7 HR technologies for managing the employee lifecycle
Employees are the foundation of any company, that's no secret, which is why many organizations consider their workforce its most valuable resource. That being said, often the best results come when great workforces are provided with great technology. Read this blog post for seven HR technologies that help manage the employee lifecycle.
It’s no secret employees are the foundation of any company: Without them, products can’t be made, services can’t be provided and customers can’t be satisfied.
That’s why an organization’s workforce is often considered its most valuable resource — because while great people can overcome a lack of process or technology, it’s much harder to forego having great people in place. Still, the best results come when great people are provided great technology and supported by great processes.
But the constant flow of employees in and out of an organization can make effectively and efficiently managing the support needed at each stage of the employee lifecycle a difficult task for employers and human resources teams. Luckily, these HR technologies can help with managing the employee lifecycle.
Applicant tracking system
An applicant tracking system is an online platform that simplifies and streamlines the entire recruitment process — from sourcing to selection — by allowing recruiters and hiring managers to seamlessly direct every stage of the process all from one electronic system, eliminating the never-ending paper chase of traditional recruiting. Every ATS is different, but most will include access to an online resume database, automated hiring workflows, communication capabilities and reporting tools.
Onboarding
Half of all new workers leave their jobs within the first 90 days of employment. Organizations with successful onboarding programs, however, have significantly better new hire retention rates.
A big component of a successful onboarding program is removing the hassle of all that tedious paperwork employees have to complete. The first day on the job is already stressful enough for a new hire without the added inconvenience of required employment paperwork. Investing in an online employee onboarding technology platform allows employees to complete the majority of this paperwork (like W-4s, direct deposit authorizations, I-9 forms and other consent forms) well before their first day. Electronic employee onboarding programs also reduce paper costs while minimizing the possibility of errors by providing new hires online access to all necessary employment forms so they can easily review, complete, sign and submit their forms within minutes.
Benefits enrollment
Switching from a paper-based benefits enrollment process to an online enrollment process comes with a wide array of advantages. Not only does an online benefits enrollment process save time, but it also gives employees the time and independence to make their own elections, and helps reduce costly mistakes and errors.
Time and attendance
Online time and attendance platforms not only reduce errors and help managers keep track of days of requests, they also are vastly more efficient for employees to use than paper-based timekeeping systems. (Along with some other really great advantages.)
Payroll processing
Payroll is one of the biggest line items in an organization’s budget. Processing payroll also can be one of the most time-consuming aspects of an organization’s HR functions, and when it’s not done right it can also be the source of some serious employee complaints.
Payroll technology platforms help minimize the potential for errors, and can greatly reduce the time it takes to process a payroll.
eLearning/learning management systems
With the “skills gap” widening as older employees exit the workforce faster than new employees can fill their shoes, employee development initiatives and corporate training programs have become a priority not only amongst large employers, but small and mid-size businesses as well.
Online learning management systems provide employers with convenient options to help train and develop their workforce’s skills and abilities.
Performance management
As with many employee management functions, employers are now taking advantage of online HR technology platforms that allow them to more efficiently streamline the performance management process. In many cases, an online performance management tool allows employers to more effectively evaluate and record employee performance, as well as providing a place for managers and employees alike to keep track of organizational and personal performance goals, record journal entries and maintain an ongoing performance record. These platforms tend to be more popular among larger organizations, mostly because small and medium-sized businesses often feel the price is prohibitive unless they can access discounted rates through an HR outsourcing provider.
SOURCE: Grijalva, A. (5 June 2019) "7 HR technologies for managing the employee lifecycle" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/list/hr-technology-for-managing-the-employee-lifecycle
What HR can do about the measles — and what it can't
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), measles has been confirmed in 26 states since the beginning of 2019, affecting not only schools, medical facilities and public areas, but also the workplace. Continue reading to learn more.
After decades of near-eradication in the U.S., measles is making a comeback. Its return affects not only schools, medical facilities and public areas, but also the workplace.
As of May 24th, there were 535 confirmed cases of measles in Brooklyn and Queens since September, according to the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. On the other side of the country, the Los Angeles Times recently reported a confirmed case of measles linked to Google's Mountain View campus.
Measles has been confirmed in 26 states since the start of 2019, as of May 24, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) — the greatest number of cases reported in the U.S. since 1994; measles was actually declared eliminated in 2000.
Given that measles is "very contagious" and can lead to serious health complications, HR needs to know how to keep employees safe while at the same time remaining in compliance with all applicable health privacy and anti-discrimination laws.
Measles transmission and symptoms
"Measles spreads when a person infected with the measles virus breathes, coughs, or sneezes," said Martha Sharan, Public Affairs Specialist at the CDC, speaking to HR Dive via email. "It is very contagious. You can catch measles just by being in a room where a person with measles has been, up to two hours after that person is gone. And you can catch measles from an infected person even before they have a measles rash."
In addition to a fever that can get high, Sharan said, other possible symptoms include cough, runny nose, and red eyes; a rash of tiny red spots that starts at the head and spreads to the rest of the body; diarrhea; and an ear infection.
Can employers require vaccinations?
In general, requiring employees to get vaccinated is a legally risky proposition for employers; there are some limited exceptions for employers in the healthcare field.
However, many employers — particularly those in the healthcare field — are "starting to be a little more aggressive in terms of asking employees whether they have been vaccinated as the [measles] outbreak continues and in some cases continues to grow," according to attorney Bradford T. Hammock, a shareholder at Littler Mendelson P.C.
"Employers must be very careful about these types of inquiries, but some healthcare employers have made the determination that this is permissible under the [Americans with Disabilities Act] as job-related and consistent with business necessity," Hammock said. He added that employers must also be aware of state and local considerations.
Steve Wojcik, VP of public policy at the National Business Group on Health, said the current concern about measles provides employers with an excellent opportunity to communicate the importance of vaccines and immunizations generally. "Remind employees that the measles vaccine is free, essentially, with no cost-sharing as it is one of the preventive services under the Affordable Care Act. It's a good reminder about preventive services in general."
Wojcik added that employers should encourage employees to check their specific vaccination records to confirm not only that they have received the measles vaccine, but that they have been effectively vaccinated. "Depending on age and when you were vaccinated, some early vaccines may not have been as effective as once thought," he said. Wojcik said that employees born in or before 1956 are assumed to have been exposed to the measles at some point and have some natural immunity, but in the early 1960s, the measles vaccine was "not so good," he said. "It's not as simple as flu or other vaccines."
If your workplace has been exposed
Whatever you do, "be incredibly careful about privacy," said attorney Carolyn D. Richmond, a partner at Fox Rothschild LLP. "Don't go announcing that 'Joe Smith has measles!'" Instead, Richmond advised, "call the local department of health first and find out what they have to say. Every jurisdiction has little tweaks that may affect reporting."
While you can send out a notice to employees stating they may have been exposed to measles, "again, be super careful and don't hint who it might be," she cautioned. "Your local health department will be able to tell you what you can say."
Get your leave policies in order
"Those sick with measles should stay at home for at least four days after developing the rash," said Sharan. "Staying home is an important way to not spread measles to other people. They should talk to their doctor to discuss when it is safe to resume contact with other people."
Wojcik recommended working from home and flexible work arrangements for employees who may have been exposed, particularly those who live in (or have traveled to) areas with known outbreaks. Richmond also suggested providing PTO or work-from-home arrangements for employees who have not been vaccinated or who are immunocompromised.
"We assume that those with measles will absent themselves from the workplace, and an employee with measles may be out for a number of days or longer. Follow your policies and practices with return to work," Richmond told HR Dive in an interview.
Stay in touch with your local health department and the CDC
"Continue to be in contact with your local health department, and follow along with the CDC in terms of guidance," advised Hammock. "Depending on the status of the measles outbreak in your particular area, the analysis may be different."
Richmond concurred. "Contact your local health department and your local counsel — and contact your local health department first. The bottom line is privacy, privacy, privacy."
SOURCE: Carsen, J. (29 May 2019) "What HR can do about the measles — and what it can't" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrdive.com/news/what-hr-can-do-about-the-measles-and-what-it-cant/555219/
Do career fairs still have value?
Are you participating in career fairs? Now more than ever, employers need to sell themselves to their potential hires. Continue reading this blog post to learn if career fairs still add value to recruiting.
In today's tight applicant market, job seekers are in charge. To meet their demands, recruiters have set aside old red flags and even some traditional sourcing methods. But do career fairs still make the cut?
Candidates want to be courted and, now more than ever, employers need to sell themselves to potential hires. Many young candidates, in particular, hope to land at a cutting-edge company — and a booth at a job fair may seem a bit old fashioned unless employers make a few modifications. Though a career fair is not always enough on its own, many employers have found ways to use this old-school technique to send today's job seekers the right messages about their organizations.
Do career fairs actually net hires?
Vicki Salemi, career expert for Monster, doesn't think job fairs are an effective use of employer resources. "Generally speaking, career fairs — as a standalone — do not net talent," she told HR Dive in an email. "For the job seeker, it can be challenging to stand out among stacks of resumes and, for the employer, it's not time well spent." A former financial services corporate recruiter, she said she rarely made a hire from a fair.
But they can be useful for specific industries, roles and skill sets, she added. Employers can maximize the potential of a job fair by using them in conjunction with other innovative hiring solutions as part of an integrated hiring mix. "One way employers can maximize their time at a career fair is to pre-screen resumes of candidates so that they can arrange on-site interviews," Salemi said.
Mike Cooke, account executive at Montage, said that the traditional career fair has become outdated. "Consider the amount of time and money that is typically spent on a traditional career fair," he said to HR Dive in an email. Costs can include sponsorship fees, travel expenses and swag, plus the amount of time recruiters are spending at the event and sifting through resumes received — often with little positive return on investment. "Additionally, if a company isn't able to engage candidates' pre-event, the recruiter could very well be spending face to face time with a candidate that isn't a fit," he added.
Fairs can be a challenge for candidates, as well, Salemi said: "It's often hard to make an impact with a 30-second introduction to each employer — and that can be draining." Generally, recruiters should look at the career fair as only one aspect of their hiring toolkit.
Raising awareness instead of reaping resumes
For many businesses, career fairs offer an opportunity to showcase what they do and how job seekers can be a part of the team. They can illustrate what may be available to both students and those looking to change their career trajectory, particularly for employers offering jobs that do not require a traditional degree. For organizations not known as a hiring player in certain disciplines, especially tech, exposure can offer options. At a tech-oriented career fair, employers who may not have been considered in the past by any tech workers can entice them to look closer to home before jockeying for a slot in Silicon Valley.
"Career fairs are a valuable way to drive awareness for companies across a large subset of potential talent," Mike Rogers, senior director of maintenance and refrigeration at Tyson Foods, told HR Dive in an email. For Rogers, awareness is invaluable; industrial maintenance, a trade specialty with 85 different skills, has a critical skills gap. Nearly 40% of his maintenance and refrigeration hourly team members are 50-years old or older, keeping his team on the hunt for ways to build out the talent pipeline for trade-focused jobs.
Tech takes career fairs to the next level
To offer today's job seeker the recruiting experience they want, virtual career fairs are taking off. Connecting through video saves candidates and employers time and money. Individual connections are made in a private setting, without others vying for attention. These types of fairs cast a wider net to help meet inclusion efforts as well, Cooke said. "Virtual career fairs allow recruiters to reach a larger and more diverse pool of candidates — including students located on smaller and more rural campuses — that they wouldn't normally have access to due to time, cost and travel restrictions."
Joe Milner, talent acquisition manager at Pearson, worked with Montage's recruiting technology for their own virtual career fair. To attract a more diverse level of qualified entry-level talent, their hiring managers were able to interview a number of candidates at a quick pace. "Because they were able to talk with such a wide variety of candidates, our hiring managers were able to make job offers to candidates they normally wouldn't have spoken with or even considered at a traditional job fair or through other recruiting tactics," Milner said in an email.
The other experts agreed. Virtual career fairs save time and money and can be an effective way for employers and job seekers to connect, Salemi said, and while they don't work well as a stand-alone strategy, an integrated hiring mix is incomplete without them. Gen Z candidates are digital natives, so meeting these job seekers where they're already living — on their mobile devices and laptops — will be the best approach in attracting them to your company, Cooke added.
SOURCE: O'Donnell, R. (20 May 2019) "Do career fairs still have value?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrdive.com/news/do-career-fairs-still-have-value/554107/
Bad Relationship with Your Boss? How to Fix it
Do you have a poor relationship with your manager? Often, poor relationships with managers can be detrimental to both the work employees' produce and their quality of life. Read this blog post from SHRM for tips on how to repair your relationship with your boss.
A poor relationship with your manager can be detrimental: both in the work you produce and your quality of life. LaSalle Network COO, Maureen Hoersten, uncovers ways to get to the root of bad relationships at work, and tangible tips to repair them, including:
Signs you have a bad relationship with your manager:
There are common signs your relationship may be less than healthy like disengagement and short communication. Ask yourself: has something changed? Are you getting less feedback or training as you did before, or is the opposite true and you’re suddenly being micromanaged? Evaluate how the relationship is evolving to determine if it’s going down the right path.
Determining the source of the problem:
The key to getting to the root of the relationship issue is to communicate. For instance, you may think something’s going on at work, but it the issue could really lie in your personal life. Whether it’s health related or a family issue, you may be bringing it into work with you, causing you to overanalyze the relationship with your boss. On the flip side, personal factors could be affecting your boss! The less time and attention they’re providing may have more to do with their personal stressors than your work. But you won’t know until you communicate.
Have a one on one and ask if you’re not hitting expectations. Try to open up and be vulnerable to pinpoint where the problem is. It may have nothing to do with you and your work, but you must overcommunicate to get to the root of the problem.
How to fix the relationship:
Not only can the problem be determined by communication, it can be solved. They key is not just to communicate, but overcommunicate. For instance, if you’re working on a project with deadlines, consider (over) communicating the process as you go. Instead of waiting till it’s complete, give an email update or leave a voicemail with your progress. In other words- go above and beyond, exceeding expectations for communication. When your boss is running multiple groups or has a lot going on, little updates go a long way. No one wants to be left in the dark, and overcommunication can help your manager keep you on track as you go.
To mend a poor relationship with your boss, ask what you can do to get better. If it’s due to the quality of your work, what courses can you take, or books can you read to improve? Ask yourself: are you approachable, do you overcommunicate, do you come to the office a bit earlier or stay later to show that you care? If your boss doesn’t think you’re committed, show them that you can go above and beyond.
If you feel you’re being micromanaged, you may need to dig deep and think about why your boss is micromanaging you. Is there an issue with the quality of your work or hitting deadlines? Are you meeting and exceeding expectations? You need to know how you are performing before you can move on.
When to look elsewhere:
If you’ve done everything you can to repair the relationship, given it time and nothing’s changed. Evaluate whether it’s time to move on. When it’s starting to affect your personal life, you keep asking the same questions with no acknowledgment or results, you may not be in the right position. Even if you feel it may not be the right place for you, try to give it time. Mending relationships with a manager may not be an overnight fix. People can turn relationships around; you just have to make sure you’re in alignment with your boss and their expectations through effective communication.
Originally posted on LaSalle Network blog.
SOURCE: Hoersten, M. (19 May 2019) "Bad Relationship with Your Boss? How to Fix it" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://blog.shrm.org/blog/bad-relationship-with-your-boss-how-to-fix-it
Boost employee engagement with these key people skills
Employers most likely won't be able to get every single employee to give their best every day, but with the right amount of effort, they could get the majority of employees to give their best. Continue reading for key people skills employers can use to boost employee engagement.
With all the talk about “employee engagement,” it’s only fair to ask, “Can I really get all the people in my organization to give their best – every day?”
The short answer is probably not “all.” But with the right amount of effort you can get “most” of them to give their best … most of the time. And that’s a lot better than where most companies are right now.
Boiled down to its simplest parts, employee engagement is about connecting with employees and getting them focused. It requires an ongoing and consistent effort by managers to bring out the best in people.
Employee engagement takes practice
You don’t need to be good friends with every employee – but it does help to build cordial relationships. That makes working with people more productive and cohesive.
People get more engaged in their work when the work means something to them, when they understand their role in the organization, and when they can see and appreciate the results of their own efforts.
Here are some “hands on” ways leaders can work to improve interactions and create a deeper connection with employees and colleagues:
- Make it personal. Use people’s names when talking to them – from the janitor to the CEO. Even better, use the names of their significant others – spouses, kids, parents – when possible.
- Say more than hello. Sometimes it’s necessary to cut to the chase and get to the business at hand – a project, deadline, important question, etc. But in other circumstances, there’s time to show interest in employees’ and colleagues’ lives. Instead of a generic “How are you?” ask about something that affects them.
- Talk about their interests. People surround themselves with hints of what interests them outside of work (for instance, sports ticket stubs, photos of beach trips, logo T-shirts from local events, race medals, certificates of appreciation from philanthropic groups, etc.). Look for those hints and ask about them. Once you know a little about what they do outside work, you have a starter for other conversations: “How did your son’s soccer game turn out?” “Where did you volunteer this weekend?” “Planning any vacations?”
- Show appreciation. Avoid waiting for the end of a project or annual reviews to thank employees and coworkers for their contributions. And it’s OK to say thanks for the little things they bring to the table – a good sense of humor, a sharp eye for errors, an impeccable work station, a positive attitude.
- Make others feel important. Feeling important is slightly different than feeling appreciated. Employees need to know they’re relevant. Let them know you recognize their contributions by referring to past successes when you talk to them personally and to others in meetings. Explain why their work was important.
- Recognize emotions. Work and life are roller coasters of emotions. Leaders don’t have to react to every peak and valley, but they’ll want to address the highs and lows they see. For instance, “You seem frustrated and anxious lately. Is something wrong that I can help with?” Or, “I can sense you’re very excited and proud. You deserve to be.”
Building morale
The best morale exists when you never hear the word mentioned. If you have employees, you’ll have morale problems. No matter how thorough a company’s hiring process is, at some point leaders will have to handle morale issues because employees get stressed, are overworked and deal with difficult people.
The good news: Most of the time, employees won’t be down if their managers build and maintain morale. To stay ahead of morale issues:
- Communicate. Employees left in the dark will become fearful and anxious and likely make up negative news to fill the gap. This can be avoided by regularly reporting information, changes and company news.
- Listen. While sharing information is a must, employees must also be heard. Give them different options to share their concerns and ideas. Offer the floor at department meetings, have regular one-on-one meetings, put up a suggestion box or anonymous e-mail account for submissions, invite executives to come in and listen, etc.
- Appreciate. People who aren’t recognized for their contributions may assume they’re not doing well. Leaders should take the time to thank employees for their everyday efforts that keep the operations running smoothly. In addition, extra effort should be recognized and rewarded.
- Be fair. Nothing hurts morale like unfair treatment. Leaders can’t turn their backs on poor performances, and they can’t play favorites. It’s best to document what’s done in response to good and bad behaviors so leaders can do the exact same thing when the situation arises again – and have a record of it.
- Provide opportunities to grow. Growth is often equated with moving up the career ladder. But it doesn’t have to be. Many employees are motivated by learning and creating a larger role for themselves. So if people can’t move up a career ladder (because there aren’t positions available), encourage them to learn more about the company, industry or business through in-house or outside training. Or give them opportunities to grow socially by allowing them time to volunteer.
- Create a friendly environment. Research shows people who have friends at work are more motivated and loyal to their employer. While this can’t be forced, opportunities to build friendships can be provided through potluck lunches, team-building activities and requesting staff to help in the recruiting process.
- Paint the picture. Employees who know their purpose have higher morale than those who are “just doing the job.” Regularly explain to employees how their roles fit into the company’s mission and how they affect the department and the company.
Praise what you want to see repeated
Handing out recognition takes a little more skill than just saying “Good job” and giving a pat on the back, though that’s a good start.
Giving recognition well is a skill all leaders could improve upon to keep their employees encouraged and productive.
Here are five guidelines for recognizing good work:
- Make it a policy, not a perk. Set rules for different types of recognition. For instance, recognize people for tenure and meeting goals – things everyone can accomplish.
- Stay small. Handshakes and sincere appreciation are always welcome (especially since 65% of employees say they haven’t been recognized in the past year, according to a Gallup Poll). Leaders need to look their employees in the eye, thank them for specific work and explain why it made a difference.
- Add some fanfare. Recognize people at meetings when others can congratulate them.
- Include the team. In addition to praising individuals, recognize a whole group for coming through during an unexpected hard time, meeting a goal, working together, etc.
- Make it personal. When recognizing employees, match the reward and praise to the person. One person may like a quiet thank-you and a gift card to a favorite store. Someone else might thrive on applause and a certificate given at a group lunch. Find out what people like and cater to them when possible.
SOURCE: Henson, R. (7 May 2019) "Boost employee engagement with these key people skills" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrmorning.com/boost-employee-engagement-with-people-skills/
How do you know when learning programs are working?
How do employers measure the success of employee learning programs? The demand for employee learning programs is increasing, as well as the spend that employers are allocating for these programs. Continue reading to learn more.
Demand for learning is up and the spend that employers allocate to it is climbing — but as employers spend more money, they may also need to increase expectations for learning's success.
What outcomes do employers expect from learning programs? Whenever a company initiates training, that company must also ensure it has clear, definable results in mind, experts told HR Dive. Training to increase practical knowledge — how to utilize equipment, for example — should be task-oriented and measurable. Other training goals, like developing soft skills, may be more intangible, but success metrics can still be necessary.
Quantifying learning and finding success
The classic Kirkpatrick Model to evaluate training is widely used, Tom Griffiths, CEO and co-founder of Hone, explained to HR Dive. It covers four measurements:
- Reaction. Were workers actively engaged and participating in the program? Observation and reaction surveys can help with this metric.
- Actual learning. Did they come away from the session knowing more than they went in knowing? Baseline quizzes before and after give a snapshot of whether or not the session met objectives.
- Behavioral change. Are you seeing a change in the way people perform their work? If training isn't directly relatable and usable, this might be more difficult to quantify.
- Results. What is the final impact on the business overall following the training? Have errors decreased? Has productivity increased? Is customer satisfaction up? These measurements may take longer to quantify, but they're worthwhile metrics to obtain.
Ultimately, employers should keep an eye out for true measures of performance improvement, Anna Robinson, CEO of Ceresa, told HR Dive in an email. Sales growth, unit cost reductions and improved throughput are all examples of potential results. "If business performance improves, that means the right person is receiving the right content, and it is having an impact on their performance," she added.
But there are other ways to measure success, Ujjwal Gupta, co-founder and COO of BenchPrep, told HR Dive in an email. A learner getting that long-sought promotion or spreading knowledge in their department are key ways to witness a development program's success, Gupta said.
Changing minds and habits
What is the goal of training — changing minds or changing behaviors? Griffiths believes both are needed for a growth mindset, but one can lead to another.
"We can inspire change by giving learners the mental models, evidence and ways of thinking to start shifting their mindset, which can have a huge effect on behavior," he said. "For example, how differently do I behave if I believe I know everything and have nothing to learn from others, versus the mindset that I have something to learn from everyone?"
Employers should do more than just encourage learning, but should aspire to have a culture of learning, which enables employees to actively look for growth because learning is readily available and development is rewarded. For Griffiths, a successful learning culture is one that is open, aware and flexible. Ideally, there is a balance between dictating what the organization wants people to learn and giving the learners choice and control over what they learn to foster an employee-driven culture of learning, he noted.
Robinson said to look for engagement and buy-in. To gauge success of their mentoring program, for example, Ceresa looks at the number of women who are interested in continuing the relationship as well as the number who begin to mentor others. "This both extends and expands the learning culture," she said.
Has it made an impact?
Employees may be participating in learning exercises, but that doesn't necessarily translate to impact, experts warned. Knowledge can keep employees on track for what they need to be doing today, but it isn't enough on its own to ready them for new challenges or spark innovation. Seeing strong numbers on employee engagement surveys and significant changes in the way people work are key indicators, but the real goal is for employees to be hungry for more. Experts have noted that offering training outside workers' current areas of expertise and comfort zones can help push them further. Training that regards growth as the goal, whether or not it's of use at work today, can have the most impact on the employee and organization.
For Gupta, the numbers are important; evaluating retention and growth are leading indicators for those seemingly outside opportunities. "Seeing that you are not only keeping your employees happy, but that you are also expanding the business leads to a win-win situation by having a great learning culture that drives ROI," he said.
SOURCE: O'Donnell, R. (7 May 2019) "How do you know when learning programs are working?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrdive.com/news/how-do-you-know-when-learning-programs-are-working/554099/
Workforce Planning Will Help You Understand the Needs of Your Organization
How are you managing your workforce? Workforce planning is one of HR's most important priorities, but many HR professionals shy away from the task. Continue reading this post from SHRM to learn how workforce planning will help HR departments understand the needs of their organization.
Managing headcount—and workforce planning overall—is one of HR's most important priorities, yet so many HR and talent acquisition (TA) leaders shy away from it.
"Very few TA organizations do it, because it's a very analytical process that scares HR," said Jeremy Eskenazi, SHRM-SCP, managing principal of Riviera Advisors, a Long Beach, Calif.-based talent acquisition consulting and training company. "It's perceived to be outside of HR's expertise, and it involves inputs that come from outside HR's ownership."
In many organizations, headcount forecasting is understood to be a financial and budgeting exercise owned by finance, Eskenazi said. "But because the function of headcount is not perceived to be owned by HR, and finance doesn't make it a priority, nobody owns it in the end."
The TA function's failure to successfully predict talent gaps and prepare for hiring needs can be chalked up to a lack of experience with workforce planning, a lack of capacity to undertake it and not understanding its benefits, said John Vlastelica, founder and managing director of Recruiting Toolbox, a global management consulting and training firm in Seattle.
"Most TA leaders operate in a transactional environment and unfortunately see their jobs as purely a fulfillment function," he said. "TA is dealing with so much need that it can't help but be reactive. There's not enough time spent with the business, outlining hiring goals, conducting quarterly business reviews, updating turnover forecasts, reviewing talent composition, going over succession planning, or starting proactive sourcing conversations."
The organizations that win at talent acquisition are those that have a pipeline of talent ready to choose from when they need it, Eskenazi said. "The only way to have that ability is to know what is coming up. If you don't know what's coming up, you're operating on assumptions."
Workforce planning connects recruiting, hiring, employee development and talent management by identifying needed skills, helping recruiters target the right candidates with those skills and assisting managers in charting the internal pathways for employee growth.
"Workforce planning is not just about hiring new people; it's [also] about the gaps between what you currently have and what you need," Eskenazi said. "If you do it right, you can discover who is capable of stepping into new roles with training and development, and who may not be able to stay on in a job because the required skill sets are changing. Workforce planning is about all movement—up, down, in, out or across the organization."
Creating a Workforce Plan
The process begins with information gathering. "You simply need to interview managers of individual workgroups inside your organization and then consolidate and analyze that data," Eskenazi said. HR should be the facilitator of the process and everyone who leads people should participate, he said.
Vlastelica outlined a top-to-bottom approach to collect the information. He advised HR to sit in on executive-level discussions on overall growth and industry challenges. "At the middle level there is a lot of work to be done on forecasting for expected growth and backfills and which job families and roles are most critical," he said. To represent the bottom, "HR should talk with individual hiring managers and department leaders about their talent priorities and workforce composition," he said.
Eskenazi explained that HR should ask department heads a series of standard questions:
- How will the business impact you over the next six months? Twelve months? Twenty-four months?
- What skills do you need to meet your goals and how does current staff meet that need?
- Who is expected to be let go? Who is expected to remain? Who is getting promoted?
After gathering and tracking information about each department's talent inventory and their future talent requirements—using a spreadsheet or a workforce planning platform—it's time to conduct a gap analysis. Estimate what types of positions, people and competencies will be needed in the future to help the organization address talent gaps and then align necessary resources.
When presenting a final analysis to leadership, don't just repeat what you heard. Categorize the findings in a way that makes sense for talent acquisition, Vlastelica said.
"Forecasting is a little bit of science and a lot of art," he added. "It's a good opportunity to teach the business about how to think about talent acquisition, the ramp up time and resource cost to meet business need."
Be Flexible
Organizations looking to be more agile in a rapidly changing environment should engage in regular workforce planning updates, Eskenazi said. "All you have to do is create the framework once, then update it every six months. Once you do it one time in a comprehensive way, it's far easier than having to start from scratch."
The workforce planning team should reach out routinely for insights from department and business line leaders to update and modify the plan based on hiring needs.
"It needs to be very flexible, because oftentimes the business's priorities change, even in a short time," Eskenazi said. "The business is constantly resetting—and faster than ever before."
SOURCE: Maurer, R. (13 May 2019) "Workforce Planning Will Help You Understand the Needs of Your Organization" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/hr-topics/talent-acquisition/pages/workforce-planning-will-help-you-understand-organization-need.aspx
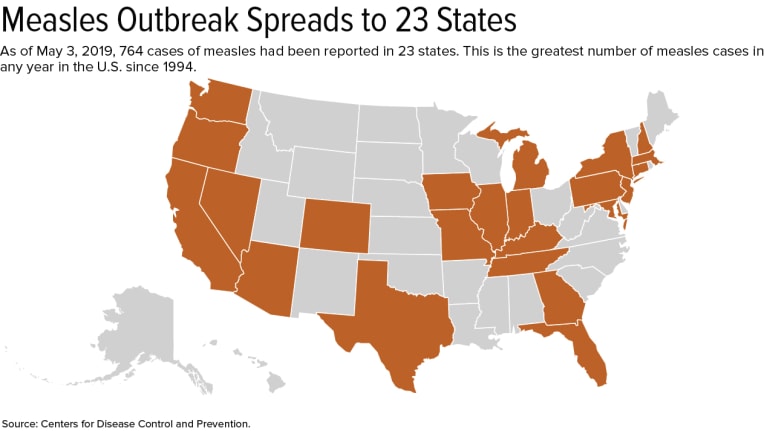
How to Respond to the Spread of Measles in the Workplace
How should employers respond to the spread of measles? With measles now at its highest number of cases in one year since 1994, employers are having to cooperate with health departments to fight the spread. Read this blog post from SHRM to learn more.
Employers and educators are cooperating with health departments to fight the spread of measles, now at its highest number of cases in one year since 1994: 764.
Two California universities—California State University, Los Angeles (Cal State LA) and the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA)—recently quarantined staff and students at the request of local health departments.
In April at Cal State LA, the health department told more than 600 students and employees to stay home after a student with measles entered a university library.
Also last month, UCLA identified and notified more than 500 students, faculty and staff who may have crossed paths with a student who attended class when contagious. The county health department quarantined 119 students and eight faculty members until their immunity was established.
The quarantines ended April 30 at UCLA and May 2 at Cal State LA.
Measles is one of the most contagious viruses; one measles-infected person can give the virus to 18 others. In fact, 90 percent of unvaccinated people exposed to the virus become infected, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes.
Action Steps for Employers
Once an employer learns someone in the workplace has measles, it should immediately send the worker home and tell him or her not to return until cleared by a physician or other qualified health care provider, said Robin Shea, an attorney with Constangy, Brooks, Smith & Prophete in Winston-Salem, N.C.
The employer should then notify the local health department and follow its recommended actions, said Howard Mavity, an attorney with Fisher Phillips in Atlanta. The company may want to inform workers where and when employees might have been exposed. If employees were possibly exposed, the employer may wish to encourage them to verify vaccination or past-exposure status, directing those who are pregnant or immunocompromised to consult with their physicians, he said.
Do not name the person who has measles, cautioned Katherine Dudley Helms, an attorney with Ogletree Deakins in Columbia, S.C. "Even if it is not a disability—and we cannot assume that, as a general rule, it is not—I believe the ADA [Americans with Disabilities Act] confidentiality provisions cover these medical situations, or there are situations where individuals would be covered by HIPAA [Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act]."
The employer shouldn't identify the person even if he or she has self-identified as having measles, Mavity noted.
Shea said that once the person is at home, the employer should:
- Inform workers about measles, such as symptoms (e.g., dry cough, inflamed eyes, tiny white spots with bluish-white centers on a red background in the mouth, and a skin rash) and incubation period—usually 10 to 12 days, but sometimes as short as seven days or as long as 21 days, according to the CDC.
- Inform employees about how and where to get vaccinations.
- Remind workers that relatives may have been indirectly exposed.
- Explain that measles exposure to employees who are pregnant or who might be pregnant can be harmful or even fatal to an unborn child.
- Explain that anyone born before 1957 is not at risk. The measles vaccine first became available in 1963, so those who were children before the late 1950s are presumed to have been exposed to measles and be immune.
Employers may also want to bring a health care provider onsite to administer vaccines to employees who want or need them, Shea said.
"Be compassionate to the sick employee by offering FMLA [Family and Medical Leave Act] leave and paid-leave benefit options as applicable," she said.
When a Sick Employee Comes to Work Anyway
What if an employee insists on returning to work despite still having the measles?
Mavity said an employer should inform the worker as soon as it learns he or she has the measles to not return until cleared by a physician, and violating this directive could result in discipline, including discharge. A business nevertheless may be reluctant to discipline someone who is overly conscientious, he said. It may opt instead to send the employee home if he or she returns before being given a medical clearance.
The employer shouldn't make someone stay out longer than is required, Helms said. Rely instead on the health care provider's release.
SOURCE: Smith, A. (9 May 2019) "How to Respond to the Spread of Measles in the Workplace" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/legal-and-compliance/employment-law/pages/how-to-respond-spread-measles-workplace.aspx
4 Simple Reasons Why Texting Can Lead to Better Hires
Are your recruiters continually getting “ghosted” by job candidates? The way they communicate with job recruits may have something to do with why they are getting “ghosted” by candidates. Continue reading for four reasons texting can lead to better hires.
It’s no secret that recruiters spend the majority of their time researching to find the right candidates for the right job, and even more time reaching out to talk to these potential candidates. So it’s natural that they become frustrated when candidates ignore communications like emails and LinkedIn InMail messages from recruiters. While these communication methods can work for some, they definitely aren’t preferred for all — especially these days.
With people busier than ever before, especially passive millennial candidates, recruiters are seeing more and more recruits “ghosting” them. If you are continually getting no responses to your outreach, it likely has something to do with the other 100-plus emails that are hitting candidates’ inboxes every day. Reaching out via SMS (text messaging) can help you break through the noise and make it easy for potential candidates to take the next step.
Here are four simple ways to use text messages to make better hires:
Texting is quicker
In a highly competitive market, speed matters more than ever. How quickly you can secure the talent you need impacts how quickly your business is moving forward. Seventy-three percent of U.S. millennials and Gen Zers interact with each other digitally more than they do in real life. If you want a fast answer, texting is the way to go.
Scheduling via text is also quicker
Nothing good ever comes from never-ending email chains, especially when the topic is as dull as “Are you available Wednesday morning between 9 am and 11 am?” Sending your candidate a link to your favorite scheduling client via SMS puts an end to group-email fatigue and gets the interview on the books in a matter of minutes.
Don’t forget reminders
There’s nothing worse than a candidate showing up late or missing an interview.
A quick text message is a perfect way to give your candidates a quick heads-up, give them an extra tip, a quick pat on the back and send them in ready to win. No one likes tardiness and no-shows. A quick reminder ensures everyone’s on the same page.
Accelerate the hiring process
Text messages make the candidate experience way more enjoyable by simply shortening the hiring process. Hiring typically involves emails, scheduling, and so much admin. A great SMS can make hiring human again, not to mention faster. By communicating directly with someone at a time that works best for them, especially in a way that they’re much more likely to respond quickly, it will help shorten the overall hiring timeline.
When used alongside other awesome tools, such as a chatbot, text messaging could even help qualify leads more quickly and immediately put you in touch with the best candidates.
The bottom line: utilizing text for recruiting can help you revitalize your talent pipeline and create a more engaging candidate experience.
SOURCE: Bounds, D. (25 April 2019) "4 Simple Reasons Why Texting Can Lead to Better Hires" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://hrexecutive.com/4-simple-reasons-why-texting-can-lead-to-better-hires/
4 benefits messages to send employees in May
Tax season has come and gone, and summer is right around the corner, making it a great time of year for employers to beef up communications about certain employee benefits. Read this blog post for four benefits messages employers should send their employees this May.
With tax season behind us, summer right around the corner and the second half of the year coming up, now is a great time of year for employers to beef up communications about certain benefits.
That’s because there are a number of important messages that are specific to this time of year, including saving money for summer vacations and putting more money into a health savings account so employees can plan for healthcare expenses for the remainder of the year.
Here are four messages employers should share with their employers this month.
1. Think about putting more money in your HSA.
May is a great time for your employees to take stock of their healthcare costs from January to April, and plan ahead for the second half of the year. Here’s a breakdown you can send to help them save money and have more cash available through December to pay their bills.
- Add up this year’s out-of-pocket health care costs thus far.
- Make a new estimate of your upcoming expenses (padding that estimate for unexpected expenses that may pop up.).
- Add your estimated costs to what you’ve already spent.
- Compare that total with how much you’ll have in your HSA account at the end of the year as it is now.
- If there’s a gap, you can increase your contribution rate now to make up the difference.
2. Adjust your W-4s.
Tax season has passed, which means it’s an excellent time to…think a little more about taxes.
The tax law changes that went into effect at the start of 2018 might have made your employees’ existing W-4s less accurate. If they didn’t update their withholding amount last year, they might have been surprised by a smaller refund, a balance due, or even by a penalty owed — and chances are, they don’t feel too happy about it.
Let your employees know that they can prevent unexpected surprises like this next tax season with a visit to this IRS tax withholding calculator. There, they can estimate their 2019 taxes and get instructions on how to update their W-4 withholdings to try and avoid any surprises next year. If they can update their W-4 online, send them the link along with clear step-by-step instructions. And if they need to fill out a paper form, explain where to find it and how to submit it.
3. Revisit your budgeting tools.
Summer is almost here, and your employees are likely starting to think about hitting the beach, road-tripping across the country or eating their weight in ice cream. Since having fun costs money, May is a good time to serve up some ideas on how to squirrel away a little extra cash in the next few months.
Employers should share tips for saving money on benefits-related expenses, like encouraging high-deductible health plan employees to use sites like GoodRx.com for cheaper prescription costs, or visiting urgent care instead of the emergency room for non-life-threatening issues. Also, consider making employees aware of apps like Acorns, Robinhood, Stash, Digits and Tally, which round up credit or bank card expenses to the next dollar, and automatically deposit the extra money into different types of savings accounts.
4. Double-check out-of-network coverage.
While you’re on the subject of summer fun, remind your employees to take a quick peek at their health plan’s out-of-network care policies before they head out of town. If they need a doctor (or ice cream headache cure) while they’re away, they’ll know where to go, how to pay, and how to get reimbursed.
Employers should remind employees that their HSA funds never expire, and they’re theirs for life. So if they put in more than they need this year, it will be there for them next year.
SOURCE: Calvin, H. (1 May 2019) "4 benefits messages to send employees in May" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/list/4-benefits-messages-to-send-employees-in-may