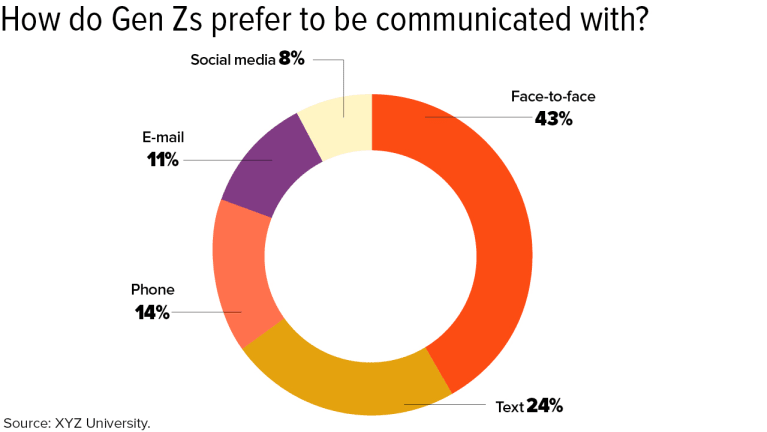What Employers Need to Know About Successful Second Chance Hiring
With today's unemployment rate at the lowest it's ever been, many companies are beginning to explore untapped talent pools and unlikely candidates. Continue reading this blog post from SHRM to learn more.
Between the First Step Act bill being passed and SHRM's efforts towards Getting talent back to work, there are a lot of discussions opening up around second chance hiring. Before, it was pretty standard to assume that if you checked that box of "have you been convicted of a felony," you weren't going to get the job.
Today, our unemployment rate is the lowest it's ever been - forcing companies to explore untapped talent pools and unlikely candidates. As the Founder of a staffing agency for second chances, this makes me very excited. But it also frightens me.
I have worked with inmates, felons, and people in recovery over the past five years by helping them find their passion and meaningful employment. It is not as simple as making a decision to hire people with a criminal background. With this being such a hot topic, I thought I'd give a few tips for those considering hiring people with a criminal background.
1. Non-violent drug charges aren't always the safest bet.
I hear it all the time. And usually people who have never been arrested or spent time in prison. They talk about just hiring people who have non-violent drug charges. In my personal experience, those are usually some of my more difficult cases. A lot of people with non-violent drug charges have one of two addictions: 1. making fast money OR 2. doing drugs. Relapse for either of these are more likely if an individual isn't seeking proper treatment or counseling. A job opportunity alone isn't always enough to keep someone on the right path. I have noticed that my best employees are the most unlikely and most overlooked: Those who lost the most. AKA: People who spent time in prison for harsher charges such as assault, robbery or murder.
2. People who spent time in prison are great manipulators.
Manipulation is a skill best learned in prison. Inmates are very resourceful and know how to get what they want. This is why the formerly incarcerated individuals who are reformed make amazing sales people, debt collectors or call center representatives. But we won't always have a reformed person with a change of heart sitting across from us as we are interviewing for a position. Even your greatest "people-reading" employee can be tricked into making the wrong hire if they are not educated on what to look for and what to ask in the interviewing process. Making the right second chance hire can grow your business tremendously but only if you make strategic hires and give the right second chances to the right people. Not everyone wants to change and we have to accept that as a possibility for responsible hiring.
3. Second chance hiring isn't charity.
When people talk about giving a second chance, it always sounds very charity or philanthropy-like. While I'm glad these discussions are happening, I'm disappointed people speak about second chance hiring like it's a favor to someone. It's actually a favor to your company to bring in a hungry, hard-working, loyal employee that will be grateful you gave them a chance. Growing a team of second chance employees can literally grow your business faster. Your second chance hires will go the extra mile, stay late and come in early. Not for a raise or recognition, but to help grow the company that helped grow them. An organic tea company came to us to make their first official second chance hire a year ago. Today, they've hired 70 people who have a criminal background.
When I first started my company, a for-profit staffing agency for second chances, people thought I was crazy. (I am, proudly) But it seemed like a far-fetched goal to bank on the success of felons. I knew how effective second chance hiring would be, so instead of starting a non-profit and spending my time raising money, I wanted to raise men and women through meaningful job placements. I have seen first-hand the successes and failures when it comes to helping people coming out of prison find employment. My biggest fear is that we are going to successfully create an awareness for second chance hiring and see poor results because of lack of education or tools. This could hurt the reputation of what we are trying to do and hurt the reputation of people who really do deserve real opportunities and have transformed their lives.
SOURCE: Garcia, C. (4 April 2019) "What Employers Need to Know About Successful Second Chance Hiring" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://blog.shrm.org/blog/what-employers-need-to-know-about-successful-second-chance-hiring
This post is the first in a series for Second Chance Month, which highlights the need to improve re-entry for citizens returning to society and reduce recidivism. One of the primary ways to do this is by providing an opportunity for gainful employment. To sign the pledge and access the toolkit with information on how to create second chances at your company, visit GettingTalentBacktoWork.org.
Making the Case for Pay Transparency
Is your organization increasing pay transparency? According to this article from SHRM, pay transparency is a strategic move that delivers measurable business benefits. Read this blog post to learn more.
Recommending to senior leadership that your organization increase pay transparency can be a difficult sell for HR professionals. However, pay transparency is a strategic move that delivers measurable business benefits – and it’s an issue on which HR should lead.
It is important to understand that most executives in America today rose through organizational ranks that viewed compensation as a private matter. Few within organizations had access to salary information, and even fewer talked about it. As a result, many leaders still believe it is appropriate to dissuade or prohibit employees from discussing their own compensation with other employees.
Yet we now understand these outdated cultural norms have contributed to the wage gap for women and minorities, among other negative outcomes. Pay transparency can help close those gaps and produce benefits for both employers and employees.
For example, providing employees with pay ranges for their current position and those positions in their career path sets realistic expectations. This is crucial, as many employees hold unrealistic expectations based on internet salary searches for job titles that often do not account for or accurately reflect important factors such as experience level, geography, company size, actual tasks and responsibilities, or other types of compensation. These unrealistic salary expectations create serious challenges, including employee disengagement, low morale and retention problems.
Clearly communicating your company’s pay ranges facilitates an open dialogue about how those ranges are set, when and why they change, and how employees can move up within them. These discussions in turn increase mutual trust and engagement and foster productive compensation communication — all of which help retain employees, which is especially important in today’s tight labor market.
Increasing pay transparency also helps businesses attract and retain a more diverse workforce, which numerous studies have demonstrated translates into better business results. Sharing compensation data advances this effort by ensuring women and minorities have a clearer picture of the going rate for their skill sets, education, experience and performance. While many factors contribute to pay gaps, women and minority groups may have accepted lower compensation in the past because they could not access the information necessary to determine what they should be making based on what they bring to the table.
While recommending greater pay transparency to senior leadership in your organization may seem daunting, it is an important discussion to have and a compelling case for HR professionals to make. In a highly competitive labor market, businesses that make the right strategic move of increasing pay transparency will ultimately attract and retain the best talent and come out ahead of those that do not.
SOURCE: Ponder, L. (4 April 2019) "Making the Case for Pay Transparency" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://blog.shrm.org/blog/making-the-case-for-pay-transparency-0
DOL Focuses on ‘Joint Employer’ Definition
On April 1, the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) announced a proposed rule that narrows the definition of "joint employer" under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Read this blog post from SHRM to learn more about this proposed rule.
The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) announced on April 1 a proposed rule that would narrow the definition of "joint employer" under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA).
The proposed rule would align the FLSA's definition of joint-employer status to be consistent with the National Labor Relations Board's proposed rule and update the DOL's definition, which was adopted more than 60 years ago.
Four-Factor Test
The proposal addresses the circumstances under which businesses can be held jointly responsible for certain wage violations by contractors or franchisees—such as failing to pay minimum wage or overtime. A four-factor test would be used to analyze whether a potential joint employer exercises the power to:
- Hire or fire an employee.
- Supervise and control an employee's work schedules or employment conditions.
- Determine an employee's rate and method of pay.
- Maintain a worker's employment records.
The department's proposal offers guidance on how to apply the test and what additional factors should and shouldn't be considered to determine joint-employer status.
"This proposal would ensure employers and joint employers clearly understand their responsibilities to pay at least the federal minimum wage for all hours worked and overtime for all hours worked over 40 in a workweek," according to the DOL.
In 2017, the department withdrew an interpretation that had been issued by former President Barack Obama's administration that broadly defined "joint employer."
The Obama-era interpretation was expansive and could be taken to apply to many companies based on the nature of their business and relationships with other companies—even when those relationships are not generally understood to create a joint-employment relationship, said Mark Kisicki, an attorney with Ogletree Deakins in Phoenix.
The proposed test aligns with a more modern view of the workplace, said Marty Heller, an attorney with Fisher Phillips in Atlanta. The test is a modified version of the standard that some federal courts already apply, he noted.
Additional Clarity
Significantly, the proposed rule would remove the threat of businesses being deemed joint employers based on the mere possibility that they could exercise control over a worker's employment conditions, Heller said. A business may have the contractual right under a staffing-agency or franchise agreement to exercise control over employment conditions, but that's not the same as doing so.
The proposal focuses on the actual exercise of control, rather than potential (or reserved) but unexercised control, Kisicki explained.
The rule would also clarify that the following factors don't influence the joint-employer analysis:
- Having a franchisor business model.
- Providing a sample employee handbook to a franchisee.
- Allowing an employer to operate a facility on the company's grounds.
- Jointly participating with an employer in an apprenticeship program.
- Offering an association health or retirement plan to an employer or participating in a plan with the employer.
- Requiring a business partner to establish minimum wages and workplace-safety, sexual-harassment-prevention and other policies.
"The proposed changes are designed to reduce uncertainty over joint employer status and clarify for workers who is responsible for their employment protections, promote greater uniformity among court decisions, reduce litigation and encourage innovation in the economy," according to the DOL.
The proposal provides a lot of examples that are important in the #MeToo era, said Tammy McCutchen, an attorney with Littler in Washington, D.C., and the former head of the DOL's Wage and Hour Division under President George W. Bush.
Importantly, companies would not be deemed joint employers simply because they ask or require their business partners to maintain anti-harassment policies, provide safety training or otherwise ensure that their business partners are good corporate citizens, she said.
Review Policies and Practices
Employers and other interested parties will have 60 days to comment on the proposed rule once it is published in the Federal Register. The DOL will review the comments before drafting a final rule—which will be sent to the Office of Management and Budget for review before it is published.
"Now is the time to review the proposal and decide if you want to submit a comment," Heller said. Employers that wish to comment on the proposal may do so by visiting www.regulations.gov.
"Take a look at what's been proposed, look at the examples in the fact sheet and the FAQs," McCutchen said. Employers may want to comment on any aspects of the examples that are confusing or don't address a company's particular circumstances. "Start thinking about your current business relationships and any adjustments that ought to be made," she said, noting that the DOL might make some changes to the rule before it is finalized.
"The proposed rule will not be adopted in the immediate future and will be challenged at various steps by worker-advocacy groups, so it will be quite some time before there is a tested, final rule that employers can safely rely upon," Kisicki said.
SOURCE: Nagele-Piazza, L. (1 April 2019) "DOL Focuses on ‘Joint Employer’ Definition" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/legal-and-compliance/employment-law/pages/labor-department-seeks-to-revise-joint-employer-rule.aspx
A 16-Year-Old Explains 10 Things You Need to Know About Generation Z
What was life like when you were a teenager? The world has been focused on understanding and adapting to Millennials. Now Generation Z is beginning to graduate and enter the workforce. Read this blog post for 10 things the world should know about Gen Z.
Think about what life was like when you were 16. The clothes you wore, the places you shopped. What was most important to you then?
Whenever I speak to an organization eager to learn about Generation Z, I always ask that question. I get responses that include everything from the fleeting fashion trends of the day (bell-bottom jeans, anyone?) to the time-honored tradition of getting a driver’s license.
What I hope to achieve as a 16-year-old in 2018 is probably not all that different from what anyone else wanted when they were my age. It’s the way people go about reaching their goals that evolves over time—and that’s what also forms the basis of most generational clashes.
For the past several years, the world has been focused on understanding and adapting to Millennials, the largest and most-educated generation in history. Born between 1981 and the mid-1990s, this group has inspired important dialogues about generational differences and challenged all industries to evolve to meet their needs. In the workplace, Millennials have helped drive a greater focus on flexibility and collaboration and a rethinking of traditional hierarchies.
Of course, any analysis of generations relies on generalities that can’t possibly describe every person or situation. It’s important to remember that generations exist on a continuum—and that there is a large degree of individual variation within them. The point of this type of research is to identify macro trends among age groups that can help foster workplace harmony. Essentially, it’s a way of attempting to understand people better by getting a sense of their formative life experiences. The generation to which one belongs is among the many factors, such as race, religion and socioeconomic background, that can shape how a person sees the world.
But there’s little doubt that gaps among the U.S. generations have widened dramatically. For example, an 8-year-old boy in the United States who grew up with a tablet will likely have more in common with an 8-year-old in China who used a similar mobile device than he will with his 70-year-old U.S. grandparents.
In thinking about the generations, a key thing to understand is that these groups are typically categorized by events rather than arbitrary dates. Generation Z’s birth years are generally recognized as 1996 to 2009. The start year was chosen so that the cohort would include only those who do not remember the Sept. 11 terrorist attacks. The belief is that if you were born in 1996 or later, you simply cannot process what the world was like before those attacks. For Generation Z, the War on Terror has always been the norm.
Like all other generations, mine has been shaped by the circumstances we were born into, such as terrorism, school shootings and the Great Recession. These dark events have had profound effects on the behavioral traits of the members of Generation Z, but they have also inspired us to change the world.
Earlier this year, XYZ University, a generations research and management consulting firm where I act as the director of Gen Z studies, surveyed more than 1,800 members of Generation Z globally and released a study titled “Ready or Not, Here Comes Z.” The results were fascinating.
We discovered key characteristics about Generation Z and what the arrival of my generation will mean for the future of work. At 57 million strong and representing the most diverse generation in U.S. history, we are just starting to graduate from college and will account for 36 percent of the workforce by 2020.
Needless to say, Generation Z matters. And it is more important than ever for HR professionals to become familiar with the following 10 characteristics so that they know how to engage with my generation.
1. Gen Z Always Knows the Score
Members of this generation will put everything on the line to win. We grew up with sports woven into the fabric of our lives and culture. To us, the NFL truly does own a day of the week. But it’s more than just professional, college or even high school teams that have shaped us; it’s the youth sports that we played or watched throughout our childhoods. This is the generation of elite young teams and the stereotypical baseball mom or dad yelling at the umpire from the bleachers.
Our competitive nature applies to almost everything, from robotics to debates that test mental fortitude. We carry the mindset that we are not necessarily at school just to learn but to get good grades that will secure our place in the best colleges. Generation Z has been thrown into perhaps the most competitive educational environment in history. Right or wrong, we sometimes view someone else’s success as our own failure or their failure as our success.
We are also accustomed to getting immediate feedback. A great example is the online grading portals where we can get frequent updates on our academic performance. In the past, students sometimes had to wait weeks or longer to receive a test grade. Now, we get frustrated if we can’t access our scores within hours of finishing an exam—and sometimes our parents do, too.
2. Gen Z Adopted Gen X’s Skepticism and Individuality
Generations are shaped by the behavioral characteristics of their parents, which is why clumping Millennials and Generation Z together is a mistake. In fact, when it comes to each generation’s behavioral traits, Millennials are most similar to their parents—the Baby Boomers. Both are large, idealistic cohorts with influences that will shape consumer and workplace behavior for decades.
Members of Generation Z, on the other hand, are more akin to their parents from Generation X—a smaller group with a skeptical, individualistic focus—than they are to Millennials. That’s why many generational traits are cyclical. Just because Millennials and members of Generation Z are closer in age does not necessarily mean they share the same belief systems.
3. Gen Z Is Financially Focused
Over the past 15 to 20 years, HR professionals have been hyper-focused on employee engagement and figuring out what makes their workers tick. What drives someone to want to get up in the morning and come to work for your organization?
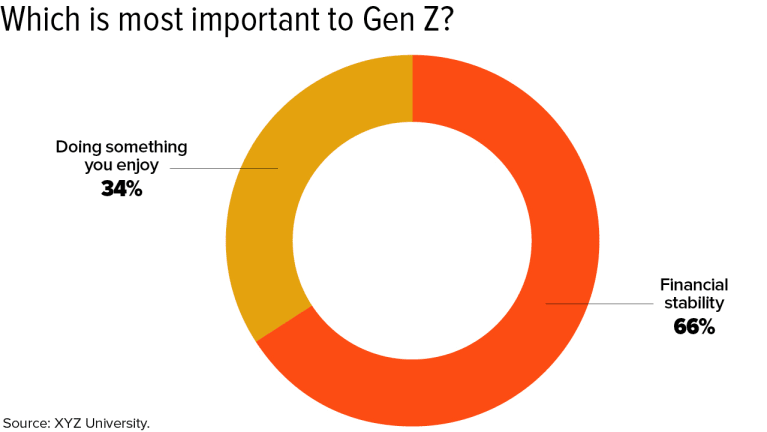
As it turns out, workplace engagement matters less to Generation Z than it did to previous generations. What’s most important to us is compensation and benefits. We are realists and pragmatists who view work primarily as a way to make a living rather than as the main source of meaning and purpose in our lives.
Obviously, we’d prefer to operate in an enjoyable environment, but financial stability takes precedence. XYZ University discovered that 2 in 3 Generation Zers would rather have a job that offers financial stability than one that they enjoy. That’s the opposite of Millennials, who generally prioritize finding a job that is more fulfilling over one that simply pays the bills.
That financial focus likely stems in part from witnessing the struggles our parents faced. According to a study by the Pew Charitable Trust, “Retirement Security Across Generations: Are Americans Prepared for Their Golden Years?,” members of Generation X lost 45 percent of their wealth during the Great Recession of 2008.
“Gen X is the first generation that’s unlikely to exceed the wealth of the group that came before it,” says Erin Currier, former project manager of Pew’s Economic Mobility Project in Washington, D.C. “They have lower financial net worth than previous groups had at this same age, and they lost nearly half of their wealth in the recession.”
Before Generation Z was decreed the ‘official’ name for my generation, there were a few other candidates, including the ‘Selfie Generation’ and ‘iGen.’
Employers will also need to recognize that members of Generation Z crave structure, goals, challenges and a way to measure their progress. After all, the perceived road to success has been mapped out for us our entire lives.
At the same time, it’s important to be aware of the potential for burnout among young overachievers—and to incorporate fun and breaks into the work environment and provide access to healthy escapes focused on relaxation and stress relief.
4. Gen Z Is Entrepreneurial
Even though they witnessed their parents grapple with financial challenges and felt the impact of the worst economic meltdown since the Great Depression, members of Generation Z believe there is a lot of money to be made in today’s economy. Shows like “Shark Tank” have inspired us to look favorably on entrepreneurship, and we’ve also seen how technology can be leveraged to create exciting—and lucrative—business opportunities with relatively low overhead. Fifty-eight percent of the members of my generation want to own a business one day and 14 percent of us already do, according to XYZ University.
Organizations that emphasize Generation Z’s desire for entrepreneurship and allow us space to contribute ideas will see higher engagement because we’ll feel a sense of personal ownership. We are motivated to win and determined to make it happen.
5. Gen Z Is Connected
Before Generation Z was decreed the “official” name for my generation, there were a few other candidates, including the “Selfie Generation” and “iGen.”
I find those proposed names both condescending and misleading. While it’s often assumed that Generation Z is focused solely on technology, talking face to face is our preferred method of communication. Sure, social media is important and has undoubtedly affected who we are as a generation, but when we’re communicating about something that matters to us, we seek authenticity and honesty, which are best achieved in person.
“Gen Z has the power of technology in their hands, which allows them to communicate faster, more often and with many colleagues at one time; but it also brings a danger when it’s used as a crutch for messages that are better delivered face to face,” says Jill Katz, CHRO at New York City-based Assemble HR. “As humans in the workplace, they will continue to seek empathy, interest and care, which are always best received face to face.”
XYZ University’s research found that cellphones and other electronic devices are primarily used for the purpose of entertainment and are tapped for communication only when the face-to-face option isn’t available.
However, successfully engaging with Generation Z requires striking a balance between conversing directly and engaging online. Both are important, and we need to feel connected in both ways to be fully satisfied.
6. Gen Z Craves Human Interaction
Given that members of Generation Z gravitate toward in-person interactions, HR leaders should re-evaluate how to best put the “human” aspect back into business. For example, hiring processes should emphasize in-person interviews more than online applications.
A great way to engage us is to hold weekly team meetings that gather everyone together to recap their achievements. Although members of Generation Z don’t necessarily need a pat on the back, it’s human nature to want to feel appreciated. This small gesture will give us something to look forward to and keep us feeling optimistic about our work. In addition, we tend to work best up against a deadline—for example, needing to have a project done by the team meeting—due to our experience facing time-sensitive projects at school.
7. Gen Z Prefers to Work Independently
Millennials generally prefer collaborative work environments, which has posed a challenge to conventional workplace cultures and structures. In fact, many workplaces have eliminated offices and lowered cubicle walls to promote more interaction. Yet recent studies indicate that totally open offices may actually discourage people from working together. The noise and lack of privacy could prompt more people to work at home or tune others out with headphones. Since different types of work require varying levels of collaboration, focus and quiet reflection, ideal workplaces incorporate room for both togetherness and alone time.
It’s important to be aware of the potential for burnout among young overachievers—and to incorporate fun and breaks into the work environment and provide access to healthy escapes focused on relaxation and stress relief.
The emphasis on privacy will likely only intensify under Generation Z. Unlike Millennials, we have been raised to have individualistic and competitive natures. For that reason—along with growing research into optimal office design—we may see the trend shift away from collaborative workplaces toward more individualistic and competitive environments.
8. Gen Z Is So Diverse That We Don’t Even Recognize Diversity
Generation Z marks the last generation in U.S. history where a majority of the population is white. Given the shifting demographics of the country, we don’t focus as much on someone’s color, religion or sexual orientation as some of our older counterparts might. To us, a diverse population is simply the norm. What we care about most in other people is honesty, sincerity and—perhaps most important—competence.
Indeed, we have been shaped by a society that celebrates diversity and openness. A black man occupied the White House for most of our lives, and we view gay marriage as a common and accepted aspect of society.
9. Gen Z Embraces Change
Compared to teenagers of other generations, Generation Z ranks as the most informed. We worry about our future and are much less concerned about typical teen problems, such as dating or cliques, than we are about becoming successful in the world.
The chaos and unrest in our political system have inspired us to want to get involved and make a difference. Regardless of which side of the aisle we are on, most of us are informed and passionate about the issues facing our society today. Witness, for example, the students of Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in Parkland, Fla., who organized a political movement around gun control in the wake of a mass shooting at their school.
Social media allows us to have a voice in our political system even before we can vote. This opportunity has forced us to develop critical-thinking and reasoning skills as we engage in sophisticated debates about important issues that might not even affect us yet.
“Gen Z has a strong ability to adapt to change,” says Paul Carney, an author and speaker on HR trends and a former HR manager with the Navy Federal Credit Union. “For those of us who have spanned many decades in the workplace, we have seen the rate of change increase and it makes most of us uncomfortable. Gen Z are the people who will help all of us adapt better.”
According to numerous polls, the political views of Generation Z trend fiscally conservative (stemming from our need for financial stability) and socially liberal (fueled by diverse demographics and society).
10. Gen Z Wants a Voice
Given how socially aware and concerned its members are, Generation Z seeks jobs that provide opportunities to contribute, create, lead and learn.
“One of the best ways I have seen leaders engage with Gen Z is to ask them how they would build a product or service or design a process,” Carney says. “Gen Z has some amazing abilities to bring together information, process it and take action. When we do allow them to share ideas, great things happen.”
We’re also an exceptionally creative bunch. Managers will need to give members of this generation the time and freedom to come up with innovative ideas and accept that, despite our young age, we have valuable insights and skills to offer—just like the generations that came before us and those that will follow.
The HR tech disconnect: Are there too many digital tools?
According to a new survey of more than 500 HR employees, 87 percent of HR professionals reported that having tools that integrate with existing technology is key. Continue reading this blog post from Employee Benefit Advisor to learn more.
Investing in new technology that combines with current systems looks to be a priority for HR departments.
That’s according to a new survey of more than 500 HR employees from Reward Gateway, which found that 87% of HR professionals say having tools that integrate into their existing technology is key.
That priority is likely due to the fact that HR technology is siloed, the employee engagement technology company found. Many employers use separate platforms for tasks relating to employee communication, recognition, applicant tracking, onboarding and performance management.
More than a fifth of companies use 10 or more different systems and applications at work, and roughly 60% are using more than five systems every day. In addition, HR professionals spent 512 hours a year, nearly two hours a day, manually checking, responding to and keeping up with multiple HR applications, Reward Gateway says.
“Many companies have systems-of-record in place with up-to-date details on their employees,” says Will Tracz, chief technology officer at Reward Gateway. “Creating and maintaining data in other systems, outside of this, often takes time and is prone to error, particularly in fast-moving businesses.”
The new survey echoes similar findings, which indicate that while employers may be increasingly using HR tech, they may not be doing so efficiently. For instance, research from the Association of Executive Search and Leadership Consultants found that HR departments could be dropping the ball when it comes to using HR technology.
Karen Greenbaum, president and CEO of AESC told Employee Benefit News in November that total digital transformation is about more than just implementing new tech in the office.
“It’s not just, ‘Do they understand what artificial intelligence means,’ or what augmented reality means,” she says. “[It’s] ‘Do you really have an organization that can adapt to a new world?’”
Still, HR leaders are turning to tech solutions. Data from global talent acquisition and management firm Randstad Sourceright found that HR departments are going on a tech “buying spree.” The vast majority (92%) of those in the Randstad survey of more than 800 C-suite and HR leaders and 1,700 professionals believe that technology enhances the attraction, engagement and retention of talent.
Reward Gateway received similar responses. HR teams are hoping new tech will not only integrate with existing systems, but also help them achieve their goals, which include higher employee engagement, increased productivity and attracting talent.
This article originally appeared in Employee Benefit News.
SOURCE: Hroncich, C. (29 March 2019) "The HR tech disconnect: Are there too many digital tools?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/news/hr-tech-disconnect-are-there-too-many-digital-tools?brief=00000152-146e-d1cc-a5fa-7cff8fee0000
A guide to managing employee website usage
With remote workers, employers need to be mindful of the types of websites their employees are accessing on company-issued technology. Continue reading for key considerations and best practices to review when properly managing employee website usage.
Whether employees are working from home, the coffee shop or the office, employers need to be mindful of the types of websites workers are accessing on their company-issued technology.
New accessibility creates greater flexibility, but employers need to be vigilant to ensure workers maintain the expectation of productivity and workplace privacy. Now more than ever, the workplace heavily relies on technology and companies must understand how to manage it to avoid risk.
Nowhere is the tension between technology and privacy rights more prevalent than in today’s workplace. At the forefront of this discussion is whether employers should block access to certain websites on company-issued technology. Here are key considerations and best practices to review when properly managing employee website usage.
Creating boundaries between work and personal affairs, without invading privacy. Employees typically emphasize that their private affairs should not be accessed by their employer. But the federal Electronic Communications Privacy Act (ECPA) states an employer-provided computer system is the property of the employer, so when an employee visits certain websites during typical office hours using company-issued technology, what is accessed by the employee becomes the employer’s business as well.
There is no denying that placing blocks on certain websites is an effective way to separate work and personal matters, maintain professionalism, protect the company’s security, respect company property and utilize work time appropriately. However, employers should beware of potential legality issues regarding privacy. For example, employees are given some protection from computer and other forms of electronic monitoring under certain circumstances.
Productivity distractions. Blocking certain websites will not prevent an employee from utilizing company time for personal reasons, but doing so reminds employees to have integrity, focus and discipline when it comes to using technology in the workplace. Some employees will use company-issued technology to visit a plethora of websites such as social media platforms, personal email accounts, instant messengers, financial institutions, sports, entertainment and music sites, as well as inappropriate websites. It is easy to become distracted with an overabundance of virtual activity at our fingertips, and blocking sites sends a serious message to workers that business technology and time is for business-purposes only.
Security of confidential company data and information. In today’s interconnected world, employers recognize the importance of protecting confidential company information. Employers often choose to block certain websites because of the risk of a security breach. Employers are concerned with the exposure of any release of its data, work products, ideas and information not otherwise disclosed to the public or its competitors. Blocking certain websites gives an organization an opportunity to decrease the risk of its confidential information being accessed by external influences.
What employers can do to be more transparent with staff
There are no foolproof methods to preventing an employee from using their work time for personal reasons or inadvertently exposing the company to security breaches.
Employees can still access many websites of their choosing through their personal technology. However, the aforementioned reasons are convincing enough for employees to take more accountability in using company-issued technology for business purposes only. An employer that endorses a policy and practice of business technology for business reasons sets a clear expectation for employees to remember and follow.
- Enforce a written policy that sets clear expectations for in-house and remote employees about not using company-issued technology to visit certain websites and explain the reason for such policies. Policies and procedures should be well-defined, widely communicated and reviewed at least annually.
- Inform new employees that certain websites are not accessible via company technology. Highlight the written policy for both new and existing employees. Again, explain the reason for this policy.
- Offer training and other educational opportunities that motivate productivity during times when work focus suffers.
- Work with the company’s internal IT department to ensure that websites are properly blocked.
Usually, when employers remain transparent with staff regarding why a policy exists, employees are more receptive. In general, employers are encouraged to consult with an experienced HR professional or employment lawyer to avoid any potential legality pitfalls in the workplace.
SOURCE: Banks, S. (11 March 2019) "A guide to managing employee website usage" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.benefitnews.com/opinion/a-guide-to-managing-employee-website-usage?brief=00000152-14a5-d1cc-a5fa-7cff48fe0001
Do paycheck advance apps improve financial health?
Do you allow your employees access to draw money from their paycheck before payday? Many apps now let workers have early access to their money. Read this blog post to find out more about paycheck advance apps and how these may improve financial health.
Fintechs that let workers draw money from their paycheck before payday through an app are having a moment.
Such apps, including Even.com, PayActiv, EarnIn, DailyPay and FlexWage, are designed for consumers who live paycheck to paycheck — roughly 78% of the U.S. workforce according to one study.
More than 300,000 Walmart employees, for example, use this feature, called Instapay, provided by Even and PayActiv. PayActiv, which is available to 2 million people, announced a deal with Visa on Thursday that will let people put their pay advances on a feeless prepaid Visa card.

Earnin, which lets consumers retrieve up to $100 a day from upcoming paychecks, received $125 million in Series C funding from DST Global, Andreessen Horowitz, Spark Capital, Matrix Partners, March Capital Partners, Coatue Management and Ribbit Capital in December. The Earnin app has been downloaded more than a million times.
In theory, such apps are useful to those who run into timing problems due to large bills, like mortgage and rent, which come due a few days before their paycheck clears. Getting a payday advance from an employer through an app can be less expensive and less problematic than taking out a payday loan or paying overdraft fees.
But do these programs lead to financial health? Or are they a temporary Band-Aid or worse, something on which cash-strapped people can become overdependent?
Volatile incomes, gig economy jobs
One thing is clear — many working poor are living paycheck to paycheck. Pay levels have not kept up with the cost of living, even adjusted for government subsidy programs, said Todd Baker, senior fellow at the Richman Center for Business, Law and Public Policy at Columbia University.
“That’s particularly evident when you think of things like home prices and rental costs. A large portion of the population is living on the edge financially,” he said. “You see it in folks making $40,000 a year, teachers and others who are living in a world where they can’t handle any significant bump in their financial life."
A bump might be an unexpected expense like medical treatment or a change in income level, for instance by companies shifting to a bonus program. And about 75 million Americans work hourly, with unstable pay.
“Over the last several decades, we’ve changed the equation for many workers,” said John Thompson, chief program officer at the Center for Financial Services Innovation. “It’s harder to have predictable scheduling or even income flow from your job or jobs. But we haven’t changed the way we pay, nor have we changed the way bills are paid. Those are still due every month on a certain date. This income volatility problem that many people experience hasn’t been offset by giving the employee control of when they do have access to these funds.”
Where on-demand pay comes in
Safwan Shah, PayActiv's CEO, says he has been working on the problems for consumers like this for 11 years. The way he sees it, there are three possible ways to help: by paying these workers more, by changing their taxes, or by changing the timing of when they’re paid.
The first two seem out of reach. “I can’t give more money to people; that’s not what a Fintech guy does,” Shah said. “I can’t invent money. And I can’t change the tax laws.”
But he felt he could change the timing of pay.
“I can go to employers and say, your employees are living paycheck to paycheck,” Shah said. “They’re bringing that stress to work every day. And you are suffering too, because they are distracted — a Mercer study shows employers lose 15 hours a month in work from these distracted employees.”
Shah persuades employers to let their employees access a portion of the wages they have already earned. His early wins were at companies whose employees frequently request paycheck advances, which generates a lot of paperwork. Employees can access no more than 50% of what they have already earned — a worker who has earned $300 so far in a month could at most get $150.
Employees pay $5 for each two-week period in which they use PayActiv. (About 25% of the time, the employer pays this fee, Shah said.)
PayActiv also gives users unlimited free bill pay and use of a Visa prepaid card. In July, PayActiv became part of the ADP marketplace, so companies that use ADP can use its service.
PayActiv's largest employer is Walmart, which started offering it via the Even app in December 2017. In October, Walmart began allowing employees to pick up cash through the app in Walmart stores, so users who were unbanked could avoid ATM fees.
Shah said the service helps employers reduce employee turnover, improve retention and recruit employees who prefer real-time pay. He also has a guilt pitch.
“I was first in the market to this, in 2013,” Shah said. “People looked at me and said, ‘What? I’m not going to pay my employees in advance. Let them go to a payday lender.’ Then I’d show them pictures of their offices surrounded by payday loan shops. I’d say, ‘They’re here because of you.’ ”
Does early access to wages lead to financial health?
When Todd Baker was a Harvard University fellow last year, he studied the financial impact of PayActiv’s earned wage access program. He compared PayActiv’s $5 fee to payday loans and bank overdraft fees.
Baker found that a $200 salary advance from PayActiv is 16.7% of the cost of a payday loan. Payday lenders typically charge $15 per $100 borrowed, so $30 for a two-week, $200 loan. If the borrower can’t pay back the amount borrowed in two weeks, the loan gets rolled over at the original amount plus the 15% interest, so the loan amount gets compounded over time.
With PayActiv, "there is always a full repayment and then a delay before there is enough income in the employee’s payroll account for another advance," Baker said. "It never rolls over.”
Baker also calculated that the PayActiv fee was only 14.3%, or one-seventh, of the typical $35 overdraft fee banks charge.
So for people who are struggling to manage the costs of short-term timing problems and unexpected expenses, Fintech tools like PayActiv’s are a lot cheaper than alternatives, Baker said.
“Does it create extra income? No. What it does is help you with timing issues,” he said.
Aaron Klein, a fellow at the Brookings Institution, said workers should have access to money they’ve already earned, whether that’s through real-time payments or through apps that provide pay advances.
“I also am on board with the idea that by saving your $35 overdraft and saving your payday loan rate, you’ll be better off,” Klein said.
But he’s not willing to say these tools solve the problems of low-income people.
“If the core problem is I used to make $35,000 a year, now I make $30,000, and because of that shock I’m going to end up accruing $600 of payday loan and overdraft fees, eliminating that $600 makes you a lot better off,” Klein said. “But it doesn’t negate the overall income shock.”
Thompson at CFSI says it’s too soon to tell whether earned wage access brings about financial well-being.
“We’re just beginning to explore the potential for these tools,” he said. “Right now they feel very promising. They could give people the ability to act quickly in an emergency and have access to and use funds in lieu of a payday loan or some other high-cost credit or consequence they would rather avoid, like an overdraft fee.”
What could go wrong
Thompson also sees a potential downside to giving employees payday advances.
“The every-other-week paycheck is one of the few normal structures we have for people around planning, budgeting and managing their money,” he said.
Without that structure, which is a form of savings, “we’re going to have to work hard to make sure we don’t just turn people loose on their own with even less structure or guidance or advice on their financial life.”
Another common concern about payday advance tools is that if you give people access to their money ahead of time, they’ll just spend it, and then when their paycheck arrives, they will come up short.
But Klein, for one, doesn’t see this as an issue.
“I trust people more to manage their money,” he said. “The people who work paycheck to paycheck spend more time budgeting and planning than the wealthy, because it’s a necessity.”
A related fear is that people could become addicted to payday advance tools, and dig themselves into a deeper hole.
Jon Schlossberg, CEO of Even.com, somewhat surprisingly acknowledges this could happen.
“Getting access to your pay on demand is a tool you can use the right way or the wrong way,” he said. “If you offer only on-demand pay, that could cause the problem to get worse, because getting access to that money all the time triggers dopamine; it makes you want to do it more and more. If you are struggling with a very low margin and you’re constantly up against it, getting more money all the time accelerates that problem."
Quantitative and qualitative analyses have borne this out, he said.
Even has granted users $700 million worth of Instapays; they typically use Instapay 1.4 times a month. Schlossberg doesn't see high use of the feature as success.
“You shouldn’t need to be using Instapay,” he said. “You should be becoming financially stable so you don’t have to.”
Baker said addiction to payday advances isn't a danger because they don't roll over the way payday loans do. With a salary advance, “It’s conceivable you could get $200 behind permanently, but it’s not a growing obligation and it’s not damaging,” he said.
Shah at PayActiv said users tend to withdraw less than they're allowed to — about 75%.
“When it comes to usage of their own salary, instead of asking for more, people behaviorally ask for less,” he said.
They see PayActiv more as a headache reliever like Tylenol, rather than an addictive candy or drug, Shah said.
Pay advances are just one of many tools that can help the working poor. They also need help understanding their finances and saving for goals like an emergency fund and retirement.
“This conversation about on-demand pay is a double-edged sword because people are paying attention to it now, which is good, but they’re viewing it as this magic tool to solve all problems,” Schlossberg said. “It isn’t that. It is a piece of the puzzle that solves a liquidity problem. But it is by no means going to help people turn their financial lives around.”
SOURCE: Crosman, P. (14 March 2019) "Do paycheck advance apps improve financial health?" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/news/do-paycheck-advance-apps-improve-financial-health?brief=00000152-146e-d1cc-a5fa-7cff8fee0000
Editor at Large Penny Crosman welcomes feedback at penny.crosman@sourcemedia.com.
This article originally appeared in American Banker.
Pay transparency: A new tool to boost employee engagement
Some companies require new hires to sign an agreement promising not to disclose their pay to co-workers. Continue reading this blog post to learn more about pay transparency.
For many companies, discussing salaries has always been taboo. Some firms even required new hires to sign an agreement swearing they wouldn’t disclose their pay to co-workers.
This “loose lips sink ships” approach is largely illegal, of course: Employees are generally free to talk about pay rates as part of their rights under the National Labor Relations Act.
Nonetheless, for years, companies held salary information very close to the vest.
But times are changing. Many firms have now gone to a policy of transparency in matters of compensation.
2 separate approaches
Stephanie Thomas, program director of the Institute for Compensation Studies at Cornell University, writes that pay transparency comes in two flavors: salary disclosure and pay process transparency.
1. Salary disclosure: In this approach, the company distributes a spreadsheet listing employees, their titles and their salaries.
This approach can be tricky. There are always going to be cases where an employee asks, “Why is Stephanie paid more than me? We have the same title and the same duties.”
Whole Foods explains the rationale for adopting its policy in a statement on its website:
“Salary information for all –including the company’s leadership – is available to all inquiring team members. Wage transparency helps promote inclusiveness and ensures our compensation system is fair.”
2. Pay process transparency: The second approach explores how compensation decisions are made, and explains to individuals why they’re making what they are and what they need to do to earn more.
This involves having detailed discussions with employees, either individually or in a group, about the overall compensation plan – salary ranges and midpoints, goals and objectives that need to be met, performance metrics, etc. Most companies prefer this approach because it focuses the conversation away from rankings of employees toward individual performance.
Both approaches signal a new trend in employee engagement – helping workers understand the inner workings of their organizations.
SOURCE: Mucha, R. (15 February 2019) "Pay transparency: A new tool to boost employee engagement" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrmorning.com/pay-transparency-a-new-tool-to-boost-employee-engagement/
Dispelling the stigma around mental health disorders in the workplace
Forty million adults in the U.S. are affected by anxiety disorders each year, according to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America. Continue reading to learn more about the stigma associated with mental health disorders in the workplace.
It’s no secret that poor mental health impacts employee performance. Anxiety disorders, for example, affect 40 million adults in the U.S. each year, and nearly six in 10 American workers report that anxiety impacts their workplace performance, according to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
But because of the stigma often associated with mental health disorders, employees might not be using the benefits and programs clients have in place to help address the problem. That’s why just having programs in place isn’t enough, experts say. Instead, employers need to help remove the stigma of mental health conditions by creating a culture of inclusiveness in the workplace and forming employee resource groups.
Employers including Johnson & Johnson, Trulia and Verizon Media are doing just that, company executives said during a webinar last week hosted by the National Alliance of Healthcare Purchaser Coalitions.
When Margaux Joffe, associate director of accessibility and inclusion at Verizon Media, started working on a proposal to form a mental health-focused employee resource group (ERG), dispelling stigma and empowering workers was one of her first priorities.

“We wanted to create a paradigm shift,” she said, speaking as part of the webinar. “Growing up, you’re taught to think you’re ‘normal or not normal;’ you’re mentally ill or you’re not. We started with the idea there is no such thing as a ‘normal brain’ as we’re increasingly understanding neurodiversity in the human race.”
A lot of people with mental health issues don’t necessarily identify with the word disability, added Meredith Arthur, content marketing manager at Trulia.
“We struggled around removing the word disability because there was a desire to face the stigma and take it on,” she said of Trulia’s ERG. “Ultimately, we wanted to reach as many people as we could. We wanted to be sharper in our focus on mental health.”
Trulia expanded its ERG statement of purpose from just focusing on mental health education and awareness to advocating for the needs of different abilities.
Joffe said putting in place an ERG for mental health at Verizon was done with the support of senior leadership. “We’ve been lucky to get a lot of support from the company for ERG,” she said. “A common challenge that exists across the board is lack of organization readiness.”
Readiness is a huge component of success in mental health programs, added Kelly Greenwood, founder and CEO of Mind Share, a nonprofit organization addressing the culture of workplace mental health.
“It is so important to achieve true culture change,” she said. “Oftentimes we work with leadership first and do workshops for executive teams before rolling them out to the company to really get that buy-in and understanding from the top down to build a transparent culture.”
At Johnson & Johnson, it took the company about nine months to get its ERG program up and running. “There was a lot of conversation internally if it should be its own ERG for mental health or integrated into another employee resource group,” said Geralyn Giorgio, talent acquisition change management communications and training lead at the pharmaceutical and consumer packaged goods manufacturing company.
At that time, she said, the company had an ERG called the alliance for disability leadership. The decision was made to put mental health under that ERG umbrella. “Since than happened, there were a lot of [employees] not seeing themselves in this ERG. We felt strongly we had to rebrand the ERG, and we went live last year, using the name alliance for diverse abilities to make it more inclusive,” she said.
This year, Giorgio said, the company will work to empower managers to handle mental health conversations.
“If you have a manager open to the conversation, [employees] have a different experience than someone whose manager is ill-informed,” she said. “That’s something we need to focus on this year — helping our managers feel more comfortable with having the conversation.”
This article originally appeared in Employee Benefit News.
SOURCE: Otto, N. (12 March 2019) "Dispelling the stigma around mental health disorders in the workplace" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.employeebenefitadviser.com/news/dispelling-workplace-mental-health-stigma?brief=00000152-146e-d1cc-a5fa-7cff8fee0000
Nine Ways To Motivate Employees That Don't Always Involve Cash
Employers are reporting that recruiting and retaining talent is the single greatest challenge they've experienced since the U.S. unemployment rate hit historic lows. Continue reading this blog post from Forbes for nine ways employers can motivate their employees.
With unemployment at near historic lows in the United States, employers report that their single greatest challenge is recruiting and retaining talent. The answer for many companies is to throw money at the problem: Bonuses, incentive pay, and out-of-cycle salary increases are often seen as motivators that will entice greater effort and loyalty out of workers.
Turns out, using cash as a carrot isn’t always the best answer, according to new research by Harvard Business School Assistant Professor Ashley V. Whillans. More than 80 percent of American employees say they do not feel recognized or rewarded, despite the fact that US companies are spending more than a fifth of their budgets on wages.
What employees crave even more is to feel that their managers appreciate them and aren’t afraid to show it, not only in paycheck terms, but in other ways such as flexible work-at-home schedules, gift cards for pulling off impressive projects, or even just by saying “thank you” for a job well done.
“Cash matters in people’s lives, but it’s not all that matters,” says Whillans, who researches what makes people happy. “What really matters in the workplace is helping employees feel appreciated.”
Whillans co-wrote a recent article in Compensation & Benefits Review, “Winning the War for Talent: Modern Motivational Methods for Attracting and Retaining Employees,” with Anais Thibault-Landry of the Université du Québec à Montréal and Allan Schweyer of the Incentive Research Foundation.
Rewards that signal to employees that they did a good job and that their manager cares about them will encourage employees to want to work even harder, the research shows. Whillans provides nine tips for business leaders on how best to reward their workers in ways that will bring them greater job satisfaction and motivate them to work harder.
When recruiting, emphasize benefits. Talking up a job’s perks, such as flexible work schedules and skill training, can give companies a recruiting edge. A 2018 study that Whillans and her team conducted of more than 92,000 job ads found that the more benefits an employer described, the higher the application rates.
Cash can motivate workers—in some types of work. Cash rewards are best suited as a motivator for work that is measured quantitatively, Whillans says. But money is less meaningful as a motivator in the complex creative jobs that make up most work in our modern knowledge-based society.
If you give cash, include a meaningful note. It’s best to avoid merely adding a cash bonus to a worker’s paycheck; a separate bonus check stands out more as a recognition of their work. And managers should also include a sincere handwritten note explaining why the employee deserved the bonus.
Reconsider performance incentives. Decades of research confirms that financial incentives can boost effort and performance. But when an employee’s pay is contingent on performance, they can become obsessed with earning more. What often works better is to turn around the timing of the reward, handing it out immediately after an employee excels at a particular task, rather than dangling it beforehand.
Consider thoughtful gifts instead of cash. A 2017 study of 600 salespeople found that when a mixed cash and prize reward program was replaced with an equivalent value all-cash package, employee effort dropped dramatically, leading to a 4.36 percent decrease in sales that cost the company millions in lost revenue, Whillans’s article says. The firm may have inadvertently demotivated salespeople who preferred prizes or discouraged workers who liked having a choice.
Give the gift of time—and other intangible perks. A Glassdoor survey Whillans and her team conducted with 115,000 employees found that providing intangible non-cash benefits, like flexible work options or the ability to choose assignments, led to much stronger job satisfaction than straightforward cash rewards.
Encourage employees to reward one another. Companies can build recognition into their business practices by creating peer-to-peer recognition programs in which employees are provided monthly reward points that they can give away to colleagues for work-related wins. Employees who earn a certain number of points can redeem them for various perks, such as a restaurant gift card or an extra personal day.
Make the recognition public. If employees are receiving a $500 bonus, hold a workplace event to hand out checks, and invite the employees’ peers. Perhaps add a certificate of appreciation along with the check.
Sometimes a simple thank you is enough. Among the happiest employees, 95 percent say that their managers are good at providing positive feedback, Whillans says. A simple, heartfelt “thank you” from a manager is often enough for employees to feel like their contributions are valued and will motivate them to try harder.
Why rewarding employees works
Whillans says these types of rewards work because they tap into three strong psychological needs: Employees long for autonomy, with the freedom to choose how to do their work; they want to appear competent, armed with the skills needed to perform; and they want to feel a sense of belonging by socially connecting with colleagues in a meaningful way.
When these needs are satisfied, employees feel more motivated, engaged, and committed to their workplace—and they report fewer intentions of leaving their jobs, Whillans says.
SOURCE: HBS Working Knowledge (28 February 2019) "Nine Ways To Motivate Employees That Don't Always Involve Cash" (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/hbsworkingknowledge/2019/02/28/nine-ways-to-motivate-employees-that-dont-always-involve-cash/