply makes strategic and financial sense to get it right.
Bring Employee Benefits Out Of The Dark Ages
Hiring and retaining great talent is at the very soul of almost every company’s strategy. Not surprisingly, more companies have turned to predictive analytics to give them a leg up in recruitment. However, HR benefits have lagged behind. As John Greenwood reported to Corporate Adviser, “More than half of reward and employee benefits professionals see predictive analytics as a game-changer, but 90 percent are still using spreadsheets to manage data, research from the Reward & Employee Benefits Association shows.”
One reason for benefits lagging behind recruitment in adopting predictive analytics is that the way companies choose new benefits varies greatly from business to business. Given that the majority of HR departments keep data in disparate spreadsheets, even if some HR departments conduct employee surveys or historical cost analyses, they often do not integrate the data about their workforce. If a new benefit offering is chosen based on a needs analysis, only some know the “why” behind a request from the workforce. Knowing how many employees are logging into a benefits platform is helpful; market standard benefit utilization reports provide this level of information. Yet they do not give insight into the underlying reason for an employee to utilize a benefit. The user of deeper analytics is required to look deeper into employees' behavior.
We have found firsthand that many HR departments do not have a full understanding of how their employees are utilizing their benefits across the entire offering suite. A one-size-fits-all or a one-off strategy no longer is effective. Companies must understand not only their employees’ needs but also the underlying data related to these needs to provide a valuable benefits offering.
Put Your Existing Data To Use
For the past five years, I have watched our clients glean valuable insights into what the real underlying issues are for their employees and what must be done to address these pressing needs. I also have been watching companies realize that what they thought were the core problems at hand sometimes were not.
For example, one of our national high-tech clients, with over 50,000 benefit-eligible employees, believed that a high number of their employees had children struggling with autism. This belief was initially based on input from some of their employees. After approximately 16 months, the client reviewed the masked utilization data from their benefit platform. The data illustrated that the overwhelming majority of employee families (tenfold) in fact faced challenges associated with youth anxiety, a concern that had never been expressed to HR previously. Once they reviewed what employees were doing within our platform, their results mirrored the National Institute of Mental Health’s report that approximately 31.9% of U.S. children ages 13-18 struggle with anxiety disorders.
Their own data helped them understand much more specifically where their employees’ stress lay, and their HR department was able to focus communications around it.
Getting Started
Mining and viewing use data across all benefits is ideal. This enables an employer to determine if the benefit suite is serving employees effectively. We have found that as quickly as year over year, users' behaviors shift. If a company solely chooses a benefit based on what they saw as most heavily utilized the previous year, they are not being strategic.
For that reason, HR should utilize past and current data to better predict future patterns of need for a truly strategic approach to benefit choice. With this insight, they can make better choices and serve their workforce more effectively.
Given the limitations across many employee benefit vendors today, to start initially:
1. Embrace KPIs. Agree upon them internally, and measure benefit vendors on them.
2. Work with your current vendors to determine what data they provide to support your internal analysis. Ensure you have access to all the data you need, and if not, consider a vendor change.
3. Hold possible new vendors to similar data standards, and create a transparent relationship from the start.
4. Collect current and historical data. Existing vendors can provide this history, so make sure to collect at least 2-3 years of information.
These analytics need to go deeper than basic demographics to show patterns of activity. In order to understand the benefit needs of your workforce, you'll want to analyze trends across multiple data sets: medical, pharmacy, worker's compensation, biometric screenings, utilization patterns, FMLA requests and demographic trends. From there, you can start to pinpoint what your employees need -- and the “whys” behind the needs -- in order to make a measurable impact.
While predictive analytics is still in the nascent phase in the benefits and vendor worlds, the easiest and most proactive thing any employer can do is to focus on other insights vendors can provide related to the workforce and benefit use beyond simple utilization. In doing so, you will be able to support your employees both in their work lives and their personal lives by providing them with the benefits they need to be at their best.
SOURCE: Goldberg, A. (2 October 2018) "Predictive Analytics Will Be The Silent Game-Changer In Employee Benefits" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2018/10/02/predictive-analytics-will-be-the-silent-game-changer-in-employee-benefits/#26648166e182
How data science can help employers build better benefit plans
New approaches to data science are now allowing companies to have many different definitions of data and have them all coded. Read on to learn how data science can help you build a better benefits plan.
Is your data management system overdue for an overhaul? Benefit plan sponsors don’t need to feel stuck with old systems requiring hours of manual data entry, according to Marc Rind, chief data scientist for ADP.
“I’ve been in data for a long time,” he says. “For generations, the traditional data management approach has been people having to standardize data.”
But people in different companies — even different departments of the same company – could have different definitions and means of data. An organization’s governance team would have to come up with one definition for everyone to adhere to.
With new approaches to data science, Rind says, “you’re able to have many different definitions of your data and have them all coded. It’s not about governing the definition of data but more about enhancing and publishing that data.”
With data science, employers and those in HR can see trends much more easily using automated mapping and search capabilities. This will allow them to see trends over time, like what people are choosing for their benefit plans and how benefits impact employee productivity and engagement.
“It builds context around the data,” Rind says. “For employers, they have to not only understand which benefit offerings they have to offer to employees but the effect on retention. They can also see what similar employers are offering and if they are getting higher retention rates.”
Employees can use the data to see what benefits others with similar backgrounds have chosen to get, helping them decide what their perfect healthcare plan looks like. However, they cannot yet see how satisfied people similar to them were with these benefits. Rind says that this feedback loop is important, and will become more prominent for the next generation of data science systems.
SOURCE: Spiezio, C. (16 June 2016) "How data science can help employers build better benefit plans" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/news/how-data-science-can-help-employers-build-better-benefit-plans
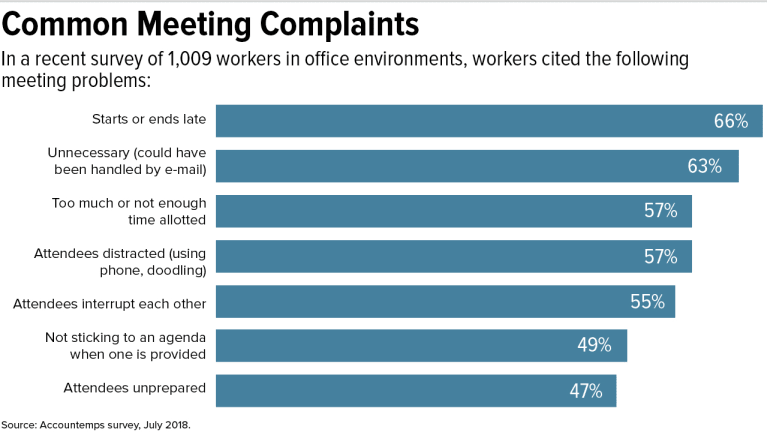
7 Steps to Running Better Meetings
A recent Accountemps survey revealed that office workers spend 21 percent of their time in meetings and feel that 25 percent of it is wasted. Read this blog post for seven steps to running better meetings.
We love to hate meetings. We groan about how annoying they are. We crack jokes about how much time gets wasted, about bureaucracy run amok.
But it’s not really a laughing matter.
Poorly run meetings can sap the lifeblood out of an organization. Not only are they mentally draining, but they can leave staff disengaged and demoralized, experts say.
On average, office workers spend 21 percent of their time in meetings and feel 25 percent of it is wasted, according to the results of a recent survey of 1,000 employees by Accountemps. One of the top complaints was that meetings are called to relay information that could have been communicated via e-mail.
Managers are also dissatisfied. In a Harvard Business School study last year, researchers found that 71 percent of the 182 senior managers interviewed said meetings were unproductive and inefficient, and 65 percent said meetings kept them from completing their work.
Fortunately, leaders can help improve how meetings are run. Indeed, their behavior is critical to achieving better results and a more positive outlook and engagement from employees, according to a 2017 study published in the Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies. In an earlier University of North Carolina study, researchers found a link between how workers feel about the effectiveness of meetings and their job satisfaction.
Other studies have found that dysfunctional communication in team meetings can have a negative impact on team productivity and the organization’s success.
What happens in these gatherings is a reflection of the workplace culture, experts say.
“It gets down to identity and performance,” says J. Elise Keith, co-founder of Lucid Meetings in Portland, Ore., and author of Where the Action Is (Second Rise, 2018). “The way in which an organization runs its meetings determines how it views itself.”
“Bad meetings are almost always a symptom of deeper issues,” Keith notes in her book.
Unfortunately, many business leaders don’t receive adequate training on how to manage or facilitate meetings, she says. “I believe that a lot of leaders have bought into the idea that poor meetings are inevitable.”
Here are 7 steps to making the time employees spend together more meaningful:
1. Prepare. Are you clear on the meeting’s purpose? What is your desired outcome? How will you achieve that?
More prep time is typically devoted to senior-level meetings compared to those held for individuals in lower-level positions, says Paul Axtell, a corporate trainer and author of Meetings Matter (Jackson Creek, 2015). He says that executive get-togethers are more effective “because people take them seriously.”
2. Limit the number of participants. The most productive meetings have fewer than eight participants, Axtell says. A larger group will leave some disengaged or resentful that their time is being wasted.
3. Send an agenda and background material in advance. If you want a thoughtful discussion, give your team members time to think about the problem or proposal that the meeting will focus on, he says.
4. Start and end on time. Don’t punish people for being punctual by waiting on late stragglers to get started. At the same time, it’s best not to jump right to the heart of the discussion in the first few minutes, Keith says. Provide a soft transition that will help those coming from other meetings to refocus.
5. Make sure all attendees can participate. One common complaint about meetings is that a few people tend to dominate the conversation. Call on other individuals to share what they think, Axtell says. Who is most likely to hold a different view? Who will be most affected by the outcome? Who has institutional knowledge that might be useful? Think about who to draw out on specific topics as you prepare. You’ll collect more ideas and leave participants with a more positive experience.
To feel good about work, people need to feel included and valued. “That means you have a voice and are allowed to express your opinions,” Axtell says.
Because you’re a leader, your views already hold more weight. If you share them too early, you may discourage others from presenting alternate perspectives. Focus on listening, and stay out of the discussion as long as you can, he says. You might learn something.
Avoid PowerPoint slides or other technology if it’s not required for an agenda item. They tend to shut down dialogue, Axtell says.
A surefire way for leaders to alienate participants is to use up most of the meeting time presenting a proposal and leave only a few minutes for questions and comments, Keith says. When people do speak up, thank them for their contributions. And use their ideas, she says.
6. Keep a written record. Posting the meeting agenda and taking notes that everyone can access will help keep participants on track. Unfortunately, many organizations fail to do so, Keith says. The written record ensures that faulty memories or differing interpretations don’t lead people down the wrong path. Are the notes detailed enough to allow you to tackle the action items days later? Are the deadlines reasonable? Be realistic. It doesn’t help the team to accept a giant list of action items that it likely can’t complete, she says.
7. Follow up. What percentage of the action items get completed by the deadlines? If you don’t achieve 85 percent, participants’ sense of effectiveness breaks down and they may disengage, Axtell says. Most groups complete just 50 percent to 60 percent.
“Whether you pay attention to them or not, meetings are in fact where your teams and your people are learning how they should behave and what they should be doing,” Keith says. “So identify the specific types of meetings your organization needs to run. Find great examples of how to run those meetings. You shouldn’t have to invent it. And set up a system that people can use successfully to become the organization that you want to become.”
SOURCE: Meinert, D. (30 October 2018). "7 Steps to Running Better Meetings" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/hr-today/news/hr-magazine/1118/pages/7-steps-to-running-better-meetings.aspx/
When Companies Should Invest in Training Their Employees — and When They Shouldn’t
Do you invest in training and development activities at your organization? According to an industry report, U.S. companies spent $90 billion in 2017 on training and development activities. Read on to learn more.
According to one industry report, U.S. companies spent over $90 billion dollars on training and development activities in 2017, a year-over-year increase of 32.5 %. While many experts emphasize the importance and benefits of employee development — a more competitive workforce, increased employee retention, and higher employee engagement — critics point to a painful lack of results from these investments. Ultimately, there is truth in both perspectives. Training is useful at times but often fails, especially when it is used to address problems that it can’t actually solve.
Many well-intended leaders view training as a panacea to obvious learning opportunities or behavioral problems. For example, several months ago, a global financial services company asked me to design a workshop to help their employees be less bureaucratic and more entrepreneurial. Their goal was to train people to stop waiting around for their bosses’ approval, and instead, feel empowered to make decisions on their own. They hoped, as an outcome, decisions would be made faster. Though the company seemed eager to invest, a training program was not the right way to introduce the new behavior they wanted their employees to learn.
Training can be a powerful medium when there is proof that the root cause of the learning need is an undeveloped skill or a knowledge deficit. For those situations, a well-designed program with customized content, relevant case material, skill-building practice, and a final measurement of skill acquisition works great. But, in the case of this organization, a lack of skills had very little to do with their problem. After asking leaders in the organization why they felt the need for training, we discovered the root causes of their problem had more to do with:
- Ineffective decision-making processes that failed to clarify which leaders and groups owned which decisions
- Narrowly distributed authority, concentrated at the top of the organization
- No measurable expectations that employees make decisions
- No technologies to quickly move information to those who needed it to make decisions
Given these systemic issues, it’s unlikely a training program would have had a productive, or sustainable outcome. Worse, it could have backfired, making management look out of touch.
Learning is a consequence of thinking, not teaching. It happens when people reflect on and choose a new behavior. But if the work environment doesn’t support that behavior, a well-trained employee won’t make a difference. Here are three conditions needed to ensure a training solution sticks.
1. Internal systems support the newly desired behavior. Spotting unwanted behavior is certainly a clue that something needs to change. But the origins of that unwanted behavior may not be a lack of skill. Individual behaviors in an organization are influenced by many factors, like: how clearly managers establish, communicate, and stick to priorities, what the culture values and reinforces, how performance is measured and rewarded, or how many levels of hierarchy there are. These all play a role in shaping employee behaviors. In the case above, people weren’t behaving in a disempowered way because they didn’t know better. The company’s decision-making processes forbid them from behaving any other way. Multiple levels of approval were required for even tactical decisions. Access to basic information was limited to high-ranking managers. The culture reinforced asking permission for everything. Unless those issues were addressed, a workshop would prove useless.
2. There is commitment to change. Any thorough organizational assessment will not only define the skills employees need to develop, it will also reveal the conditions required to reinforce and sustain those skills once a training solution is implemented. Just because an organization recognizes the factors driving unwanted behavior, doesn’t mean they’re open to changing them. When I raised the obvious concerns with the organization above, I got the classic response, “Yes, yes, of course we know those issues aren’t helping, but we think if we can get the workshop going, we’ll build momentum and then get to those later.” This is usually code for, “It’s never going to happen.” If an organization isn’t willing to address the causes of a problem, a training will not yield its intended benefit.
3. The training solution directly serves strategic priorities. When an organization deploys a new strategy — like launching a new market or product — training can play a critical role in equipping people with the skills and knowledge they need to help that strategy succeed. But when a training initiative has no discernible purpose or end goal, the risk of failure is raised. For example, one of my clients rolled out a company-wide mindfulness workshop. When I asked a few employees what they thought, they said, “It was interesting. At least it got me two hours away from my cubicle.” When I asked the sponsoring executive to explain her thought process behind the training, she said, “Our employee engagement data indicated our people are feeling stressed and overworked, so I thought it would be a nice perk to help them focus and reduce tension.” But when I asked her what was causing the stress, her answer was less definitive: “I don’t really know, but most of the negative data came from Millennials and they complain about being overworked. Plus, they like this kind of stuff.” She believed her training solution had strategic relevance because it linked to a vital employee metric. But evaluations indicated that, though employees found the training “interesting,” it didn’t actually reduce their stress. There are a myriad of reasons why the workload could have been causing employees stress. Therefore, this manager’s energy would have been better directed at trying to determine those reasons in her specific department and addressing them accordingly — despite her good intentions.
If you are going to invest millions of dollars into company training, be confident it is addressing a strategic learning need. Further, be sure your organization can and will sustain new skills and knowledge by addressing the broader factors that may threaten their success. If you aren’t confident in these conditions, don’t spend the money.
SOURCE: Carucci, R. (29 October 2018). "When Companies Should Invest in Training Their Employees – and When They Shouldn’t" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2018/10/when-companies-should-invest-in-training-their-employees-and-when-they-shouldnt
Interact Sensitively with Employees Addicted to Opioids
Opioid addiction is running rampant across the U.S. According to the National Institute of Drug Abuse, 8-12 percent of patients prescribed opioids develop an opioid use disorder. Read this blog post to learn more.
Employees who abuse opioids often are given a second chance by their employers. But well-meaning employers could wind up being sued for discriminating against those workers in violation of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) if they don't handle the situation very carefully.
Opioid addiction has been rampant in the U.S. for some time. More than three out of five drug overdose deaths last year involved an opioid, and overdoses rose 70 percent in the 12 months ending September 2017, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
So what can HR professionals do about it? If a worker admits to the problem, the path is fairly clear. But if the employer merely suspects that an employee is addicted to prescription pain relievers but has no real proof, the employee should be treated like any other employee who is having attendance or performance issues, said Kathryn Russo, an attorney with Jackson Lewis in Melville, N.Y.
An employer should never accuse someone of having an addiction, because if the employer is wrong, the accusation could lead to an ADA claim, Russo cautioned. Although current drug use isn't considered an ADA disability, a history of drug addiction is. Moreover, someone using prescription drugs might have an underlying condition covered by the ADA.

If an employee admits to opioid abuse, or the problem is discovered through drug testing, the employer should discuss it with the employee to determine if he or she needs a reasonable accommodation, such as leave to obtain treatment, Russo said. The illegal use of drugs need not be tolerated at work, she added.
Reasonably accommodate the employee so long as there's no direct threat to the health and safety of himself or herself, or others, recommended Nancy Delogu, an attorney with Littler in Washington, D.C.
Drug Testing
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission has opined that employers may ask about an employee's use of prescribed medicine or conduct a drug test to determine such use only if the employer has reasonable suspicion that its use will interfere with the employee's ability to perform the job's essential functions or will pose a direct threat.
Many employers are expanding their drug-testing panels to include semisynthetic opioids such as hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone and oxymorphone, in addition to traditional opioids such as heroin, codeine and morphine, Russo said. This is lawful in most states as long as the employer does not take adverse employment actions when drugs are used legally, she noted, which is why an employer should use a medical review officer in the drug-testing process. If the medical review officer concludes that the positive test result is the result of lawful drug use, the result is reported to the employer as negative.
Sometimes an employer will say it has reasonable suspicion that the employee came to work impaired by drug use and is considering a mandatory drug test. At that point, some employees will say the drug test would be positive and the test consequently is not necessary.
Discussions with Employees
If there are performance problems and the employee has admitted to opioid addiction, some employers tell employees that they can remain employed so long as they go through inpatient treatment. Delogu discourages that approach. Employers aren't workers' doctors, so they shouldn't be deciding whether someone needs a treatment program, she explained.
But if someone voluntarily seeks to enter an addiction-recovery program, that person may have legal protections under state law, said Wendy Lane, an attorney with Greenberg Glusker in Los Angeles. For example, California has a law requiring employers with 25 or more employees to reasonably accommodate alcohol and drug rehabilitation.
Delogu recommended that employers that believe there is a problem with substance abuse ask if the addicted employee needs assistance from the employee assistance program.
An employer can require that an employee who has violated a policy be evaluated by a substance abuse professional and complete treatment prescribed for them, without dictating what that treatment will be, she said. The employer may choose to forgo disciplinary action if an employee agrees to these terms and signs an agreement to this effect. The employer then would not have to be informed about the person's decided course of treatment, whether inpatient, outpatient or no treatment at all, she said. The employee typically will be subjected to follow-up drug testing to make sure he or she hasn't resumed the use of illegal drugs.
Many employers are willing to give employees with performance problems resulting from opioid addiction a second chance, she noted.
SOURCE: Smith, A. (1 November 2018) "Interact Sensitively with Employees Addicted to Opioids" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/ResourcesAndTools/legal-and-compliance/employment-law/Pages/employees-addicted-to-opioids.aspx
How to Handle Employee Requests for Time Off to Vote
Do you know how to handle employee requests for time off to vote? In some states, it is a requirement to give employees time off to vote. Read this blog post to learn more.
Many employees will be eligible to cast their ballot on Nov. 6, but will they have time to vote? Some states require employers to give workers time off to vote, and even in states that don't, some businesses are finding other ways to get employees to the polls.
With Election Day around the corner, employers should be mindful that, while no federal law provides employees leave to vote, many states have enacted laws in this area, said Marilyn Clark, an attorney with Dorsey & Whitney in Minneapolis. Depending on the state, employers may have to give workers notice about their voting rights and provide paid or unpaid time off to vote.
Even in states where there is no voting leave law, it is good practice to let employees take up to two hours of paid time off to vote if there isn't enough time for the employee to vote outside of working hours. "Encouraging and not discouraging employees should be the general rule," said Robert Nobile, an attorney with Seyfarth Shaw in New York City.
Encourage Employees
"Here in the United States, too many people don't vote because they don't have time due to jobs, child care and other responsibilities," said Donna Norton, executive vice president of MomsRising, an organization of more than 1 million mothers and their families. "Getting to the polls can be especially challenging for people in rural communities [or] single-parent households, and those who are juggling multiple jobs."
About 4 in 10 eligible voters did not vote in the 2016 presidential election, according to research conducted by Nonprofit VOTE and the U.S. Elections Project. And voter turnout has been historically lower for midterm elections, such as this year's, which are held near the midpoint of a president's four-year term, according to Pew Research Center.
"Businesses can help solve this problem by making sure that all employees have paid time off to vote," Norton said.
Some employers are offering solutions by making Election Day a corporate holiday, offering a few hours of paid time off for employees to vote and giving employees information about early and absentee voting, according to TheWashington Post.
Giving employees time off to participate in civic or community activities tends to improve worker performance, said Katina Sawyer, Ph.D., an assistant professor of management at George Washington University. Employers who are offering paid time off to vote will likely reap the benefits through improved employee attitudes and performance.
Know the Law
Employers in states with voting-leave laws should be familiar with the specific requirements, as some state laws have a lot of details. Even in states without such laws on the books, employers should check to see if there are any local voting leave ordinances in their cities.
Employers required to give workers time off to vote should plan for adequate work coverage to ensure that all employees can take time off, Clark said.
In many states, the employer may ask workers to give advance notice if they need time off and may require that workers take that leave at a specific time of the workday. In some states where leave is paid, employers might have the right to ask employees to prove they actually voted. Most states prohibit employers from disciplining or firing an employee who takes time off from work to vote.
"Ultimately, fostering an environment that generally encourages employees to exercise this important right is a good practice to mitigate the risk of a potential retaliation claim," Clark said.
Although state laws vary, "the general theme across the U.S. with respect to voting laws is that employees will be given time off to vote if there is insufficient time between the time the polls open and close within the state and the time employees start and finish work," Nobile said. "Typically, two to three consecutive nonworking hours between the opening and closing of the polls is deemed sufficient."
Some state laws provide unpaid leave to vote or do not address whether the leave must be paid. Oregon and Washington no longer have voting leave laws because they are "vote-by-mail" states.

In some states, such as California and New York, employers must post notices in the workplace before Election Day to inform employees of their rights. Employers might have to pay penalties if they don't comply.
The consequences for denying employees their voting rights can be harsh, with some states even imposing criminal penalties, Clark noted.
Create a Policy
At a minimum, employers should adopt a policy spelling out the voting rights available to employees under applicable laws, Clark said. For businesses that operate in states that don't have a voting-leave law, employers may still wish to adopt a policy outlining their expectations about time off for voting.
Multistate employers may elect to adopt a single policy that includes the most employee-friendly provisions of the state and local laws that cover them. "By taking this approach, employers avoid the administrative burden of adopting and promulgating multiple policies for employees working in different locales," Clark said. All voting-leave policies should be sure to include strong anti-retaliation provisions, which make clear that the employer will not take any adverse action against employees for exercising their voting rights.
"It's important to remember that the law sets the floor," said Bryan Stillwagon, an attorney with Sherman & Howard in Atlanta. "Companies with the happiest and most-engaged employees recognize that positive morale comes from doing more than what is required."
Nagele-Piazza, L. (29 October 2018) "How to Handle Employee Request for Time Off to Vote" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/ResourcesAndTools/legal-and-compliance/state-and-local-updates/Pages/How-to-Handle-Employee-Requests-for-Time-Off-to-Vote.aspx
Dana Wilkie contributed to this article.
3 steps to negotiating a better employee benefit annual renewal
Do you know how to negotiate your annual employee benefits renewal? Employee benefits are commonly the second-highest expense for employers, coming in second behind employee payroll. Read on to learn more.
Employee benefits are typically the second-highest expense for employers — right behind payroll. But unlike payroll, benefits are difficult to budget for each year because the upcoming annual renewal rate can feel like a total mystery.
Not knowing what the renewal rate will be until the end of the plan year complicates the balance that employers must strike between offering rich benefits employees appreciate at a cost the finance team can live with. It doesn’t have to be that way.
Knowing how to approach the annual renewal with your health carrier, pharmacy benefits manager and other players can help the savvy employer save some money while maintaining the same level of benefits as before. The ticket is planning for the annual renewal all year long, which removes the mystery and leads to a predictable rate.
Here are three steps to negotiating the annual renewal with your carrier.

1. Create a good carrier relationship. A great way to gain control of what happens at the end of the benefit plan year is to set the tone from the beginning. This means outlining expectations before signing a contract and communicating wants and needs throughout the plan period. If you’ve developed a good relationship with your carrier, you should have an easier time coming to an agreement on the annual renewal rate.
Building good carrier relationships extends beyond the carrier you’re currently working with to others in the market. One way to maintain a good relationship is to avoid marketing to all carriers for the best rate before each renewal period. Carriers spend time and money responding to requests for proposal (RFPs); if they respond year after year without winning the business, they may lose interest when you are ready to move your benefits plan.
2. Get plan renewals early. Left unchecked, most carriers hold the benefit plan renewal rate as long as possible (60-75 days before the end of a contract). But receiving your carrier’s initial renewal rate earlier gives you more time to evaluate the renewal and negotiate the rate. (Yes, it’s true — you don’t have to accept the first number the carrier offers.) The best way to ensure your request for an early renewal rate is heard and followed is to discuss it before signing a contract.
By receiving your renewal rate approximately 120 days before the end of your contract, you have enough time to evaluate the rate together with your health and welfare benefits broker and underwriting team and then respond with another offer. And if you feel that another carrier can offer better rates, you can also market your benefits plan and still have time to switch carriers before the contract ends.
3. Offer a fair and reasonable rate. After you receive your annual renewal rate, work with your internal team and your benefits broker to begin negotiations. Importantly, this doesn’t mean countering with a number so low that the carrier finds it untenable and unreasonable. In that case, the insurer may not meet your demand and you’ll be forced to turn to other carrier options without having planned for that possibility.
Instead, respond with a fair and reasonable rate increase backed by data. The goal is to counter offer with a number that creates stability and predictability for renewals in the future.
Learning your renewal rate for each plan year can be stressful, but it doesn’t have to be. Getting information early, negotiating a fair rate and maintaining good carrier relationships can help you create a better annual renewal with better predictability and improved budgeting year after year.
SOURCE: Strain, M (24 October 2018) "3 steps to negotiating a better employee benefit annual renewal" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/opinion/3-steps-to-negotiating-a-better-employee-benefit-annual-renewal?brief=00000152-1443-d1cc-a5fa-7cfba3c60000