4 FAQs about 2019 Medicare rates
Some high-income enrollees of Medicare Part B may experience premium increases of 7.4 percent. According to Medicare managers, Medicare Part B premium increases will be held to about 1.1 percent for most enrollees in 2019. Read on to learn more.
Medicare managers announced last week that they will hold increases in Medicare Part B premiums to about 1.1 percent for most enrollees in 2019. For some high-income enrollees, however, premiums will rise 7.4 percent.
Medicare Part B is the component of the traditional Medicare program that covers physician services and hospital outpatient care.
Here’s a look at how the monthly Part B premiums will change, by annual income level:
- Individuals earning less than $85,000, and couples earning less than $170,000:$135.50 in 2019, from $134 this year.
- Individuals earnings $160,000 to $500,000, and couples earning $320,000 to $750,000: $433.40 in 2019, from $428.60 this year.
- Individuals earning $500,000 or more, and couples earning $750,000 or more: $460.50 in 2019, from $428.60 this year.
The annual Medicare Part B deductible will increase by 1.1 percent, to $185.
Another component of the traditional Medicare program, Medicare Part A, covers inpatient hospital bills.
Medicare managers use payroll taxes to cover most of the cost of running the Medicare Part A program. Few Medicare Part A enrollees pay premiums for that coverage. But, for the enrollees who do have to pay premiums for Medicare Part A coverage, the full premium will increase 3.6 percent, to $437 per month.
The Medicare Part A deductible for inpatient hospital care will increase 1.8 percent, to $1,340.
Why are high earners paying so much more for Medicare Part B?
Congress has been increasing the share of Medicare costs that high earners pay in recent years.
For 2018, the top annual income category for Medicare Part B rate-setting purposes was for $160,000 and over for individuals, and for $320,000 and over for couples. Premiums from those Medicare Part B enrollees are supposed to cover 80 percent of their Part B claims.
In the Balanced Budget Act of 2018, Congress added a new annual income category: for individuals earning $500,000 or more and couples earning $750,000 or more. Premiums from Part B enrollees in that income category are supposed to cover 85 percent of those enrollees’ Part B claims.
Who do these rate increases actually affect?
Medicare now has about 60 million enrollees of all kinds, according to the CMS Medicare Enrollment Dashboard.
About 21 million are in Medicare Advantage plans and other plans with separate premium-setting processes.
About 38 million are in the traditional Medicare Part A, the Medicare Part B program, or both the Medicare Part A and the Medicare Part B programs. CMS refers to the traditional Medicare Part A-Medicare Part B program as Original Medicare. The rate increases have a direct effect on the Original Medicare enrollees’ costs.
How do the Medicare increases compare with the Social Security cost-of-living adjustment (COLA)?
The Social Security Administration recently announced that the 2019 Social Security COLA will be 2.8 percent.
That means the size of the COLA will be greater than the increase in Medicare premiums for all Medicare enrollees other than the highest-income Medicare Part B enrollees and the enrollees who pay the full cost of the Medicare Part A premiums.
Why should financial professionals care about Original Medicare premiums?
For consumers who already have traditional Medicare coverage, the Part A and Part B premiums may affect how much they have to spend on other insurance products and related products, such as Medicare supplement insurance coverage.
For retirement income planning clients, Medicare costs are something to factor into income needs calculations.
Because access to Medicare coverage is critical to all but the very wealthiest retirees, knowledge about how to get and keep eligibility for Medicare coverage on the most favorable possible terms is of keen interest to many consumers ages 50 and older. Some consumers may like to get information about that topic from their insurance agents, financial planners and other advisors.
Resources
Officials at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, the agency that runs Medicare, are preparing to publish the official 2019 Medicare rate notices in the Federal Register on Wednesday. A preview copy of the Part A notice is available here, and a preview copy of the Part B notice is available here.
SOURCE: Bell, A. (16 October 2018) "4 FAQs about 2019 Medicare rates" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitspro.com/2018/10/16/medicare-posts-2019-rates-pinches-high-earners-412/
Culture is key to attracting younger talent, but you can make it mutually beneficial
According to an article in Harvard Business Review, six in ten millennials are ready to change jobs at any moment, creating a great opportunity for recruitment. Read this blog post to learn how organizations can attract younger talent.
Millennials with jobs are more likely to be looking for a new job than any other generation in the workplace, according to a Harvard Business Review article by Brandon Rigoni and Amy Adkins. They report that six in ten millennials are ready to jump ship at any given time.
This is a challenge for keeping workers, but it’s also a golden opportunity for recruitment. For the most part, these are bright workers who are deconstructing the great American job search.
Firms can seize this opportunity by honing their HR brand to appeal to younger generations and balancing this with assessments that assure a good match with most new hires.
Compensation is still important, but millennials are looking for jobs that are in sync with their values and can help define who they are. Getting hired has become a matter of personal identity.
As an employer, you are being evaluated more than the candidates. How will your firm make the cut? And if you do, will you hire the right people?
Major corporations have overhauled their approach in the scramble for talent.
- General Mills began using virtual reality headsets to allow candidates to see themselves working inside General Mills, including using the company’s gym.
- Two Volvo engineers recently built a Baja racer for collegiate competitions to attract young engineers to the legacy truck builder.
- General Electric’s humorous “What’s the Matter with Owen” television campaign said bupkis about GE products. Instead, Owen touted the company’s geek chic HR brand as a bespectacled new employee being effusive about his job of programming life-changing technology to help people.
- McDonald’s eschews traditional media to engage 16 to 24-year-old candidates via Snapchat, offering “Snaplications” and video clips of young McDonald’s employees talking about their jobs.
Not everyone can serve up cold brew coffee in a corporate cafeteria. Still, there are practical steps most firms can take to enhance their HR brand for millennial and Gen Z values.
Does your organization operate with a high degree of transparency? Is it socially responsible? Do employees have paid leave for volunteer work? Are young team members valued and encouraged to contribute to relevant and visible projects and products?
Are there ways to present your products and services to be more relevant and important to society? For example, a textile manufacturer might not actually make exciting products anyone can buy, but its fabrics are used in the space program or to save lives in emergency rooms. Maybe a law firm has a pro bono clinic for low-income families.
Yes. HR needs to make your employer brand attractive to these talented but fickle job seekers, but this doesn’t mean that everyone who’s attracted to your organizational hipness is going to be cool for your company.
There are two tools to make sure both parties get what they want. The first is assessments.
Talent acquisition assessments greatly improve your odds of hiring an individual who is well matched to your company’s needs. The best are scientifically valid and EEOC compliant, focusing on the candidate’s motivation and likely work traits as compared to the job description. You’ll save a lot of money in not having to re-hire for a position.
The second tool is the “Shared Success Model,” which is a process hiring managers can establish that aligns individual development plans with organizational strategies to identify where overlap exists and where there may be gaps.
It has five components:
- Individual needs—What is important to the candidate, both professionally and personally? What aligns with their values and interests?
- Individual offer—What value does the organization bring to the candidate?
- Company needs—What does your organization require for success now and in the future? What do you need from your leaders and employees?
- Company offer—What is your corporate value proposition to the candidate? What opportunities do you provide? What culture do you provide?
- Plan—Analyze the gaps and overlap between each quadrant. Develop and implement a plan that balances your grid for shared success.
As younger candidates seek more of a cultural match, the Shared Success Model is a good way to make sure the culture you promise is a culture that supports your mission and business model.
SOURCE: Warrick, D. (8 October 2018) "Culture is key to attracting younger talent, but you can make it mutually beneficial" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitspro.com/2018/10/08/culture-is-key-to-attracting-younger-talent-but-yo/
How to Optimize Open Enrollment for Workers
From the rising cost of prescription medications to the ever-changing status of the ACA, benefit administrators are faced with many challenges when it comes to healthcare programs. Read this blog post to learn more.
Administrators of employer-sponsored healthcare programs face myriad challenges these days, from the rising cost of medications to the fluctuating status of the Affordable Care Act and state healthcare exchanges. As we head into the 2019 open enrollment season, it’s clear that these issues will continue to impact every type and rank of employee in the coming year.
To that end, I’ve outlined several key trends in open enrollment that frazzled HR leaders should explore before enrollment season begins. If it’s too late to make changes to your program this year, use these key points as a basis for measuring and evaluating current programs so you can begin planning for a more engaging, transparent and streamlined process next year.
You don’t have to take it all on yourself.
Employers are realizing that as great as some decision support and health advocacy tools may be, attempts to make employees better healthcare consumers have been only marginally effective. High-performing (aka narrow) networks may be a viable solution as they enable better rates negotiated with the carriers and providers while reducing waste, errors and unnecessary costs. It’s the steerage option, but plan designs can provide incentives for employees to elect these plans and networks. In turn, the HPNs can provide:
- more concierge-like service;
- better coordinated care between providers for high-cost claimants—where much of runaway costs reside; and
- support to ensure compliance with treatment protocols—for chronic conditions such as diabetes, CAD, COPD, etc.
In turn, these plans have the potential for shaving points off healthcare cost trend.
But it’s vital that communication strategies help reduce fears of reduced network choices (avoiding bad memories of restrictive HMO networks) while increasing confidence in the ability of the HPNs to drive results that actually enhance care while also reducing costs.
The best strategy is to provide easy-to-understand examples and scenarios that represent typical situations based on your company’s demographics and employee personas.
Use all the channels you have.
Education and engagement need to be done through a variety of channels to address the specific needs and preferences of demographic groups. Employees need to compare their options based on anticipated needs to look at both premiums (per paycheck costs) and out-of-pocket costs (deductible, copays, coinsurance), as well as employer-provided HSA contributions and incentives. The premium doesn’t tell the whole story—some people over-insure themselves by paying a higher premium for coverage that they may not use because they fear a higher deductible and out-of-pocket maximum.
Cost-comparison tools, interactive personalized assessment tools, microsites that are mobile-optimized with clear, consistent messaging, and extremely brief interactive videos make the message relevant to each individual.
Remember too that your company portal is both a useful tool in ensuring a personalized message to the employee, and a way for you to collect aggregated data about your employees’ interests, needs, action or inaction, and the user experience.
Don’t try to hit all the bases.
Trying to communicate too much information at one time tends to obscure the key message. Focus only on providing information needed to make effective enrollment decisions and use other points during the year to educate about broader topics like wellness.
A common failure is going paperless and forgetting that you really need to drive employees to resources to get them to pay attention. There may be very robust online content and resources but a very low rate of use of that valuable information. Remember that spouses at home often may be making the majority of the healthcare decisions for a family or, at the very least, for themselves. So going too far with the paperless approach can miss getting the message—and the needed information—to those key stakeholders.
Don’t fear transparency.
It’s intriguing to me that some employers are wary about communicating their level of cost-sharing with employees and how it benchmarks against peer companies. Employees often assume they are paying a far larger share than they are. There are other ways of being transparent about cost-sharing beyond the employer-employee split. For instance, we created an infographic for a client to explain the concept of self-insurance and are using it in an ongoing educational series with fact sheets and videos, getting across the idea that the decisions each of us make about our health and informed healthcare purchasing affect the costs in our individual as well as collective pockets.
The bottom line is that helping employees get smart about how they use healthcare and choose insurance options will save your company money. That’s not as callous as it sounds. If employers can’t find more and better ways to control healthcare and benefits costs, they’ll simply have to shift more of the burden to employees. Healthcare access is onerous enough. No one wants to make it harder or deprive workers of needed care. Healthy, satisfied, financially stable workers are better for business, productivity and the overall economy. Commit to exploring these key trends and making meaningful improvements to open enrollment in 2019 and beyond.
SOURCE: Brooks, B. (16 October 2018) "How to Optimize Open Enrollment for Workers" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://hrexecutive.com/how-to-optimize-open-enrollment-for-workers/
5 ways employers can leverage tech during open enrollment
Are you leveraging technology advancements during open enrollment? Advances in technology are creating a more seamless and interactive healthcare experience for employees. Read on for five ways employers can leverage technology during 2019 open enrollment.
Technology continues to reshape how employers select and offer healthcare benefits to employees, putting access to information at our fingertips and creating a more seamless and interactive healthcare experience. At the same time, these advances may help employees become savvier users of healthcare, helping simplify and personalize their journey toward health and, in the process, help curb costs for employers.
The revolution can be important to remember during open enrollment, which occurs during the fall when millions of Americans select or switch their health benefits for 2019. With that in mind, here are five tips employers should be aware of during open enrollment and year-round.
Make sense of big data
Help people understand their options
Encourage your people to move more
Offer incentives to employees who comparison shop for care
Integrate medical and ancillary benefits
5 things small business owners should know about this year's open enrollment
For small business owners, the benefits they offer are crucial to the way they attract and retain employees. Read this blog post for five things small business owners should know for 2019 open enrollment.
As a small business owner, offering competitive employee benefits is a crucial way to attract and retain strong talent. Whether you currently provide them and are planning next year’s renewal, or you are thinking of offering them for the first time, here are five things you should consider before your employees enter the open enrollment period for next year on November 1st:
1. Small businesses don’t have to wait until open enrollment to offer benefits to their employees
While your employees won’t be able to enroll in health insurance plans until November comes along, small business owners don’t have to wait at all to secure health insurance for their employees. The sooner you act, the better, to guarantee that you and your employees are protected. According to recent studies, healthier employees are happier employees, and as a result, will contribute to a more productive workplace. And a more positive and constructive work environment is better for you, your employees, and your business as a whole.
2. Health literacy is important
Whether you’ve provided health insurance to your employees before, or you’re looking into doing so for the first time, it is always worthwhile to prioritize health insurance literacy. There is a host of terminology and acronyms, not to mention rules and regulations that can be overwhelming to wrap your head around.
Thankfully, the internet is full of relevant information, ranging from articles to explainer videos, that should have you up to speed in no time. Having a good understanding of insurance concepts such as essential health benefits, employer contributions, out-of-pocket maximums, coinsurance, provider networks, co-pays, premiums, and deductibles is a necessary step to being better equipped to view and compare health plan options side-by-side. A thorough familiarization with health insurance practices and terms will allow you to make the most knowledgeable decisions for your employees and your business.
3. Offering health insurance increases employee retention
Employees want to feel like their health is a priority, and are more likely to join a company and stay for longer if their health care needs are being met. A current survey shows that 56 percent of Americans whose employers were sponsoring their health care considered whether or not they were happy with their benefits to be a significant factor in choosing to stay with a particular job. The Employee Benefit Research Institute released a survey in 2016 which showed a powerful connection between decent workplace health benefits and overall employee happiness and team spirit—59 percent percent of employees who were pleased with their benefits were also pleased with their jobs. And only 8 percent of employees who were dissatisfied with their benefits were satisfied with their jobs.
4. Alleviate health insurance costs
High insurance costs can be an obstacle for small business owners. A new survey suggests that 53 percent of American small business owners stress over the costs of providing health care to their employees. The 2017 eHealth report reveals that nearly 80 percent of small businesses owners are concerned about health insurance costs, and 62 percent would consider a 15 percent increase in premiums to make small group health insurance impossible to afford. However, there are resources in place to help reduce these costs, so they aren’t too much of a barrier. One helpful way to cut down on health insurance costs is to take advantage of potential tax breaks available to small business owners. All of the financial contributions that employers make to their employees’ premiums are tax-deductible, and employees’ financial contributions are made pre-tax, which will successfully decrease a small business’ payroll taxes.
Additionally, if your small business consists of fewer than 25 employees, you may be eligible for tax credits if the average yearly income for your employees is below $53,000. It is also beneficial to note that for small business owners, the biggest driver on insurance cost will be the type of plan chosen in addition to the average age of your employees. Your employees’ health is not a relevant factor.
5. Utilize digital resources
You don’t have to be an insurance industry expert to shop for medical plans. There are resources and tools available that make buying medical plans as easy as purchasing a plane ticket or buying a pair of shoes online – Simple, transparent. Insurance is a very complex industry that can easily be simplified with the use of the advanced technology and design of online marketplaces. These platforms are great tools for small business owners to compare prices and benefits of different plans side-by-side. Be confident while shopping for insurance because all of the information is laid out on the table. Technological solutions such as digital marketplaces serve as useful tools to modernize the insurance shopping process and ensure that you and your team are covered without going over your budget.
SOURCE: Poblete, S. (15 October 2018) "5 things small business owners should know about this year's open enrollment" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitspro.com/2018/10/15/5-things-small-business-owners-should-know-about-t/
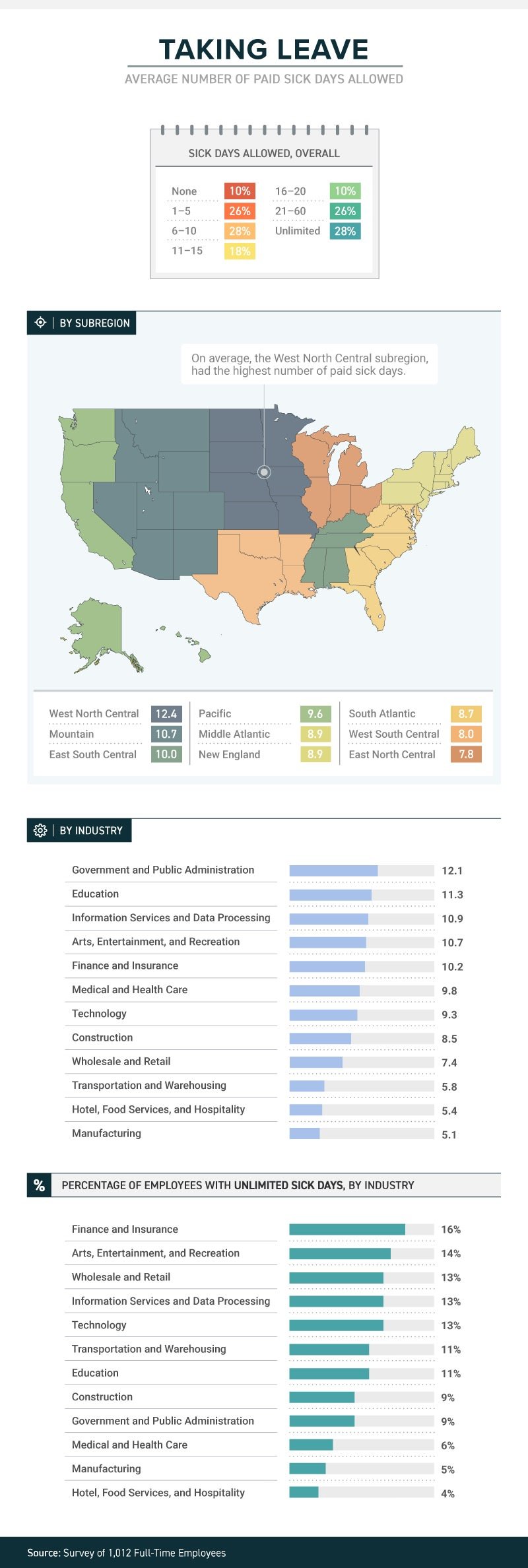
Ready for the sounds of office sniffles?
A recent study by law firm, Farah and Farah, states that one in four full-time workers receive between 1 and 5 sick days. Continue reading to learn more.
It’s not just a matter of whether they feel well enough to work, or whether they have sick days. The boss’s attitude about whether workers should take sick days or not can determine whether they actually do stay home when they’re sick, or instead come to work to spread their germs to all and sundry.
A new study from law firm Farah & Farah finds that even though it can take a person some 10 days to fully recover from a cold, approximately 10 percent of full-time workers in the U.S. get no sick days at all (part-timers don’t usually get them either), while more than 1 in 4 have to make do with between 1 and 5 sick days. Just 18 percent get enough sick time to actually recover from that cold—between 11 and 15 days.
The amount (or presence) of sick time varies from industry to industry, with government and public administration providing the most (an average of 12.1) and both hotel, food services and hospitality and manufacturing providing the least (an average of 5.4 for the hospitality industry and 5.1 for manufacturing). Some lucky souls actually get unlimited sick days, although even then they don’t always use them.
Regardless of industry, or quantity, just because workers get sick days it doesn’t mean they use them. Workers often worry that they’ll be discouraged from using them, with employers who may provide them but not encourage employees to stay home when ill. In fact, 38 percent of workers show up to work whether they’re contagious or not. Sadly for the people they encounter at work, the most likely to do so are in hospitality, medical and healthcare and transportation. Plenty of germ-spreading to be done in those professions!
And their employers’ attitudes play a role in how satisfied they are with their jobs. Among those who work for the 34 percent of bosses who encourage sick employees to stay home, 43 percent said they’re satisfied with their jobs in general. Among those who work for the 47 percent of bosses who are neutral about the use of sick days, that drops to 21 percent—and among the unfortunate workers who work for the 19 percent of bosses who actually discourage workers from staying home while ill, just 12 percent were satisfied with their jobs.
When it comes to mental health days (no, not that kind; the ones people really need to deal with diagnosed mental health conditions), fewer than 1 in 10 men and women were willing to call in sick. Taking “mental health days” when physically healthy, however, either to play hooky or simply have a vacation from the office, is something that 15 percent of respondents admitted to.
SOURCE: Satter, M (5 October 2018) "Ready for the sounds of office sniffles?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitspro.com/2018/10/05/ready-for-the-sounds-of-office-sniffles/
Original report retrieved from https://farahandfarah.com/studies/sick-days-in-america
U.S. Unemployment Drops to Lowest Rate in 50 Years
Last month the U.S. unemployment rate fell to 3.7 percent, the lowest it’s been in 50 years. Continue reading to learn how the low jobless rate is affecting the U.S. labor market.
Unemployment in the U.S. fell to 3.7 percent in September—the lowest since 1969, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
The low jobless rate, down from 3.9 percent in August, is further evidence of a strong economy—employers added 134,000 new jobs in September, extending the longest continuous jobs expansion on record at 96 months. The continued gains run counter to economists' expectations for a significant slowdown in hiring as the labor market tightens. Through the first nine months of the year, employers added an average of 211,000 workers to payrolls each month, well outpacing 2017's average monthly growth of 182,000.
"This morning's jobs report marked a new milestone for the U.S. economy," said Andrew Chamberlain, chief economist at Glassdoor. "With good news in most economic indicators today, it's likely the economy will continue its march forward through the remainder of 2018."
Cathy Barrera, chief economist at online employment marketplace ZipRecruiter, pointed out that the jobless rate ticked down for all education levels. "Anecdotal evidence has suggested that employers have experienced labor shortages for entry-level positions, and the decline in unemployment for these groups reflects that," she said. "More of those joining or rejoining the labor force are moving directly into jobs, reflecting the high demand for workers."
The sectors showing the strongest jobs gains in September include:
- Professional and business services (54,000 new jobs).
- Healthcare (26,000).
- Transportation and warehousing (24,000).
- Construction (23,000).
- Manufacturing (18,000).
"Retail job losses—20,000 jobs—were widespread, and the leisure and hospitality sector lost 17,000 jobs, largely confined to restaurants," said Josh Wright, chief economist for recruitment software firm iCIMS, based in Holmdel, N.J.
"We can clearly point to a slowdown in retail trade for the dip in [overall] payroll numbers in September," said Martha Gimbel, research director for Indeed's Hiring Lab, the labor market research arm of the global job search engine. "Retail trade had a strong first half of the year but has slowed down in recent months. In addition, recent Hiring Lab research saw a slight dip in the number of holiday retail postings, suggesting that the sector may struggle in months to come."
Prior to September, employment in leisure and hospitality had been on a modest upward trend and the losses last month may reflect the impact of Hurricane Florence.
The Department of Labor said it's possible that employment in some industries was affected by Hurricane Florence which struck the Carolinas in September. Nearly 300,000 workers nationwide told the BLS that bad weather kept them away from their jobs last month.
"That's far below the level in September 2017 amid hurricanes Harvey and Irma, but significantly above the average of about 200,000 over the prior 13 years," Wright said. Upward revisions are likely, he added.
Wages Stubborn but Rising
In September, average hourly earnings for private-sector workers rose 8 cents to $27.24. Over the year, average hourly earnings have increased by 73 cents, or 2.8 percent.
"That's down slightly from the 2.9 percent pace last month, but consistent with a steady upward trend in wage growth we've seen as the job market tightens and more employers face labor shortages," Chamberlain said. "We expect to see that pace continue to rise throughout the holiday season, likely topping 3 percent within the next six months."
Glassdoor has recorded strong wage growth in tech-heavy metropolitan areas such as San Francisco, New York and Los Angeles.
"If the true wage growth rate is at or below 2.8 percent year-over-year, it is disappointing that it is not growing faster," Barrera said. "Given how tight the labor market has been not only with overall unemployment below 4 percent, but particularly so at the entry level, we would expect wage growth to be higher. The labor turnover numbers suggest that mobility is lower than it historically has been in periods where unemployment is very low. This is one reason wages may not be rising as quickly as we'd expect."
Labor Force Participation Stalled?
The nation's labor force participation rate held at 62.7 percent.
"Looking at the labor flows data, the rate of movement of the civilian population into the labor force hasn't moved much in the last couple of years, however, more of those folks are moving directly into employment rather than into unemployment," Barrera said.
Wright noted that the number of new labor force entrants and reentrants going directly to unemployment was just 33,000. "This raises interesting questions—whenever we get a recession, how long will these reentrants and new entrants continue searching for jobs before leaving the labor force?" he asked.
The percentage of the population in their prime working years with a job also held around 79 percent, where it's been for about eight months, Gimbel said, adding that the measure suggests that the number of workers remaining to pull into the labor force may be exhausted.
"The share of the labor force working part-time but who wants a full-time job unfortunately ticked up," she said. "Any remaining slack in the economy may be concentrated in part-time workers who want more hours."
SOURCE: Maurer, R. (5 October 2018) "U.S. Unemployment Drops to Lowest Rate in 50 Years" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/hr-topics/talent-acquisition/pages/us-unemployment-drops-lowest-50-years-bls-jobs.aspx/
IRS updates required tax notice to address plan loan offsets
The model notices that all plan sponsors are required to send to plan participants before they receive an eligible rollover distribution from qualified plans were recently updated by the IRS. Continue reading to learn more.
The IRS has updated the model notice that is required to be provided to participants before they receive an “eligible rollover distribution” from a qualified 401(a) plan, a 403(b) tax-sheltered annuity, or a governmental 457(b) plan.
Notice 2018-74, which was published on September 18, 2018, modifies the prior safe-harbor explanations (model notices) that were published in 2014. Like the 2014 guidance, the 2018 Notice — sometimes referred to as the “402(f) Notice” or “Special Tax Notice” — includes two separate “model” notices that are deemed to satisfy the requirements of Code Section 402(f): one for distributions that are not from a designated Roth account, and one for distributions from a designated Roth account. The 2018 Notice also includes an appendix that can be used to modify (rather than replace) existing safe-harbor 402(f) notices.
The model notices were updated to take into consideration certain legislation that has been enacted, and other IRS guidance that has been published, since 2014. They include:
- changes related to qualified plan loan offsets under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017;
- changes in the rules for phased retirement under the Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act (“MAP-21”);
- changes in the exceptions to the 10% penalty for early distributions from governmental plans under the Defending Public Safety Employees’ Retirement Act; and
- IRS guidance (in Revenue Procedure 2016-47) regarding a self-certification procedure for waivers of the 60-day rollover deadline.
The model notices also make some “clarifying” changes to the 2014 notices, including:
- clarification that the 10% additional tax on early distributions applies only to amounts includible in income;
- an explanation of how the rollover rules apply to governmental 457(b) plans that include designated Roth accounts;
- clarification that certain exceptions to the 10% tax on early distributions do not apply to IRAs; and
- recognizing that taxpayers affected by federally declared disasters and other events may have an extended deadline for making rollovers.
The updated model 402(f) notices should be particularly useful in communicating to participants the extension, under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, of the time to roll over a “qualified plan loan offset amount.”
Inside the plan load offset
By way of background, Notice 2018-74 reminds us that distribution of a “plan loan offset amount” is an eligible rollover distribution, and that a “plan loan offset” occurs when, under the plan terms governing a plan loan, the participant’s accrued benefit is reduced, or offset, in order to repay the loan. According to the Notice, this can occur when, for example, the terms of the plan loan require that, in the event of an employee’s termination of employment or request for a distribution, the loan is to be repaid immediately or treated as in default.
The Notice also indicates that a plan loan offset may occur when, under the terms of the plan loan, the loan is canceled, accelerated, or treated as if it were in default (for example, when the plan treats a loan as in default upon an employee’s termination of employment or within a specified period thereafter). The Notice also reminds us, however, that a plan loan offset cannot occur prior to a distributable event.
This is helpful guidance for distinguishing between a “deemed distribution” of a defaulted loan (a taxable event which is not eligible for rollover) and a “plan loan offset amount,” which is an eligible rollover distribution.
Generally, if a default occurs before the participant has a distributable event (such as termination of employment, or attainment of age 59½), and the default is not cured by the last day of the cure period, it must be treated as a “deemed distribution” and reported on Form 1099. Such defaulted amounts are not eligible for rollover.
However, if the default occurs at or after a distribution event, and the plan terms require that the participant’s account be offset to pay off the loan, then the reduction of the account may be treated as a plan loan offset, which is an eligible rollover distribution.
Notice 2018-74 (and the new model notices) also reflect that, prior to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, participants who incurred a “plan loan offset” only had 60 days to “roll” an equivalent amount of money to an IRA or another employer plan (to avoid the offset being treated as a taxable distribution). However, for plan loan offsets that occur after December 31, 2017, if the plan loan offset is a “qualified plan loan offset” (meaning it occurs in connection with termination of employment or termination of the plan), then the participant has significantly more time (until the extended due date of the participant’s tax return for the year of the offset) in which to roll an amount equal to the loan offset amount to an IRA or another employer plan.
SOURCE: Browning, R (4 October 2018) "IRS updates required tax notice to address plan loan offsets" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/opinion/irs-updates-required-tax-notice-to-address-plan-loan-offsets?brief=00000152-146e-d1cc-a5fa-7cff8fee0000
8 keys to developing a successful return to work program
What does your return to work program look like? Read this blog post for 8 tips to developing a successful return to work program at your organization.
No matter the size of your organization, there’s about a 99% chance at some point dealing with employees going on leave. Most HR professionals are well-versed on the logistics of what to do when an employee is on short- or long-term disability — but what sort of culture do you have in place that encourages and supports them with a return to work (RTW)? Developing a positive and open RTW culture benefits not only the organization but the employee and their teams as well.
An effective RTW program helps an injured or disabled employee maintain productivity while recuperating, protecting their earning power and boosting an organization’s output. There also are more intangible benefits including the mental health of the employee (helping them feel valued), and the perception by other team members that the organization values everyone’s work.
See also: 7 Ways Employers Can Support Older Workers And Job Seekers
Some other benefits of an RTW program can include improvement of short-term disability claims, improvement of compliance and reduction of employer costs (replacing a team member can cost anywhere from half to twice that employee’s salary, so doing everything you can to keep them is a wise investment).
Some of these may seem like common sense, but I’m continually surprised how many (even large) organizations don’t have an established RTW program. Here are eight critical elements of a successful program.
1. Support from company leadership.
2. Have a written policy and process.
3. Establish a return to work culture.
4. Train your team members.
5. Establish an RTW coordinator.
6. Create detailed job descriptions.
7. Create modified duty options.
8. Establish evaluation metrics.
Severance plans: How savvy employers can stay ERISA compliant
How can employers’ severance plans stay ERISA compliant? There are significant advantages associated with ERISA severance plans. Continue reading to learn more.
An employer’s promise to provide severance benefits may be written or oral, formal or informal, and individual or group. Determining whether an ERISA plan already exists, or whether an employer wants its severance arrangement to be subject to ERISA, is an important consideration in determining an employer’s obligation and liabilities associated with a severance arrangement.
There are significant advantages associated with a severance arrangement that is an ERISA plan as discussed in detail below. An employer, however, cannot unilaterally decide that the severance arrangement is an ERISA plan. Instead, an employer, when designing and administering a severance arrangement, can take definitive steps to ensure that the arrangement is treated as an ERISA plan.
Employers may assume that the first step to ensure the existence of an ERISA plan is to have a written plan document, which is required by ERISA. Surprisingly, this is not necessarily determinative as to whether an ERISA plan exists. Courts have held that ERISA plans can exist without a written plan document and vice versa.
Case law has provided the broad outlines of the nature of an ERISA-governed severance plan. An essential characteristic of ERISA severance plans is that, by their nature, they necessitate “an ongoing administrative scheme.” Courts have looked at the following indicators when determining what constitutes an ongoing administrative scheme:
- The employer’s discretion in determining (1) eligibility for benefits or (2) available plan benefits
- The form of payment such as lump sums versus periodic payments
- Any ongoing demand on the employer’s assets such that there is an ongoing scheme to coordinate and control the distribution of benefits
- Calculations based on certain factors such as job performance, length of service, reemployment prospects, and so forth.
Severance plans or arrangements that normally do not require an ongoing administrative scheme, and therefore, do not implicate ERISA, are plans that have lump-sum payments that are calculated under a formula and are mechanically triggered by a single event (such as termination). Where severance payments are made over time (through payroll, for example) and/or additional benefits (such as continuation of benefits or outplacement services) are provided, the severance arrangement is likely subject to ERISA.
As a practical matter, whether severance arrangements are ad hoc or recognized in a formal plan document, they may end up providing ERISA-covered benefits. In a dispute, an employer generally prefers that ERISA applies because of ERISA’s preemption of state laws. Preemption protects employers from state laws that may favor employees and generally limits the dispute to an ERISA claim for benefits, thereby avoiding the potential exposure to punitive, extra-contractual or special damages under state laws. In addition, ERISA’s claim procedure, which provides a pre-litigation administrative process for dispute resolution, will apply if proper plan language is provided. If employees with a severance claim fail to faithfully follow the ERISA claims procedure, their lawsuits may be dismissed for failure to exhaust administrative remedies.
Typically, the plan document gives the employer, in its capacity as plan administrator, the discretionary authority to interpret the plan’s language and make decisions about the plan. If the employee follows the claim procedures and the claim is denied, the decision-making process of the employer (or its designee) if done properly, is given deferential treatment by a reviewing court. Moreover, in many cases, judicial review is limited to only those matters addressed in the administrative record of the claim. In other words, many federal courts would decline to consider factual matters that were not raised by the employee in the claim procedure process.
Another consideration for the savvy employer is that severance benefits are almost always considered to be “welfare” benefits. Welfare benefits, as opposed to pension benefits, are afforded an extremely low level of protection under ERISA. Essentially, the employer’s exposure as to promised severance benefits is only as broad as its express contractual commitment to them. By appropriately documenting the benefits with “best practices” language (such as specifying that the amendment or termination of benefits may be done with or without advance notice), employers can take advantage of the opportunity afforded by the relatively thin protections provided by ERISA. On the other hand, poor or no documentation of a severance arrangement may leave an employer with difficult-to-prove assertions as to what severance commitments were actually made.
In summary, an ERISA-governed plan provides an employer with significant advantages in litigation. In addition, a severance arrangement subject to ERISA will enjoy the powerful benefits of ERISA preemption and the ERISA claims procedures.
SOURCE: Rothman, J.; Ninneman, S. (3 October 2018) "Severance plans, Part 1: How savvy employers can stay ERISA compliant" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/opinion/how-employers-can-stay-erisa-compliant-with-severance-plans